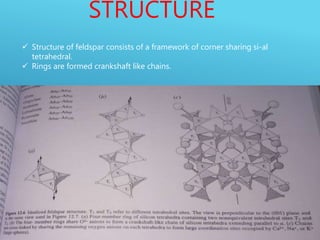
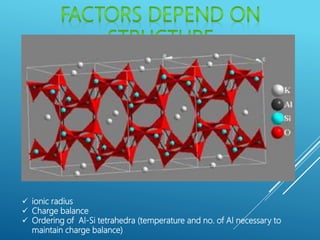
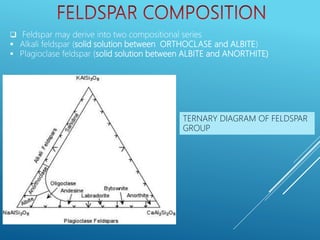
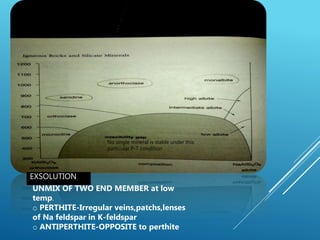
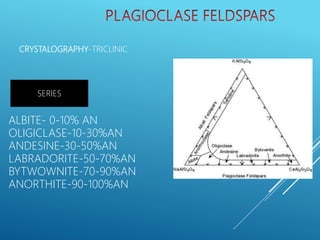
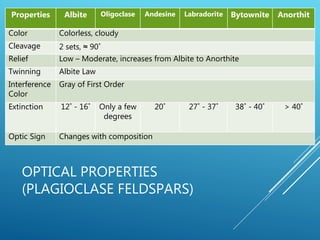
This document provides a summary of alkali feldspar and plagioclase feldspar. It discusses their crystal structure, composition, physical and optical properties, paragenesis, and applications. Alkali feldspar includes orthoclase, sanidine, and microcline. Plagioclase feldspar is a solid solution between albite and anorthite. Both have important industrial uses such as in ceramics, glass, paints, plastics, and as gemstones. The document is presented by Atish Kumar Sahoo for his MTech course at the Department of Applied Geology.