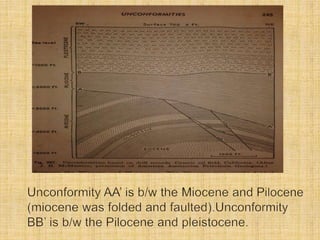
The document discusses different types of unconformities:
- Angular unconformity occurs when rock layers above and below are not parallel due to erosion and deposition over a long period of time with changes in bedding orientation.
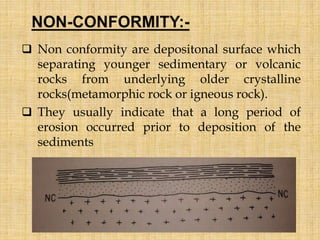
- Nonconformity separates older crystalline rocks from overlying younger sedimentary or volcanic rocks, representing a long period of erosion.
- Disconformity has parallel bedding above and below, separated by erosion over some time.
- Local unconformity is similar to a disconformity but represents only a short period of non-deposition over a small area.