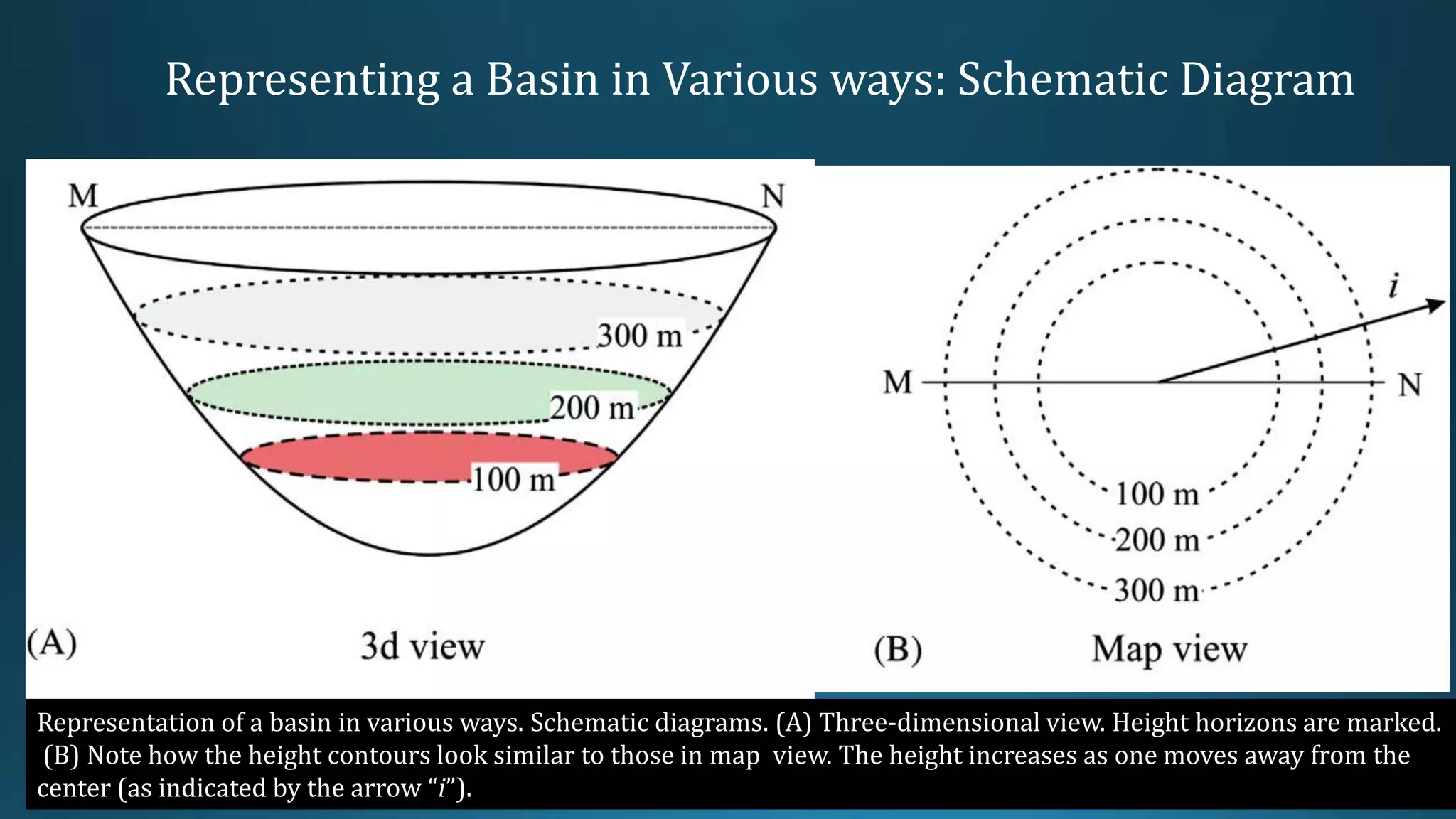
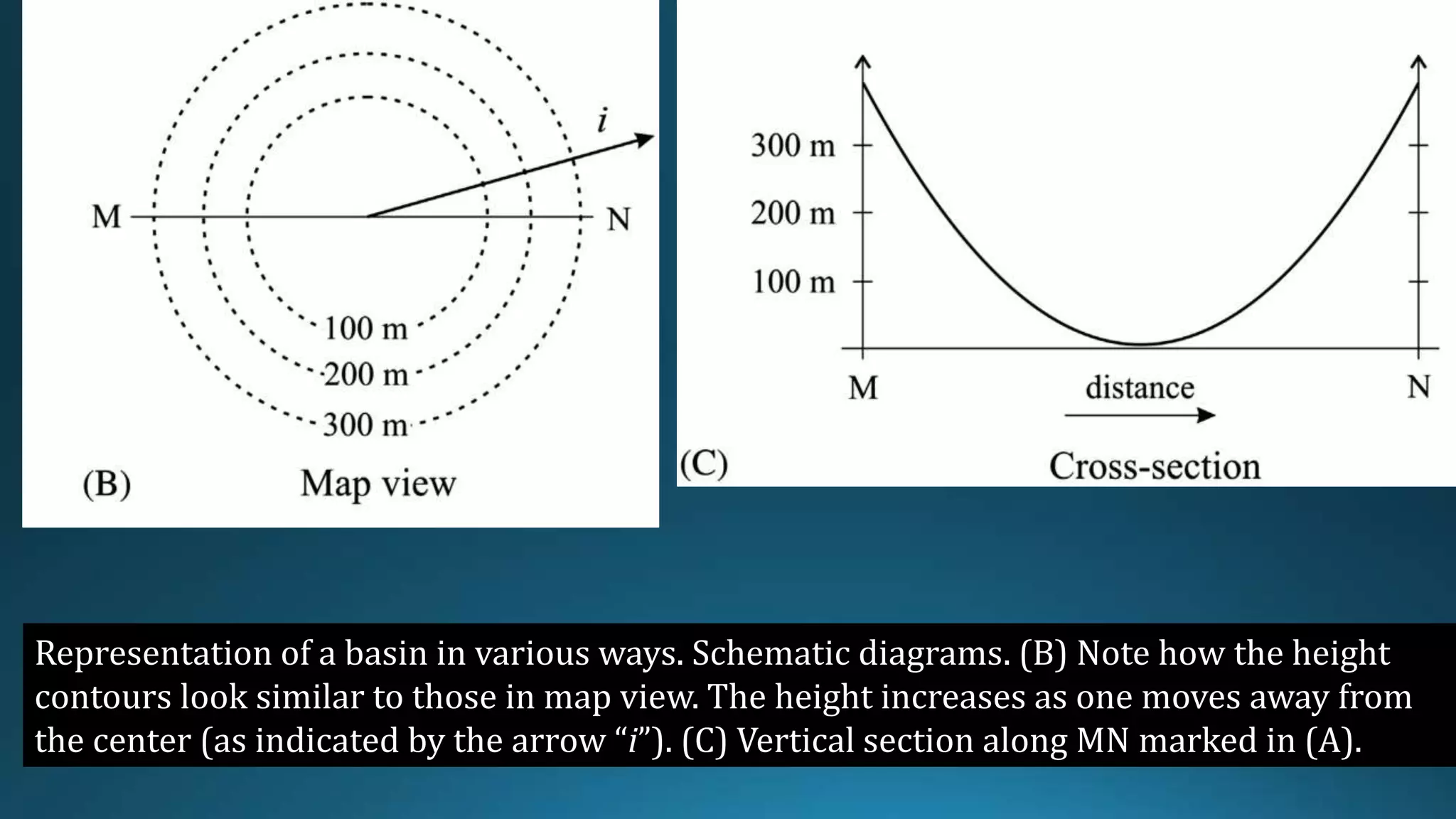
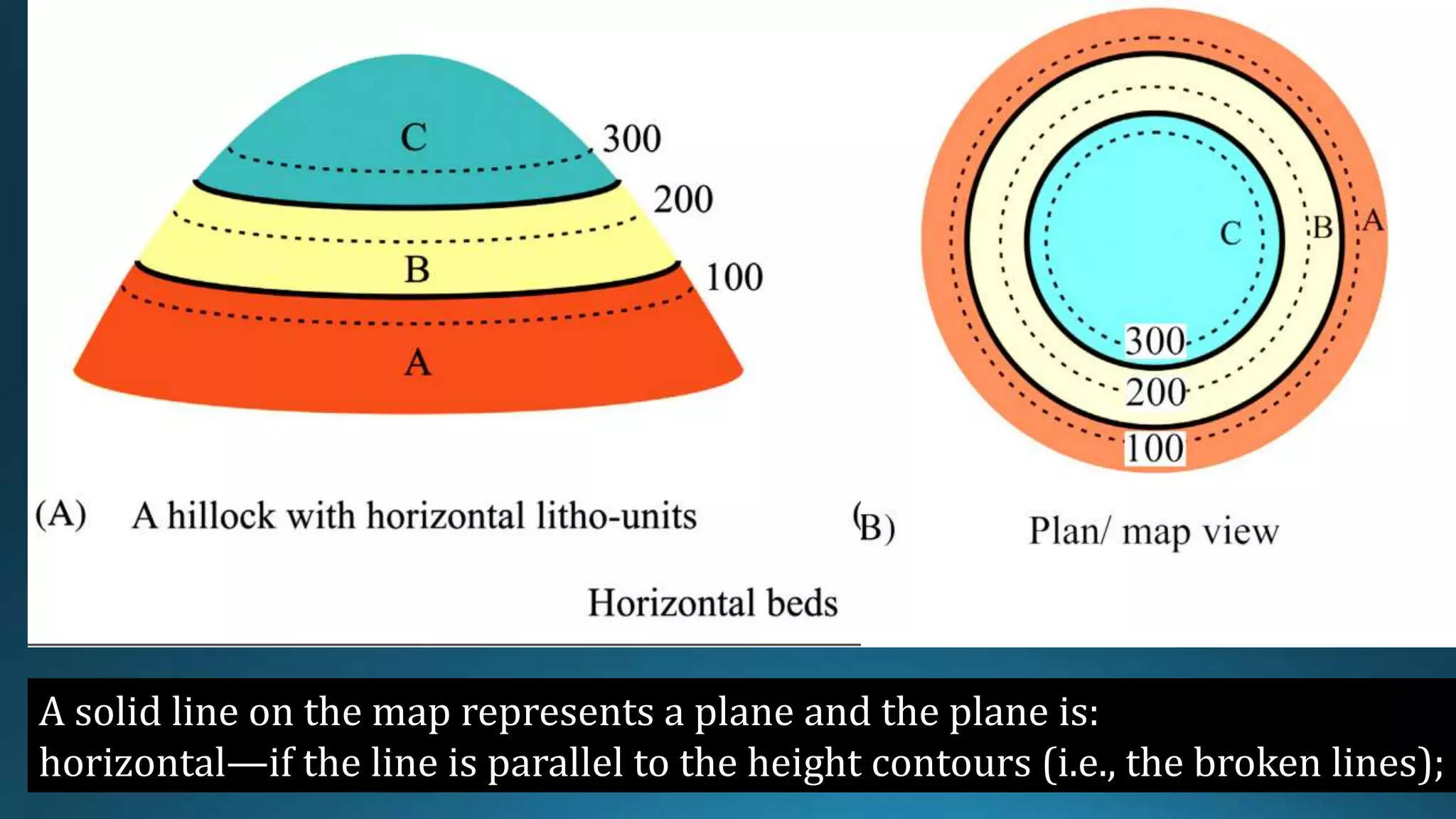
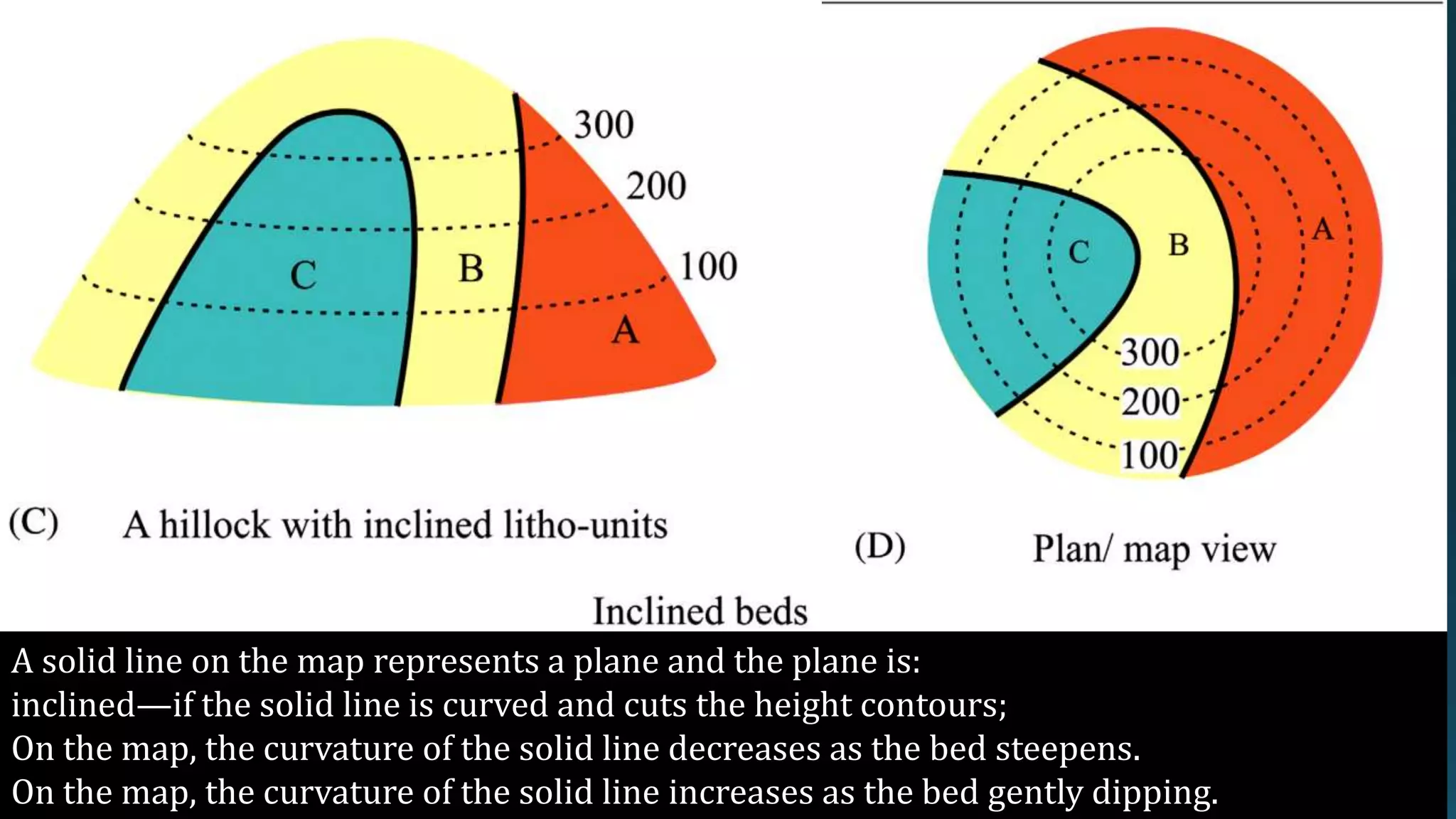
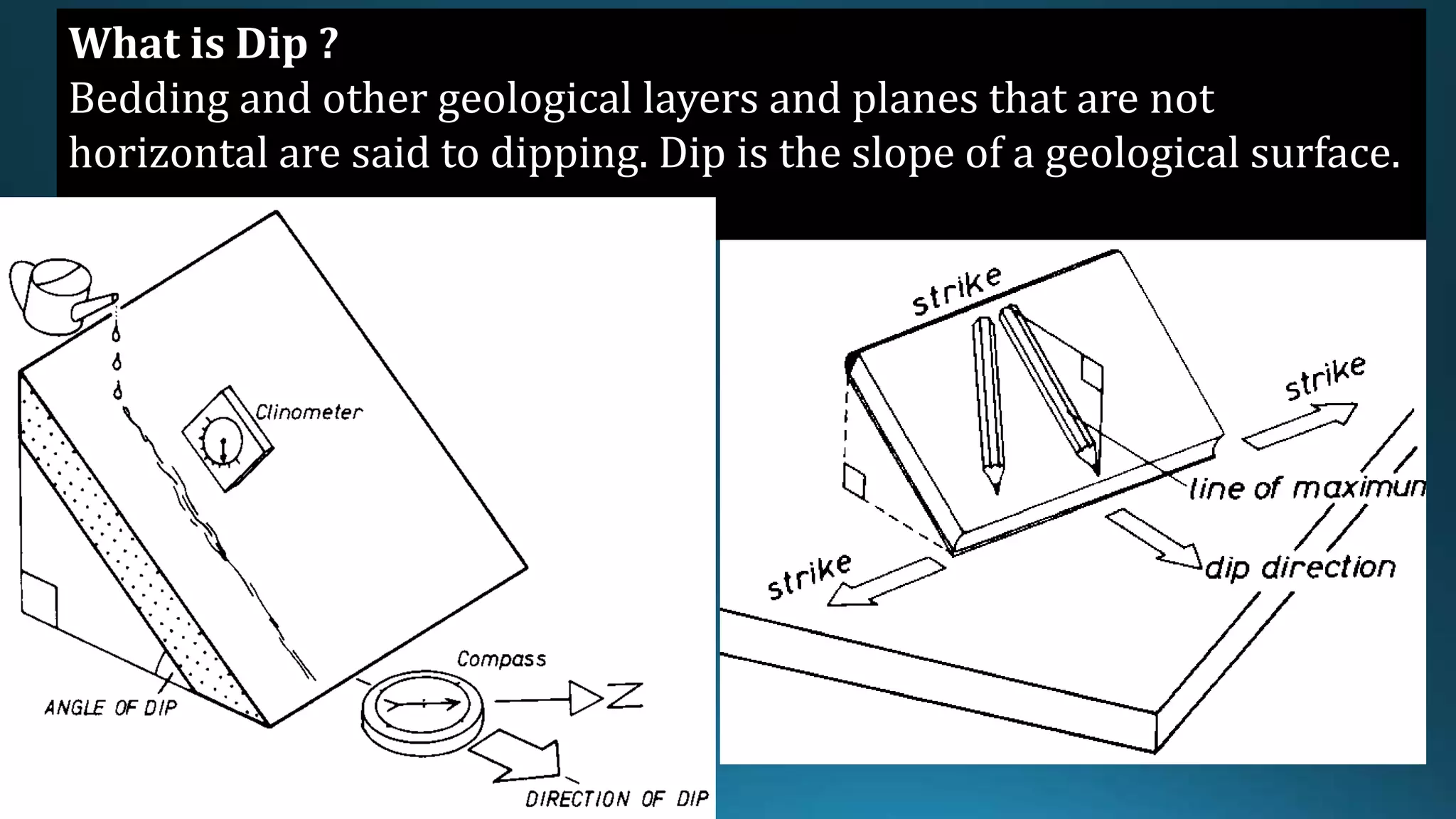
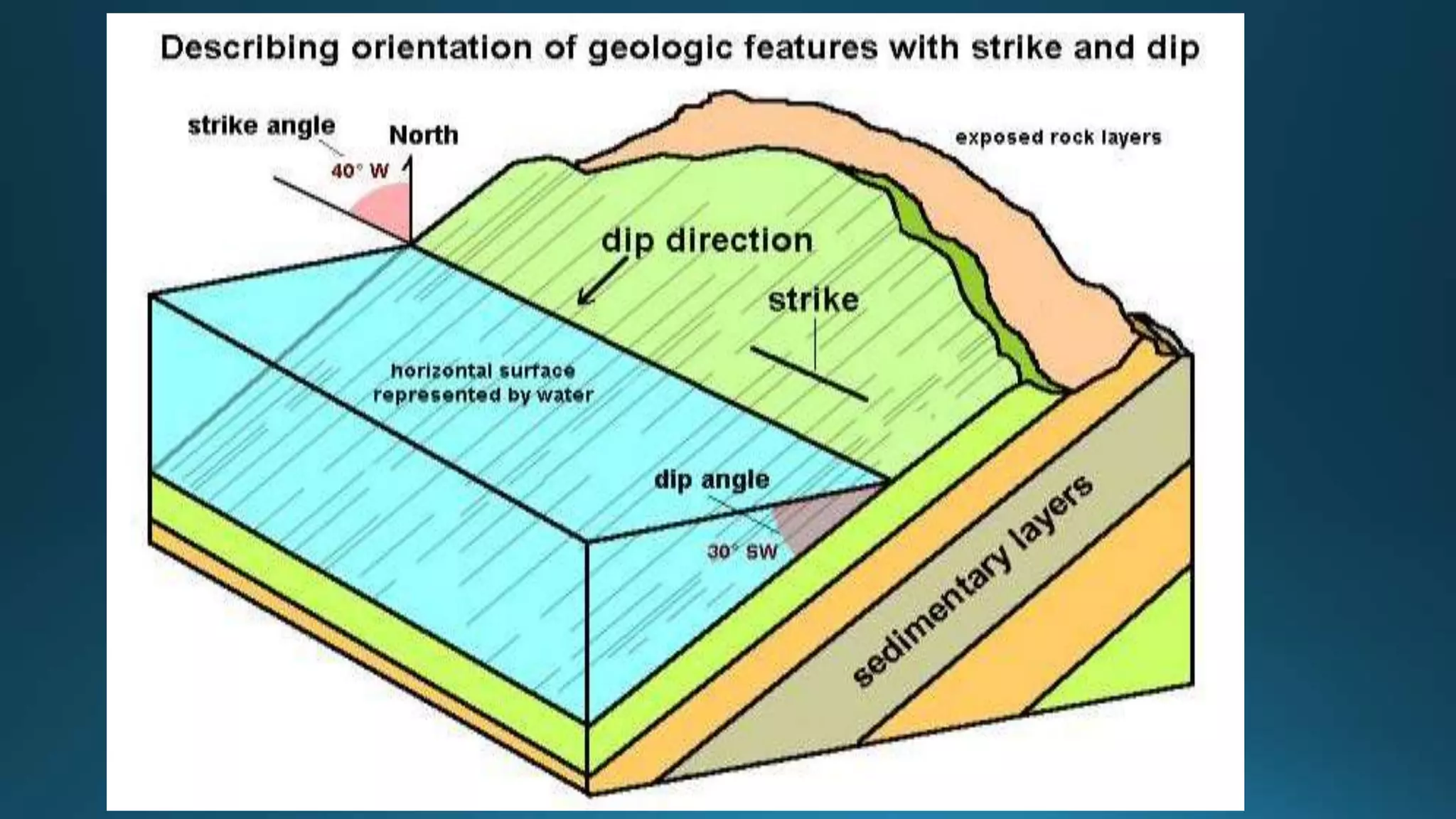
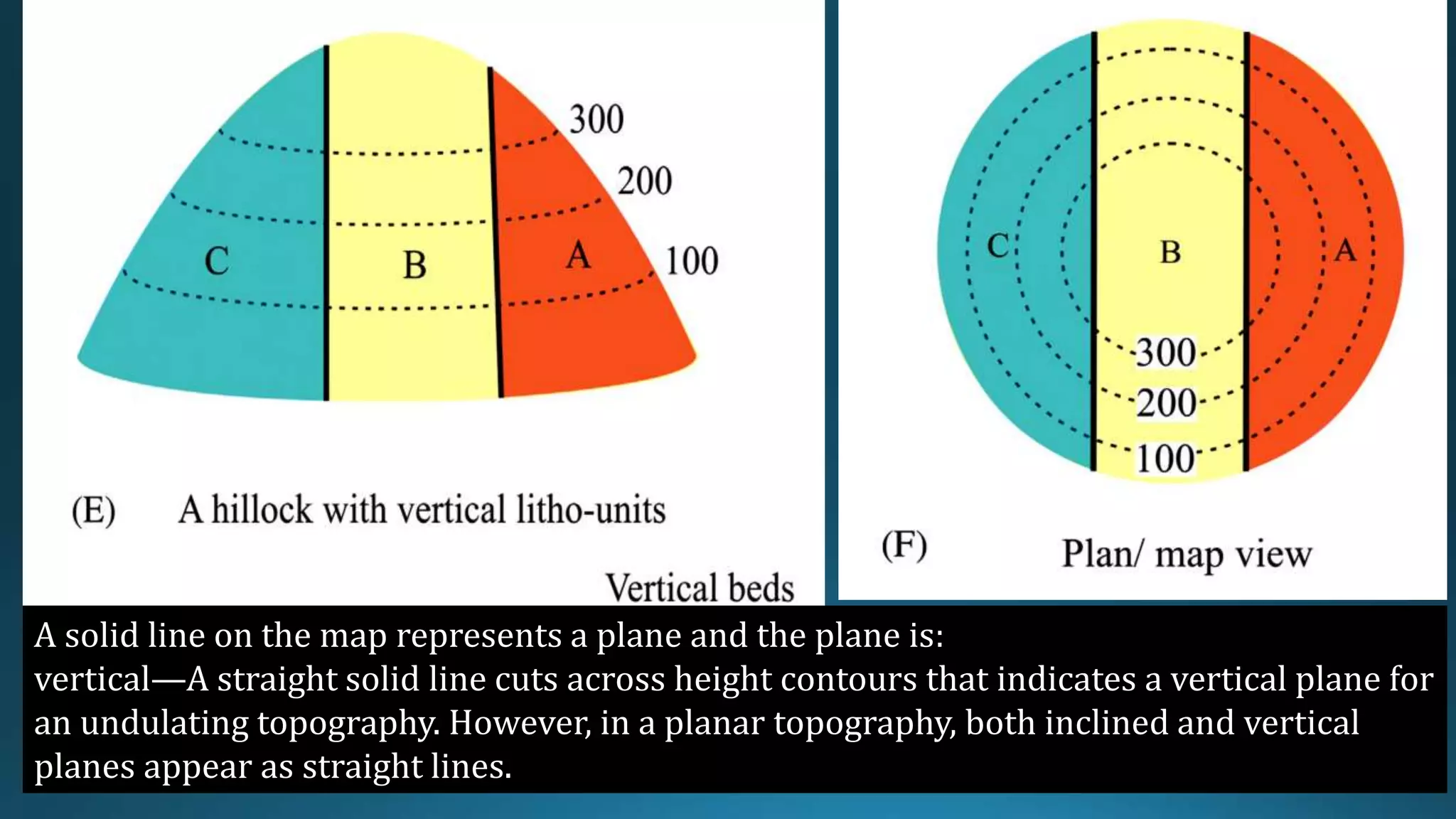
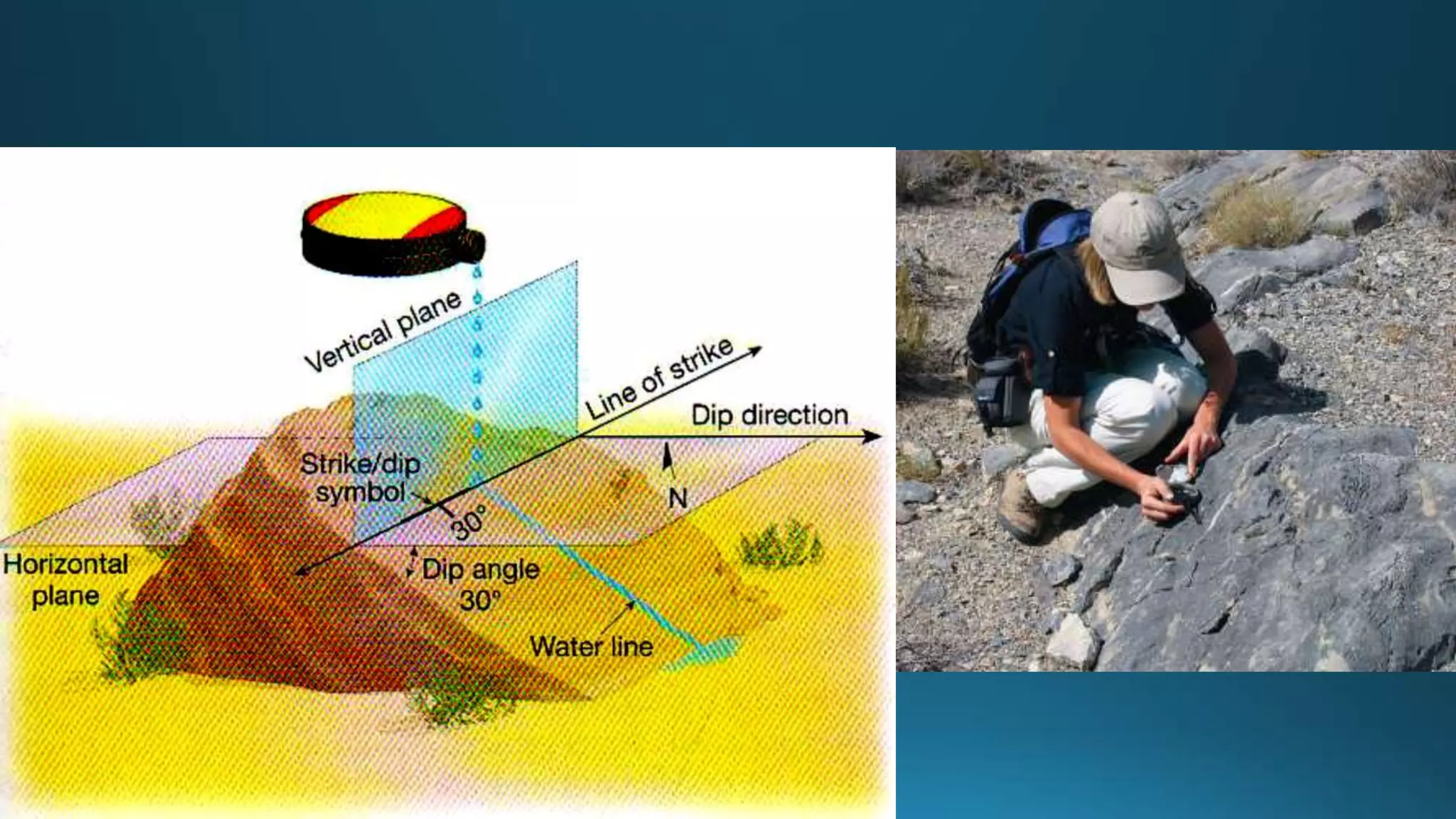
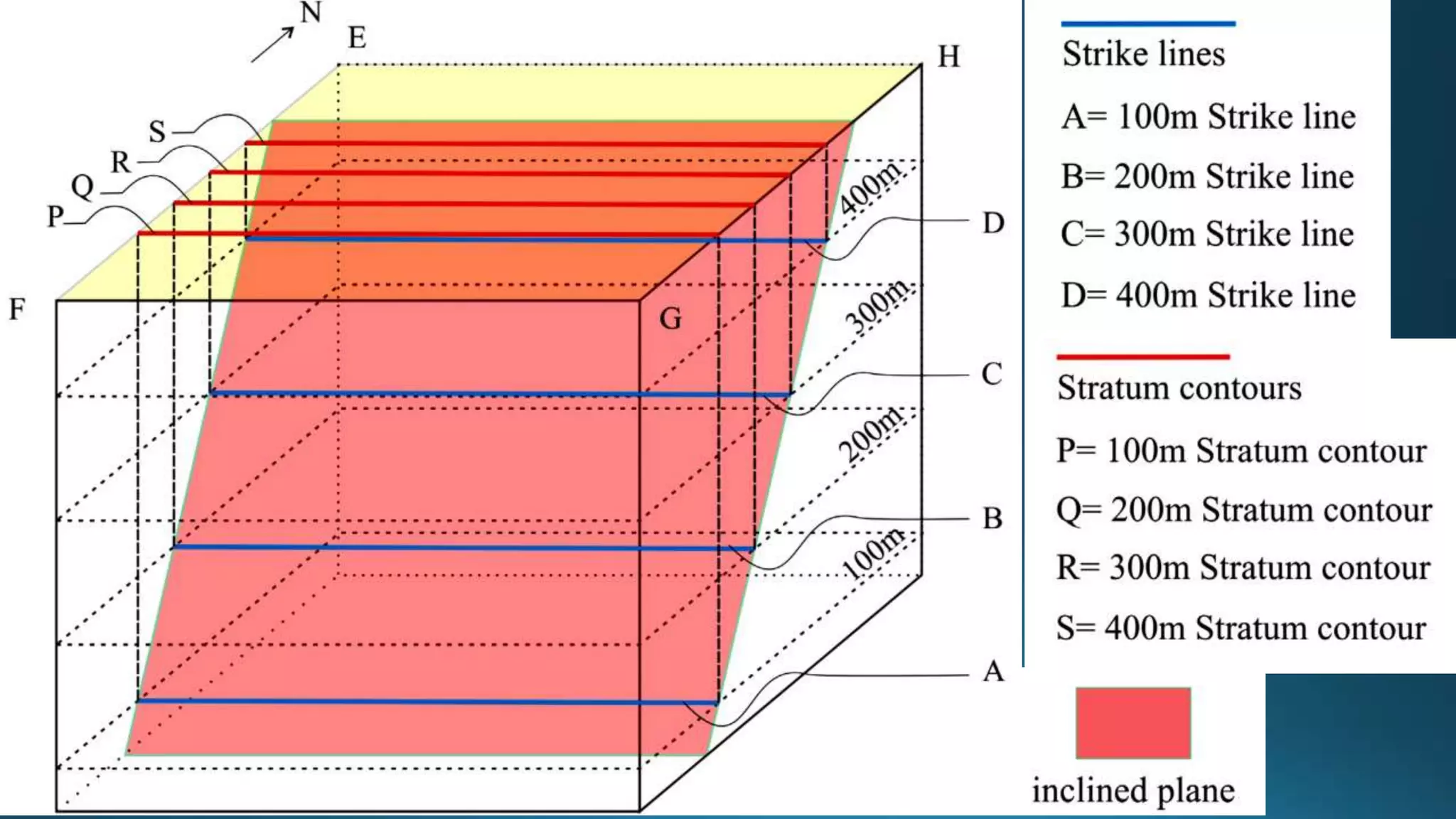
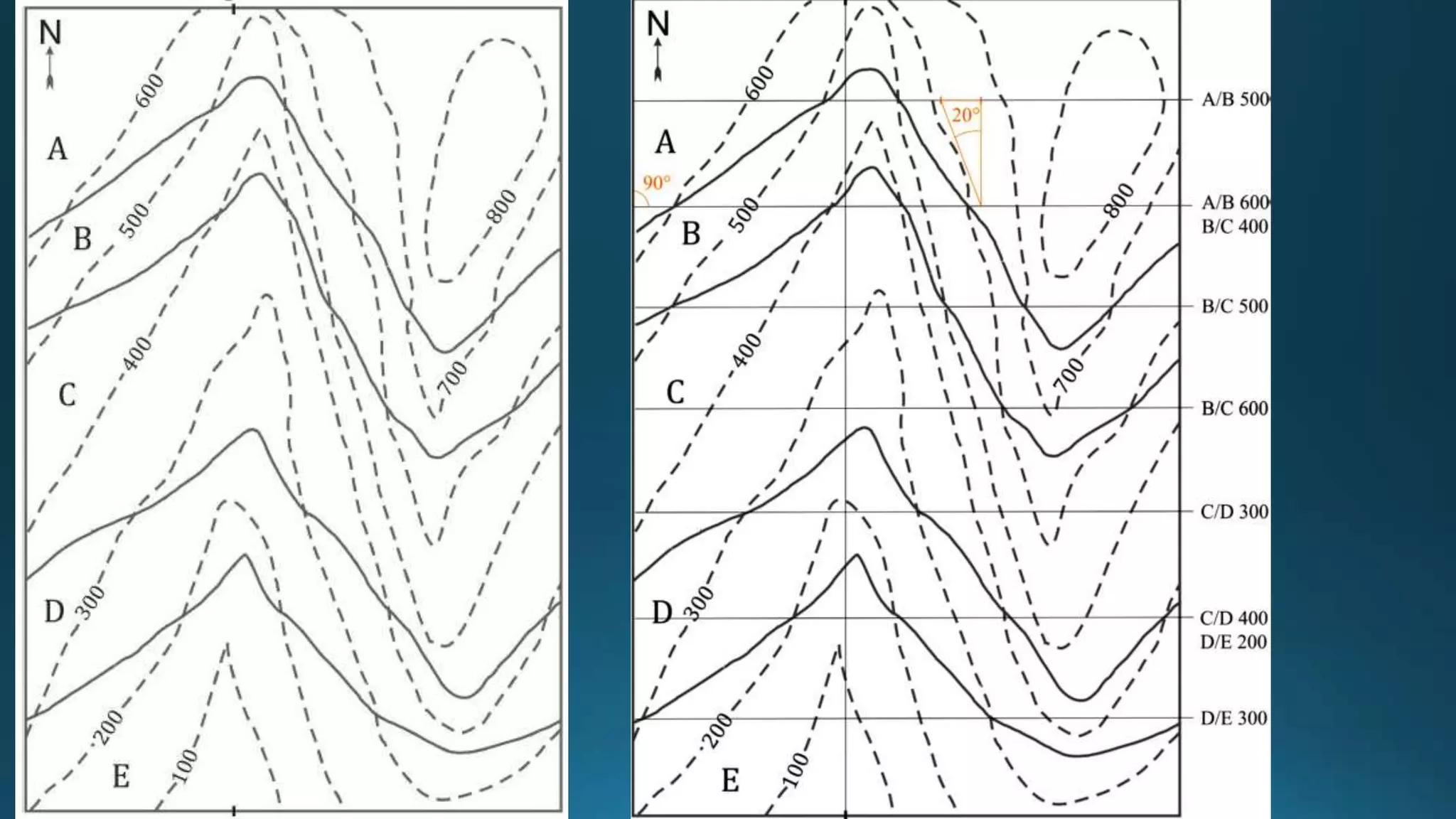
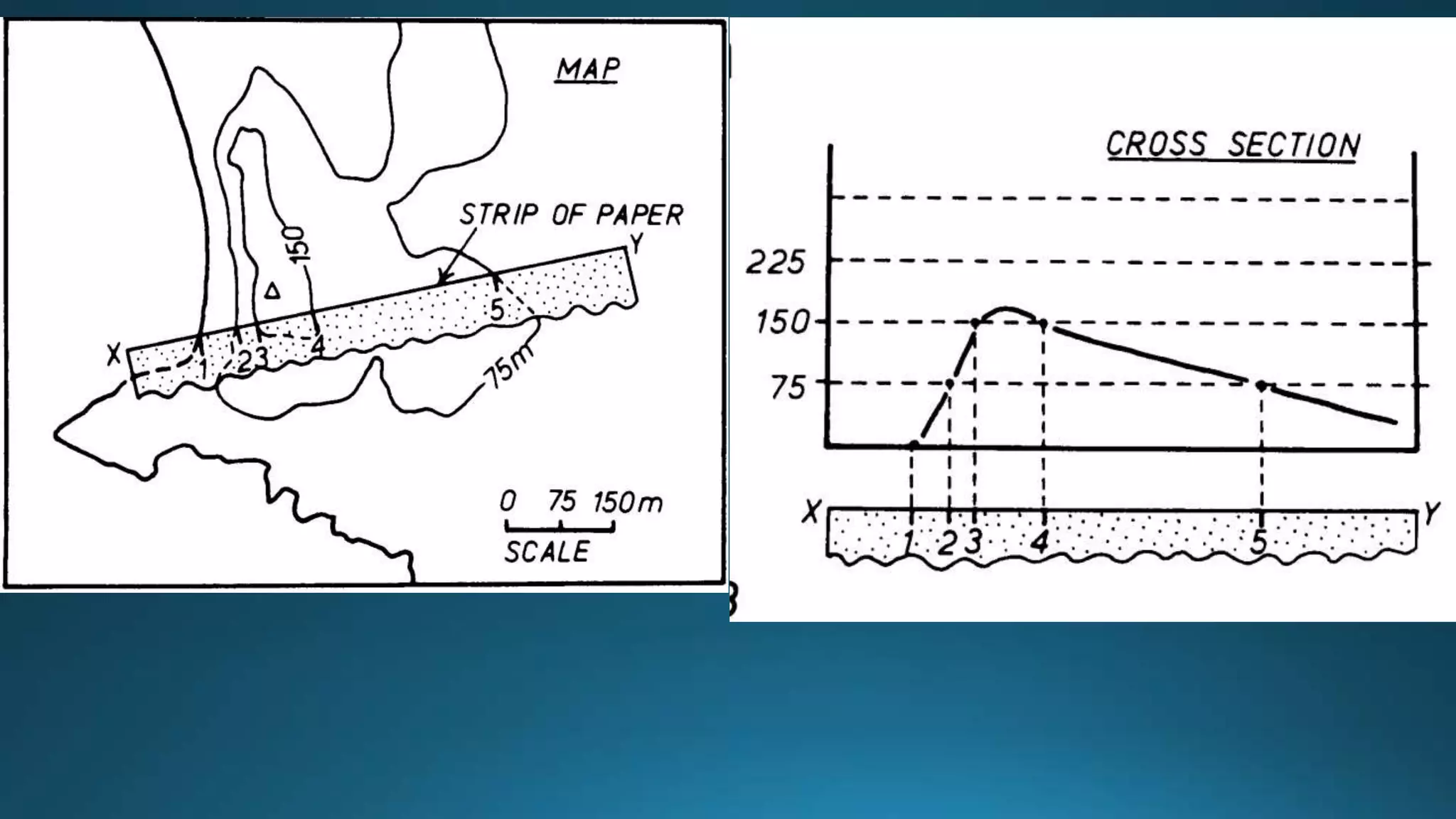
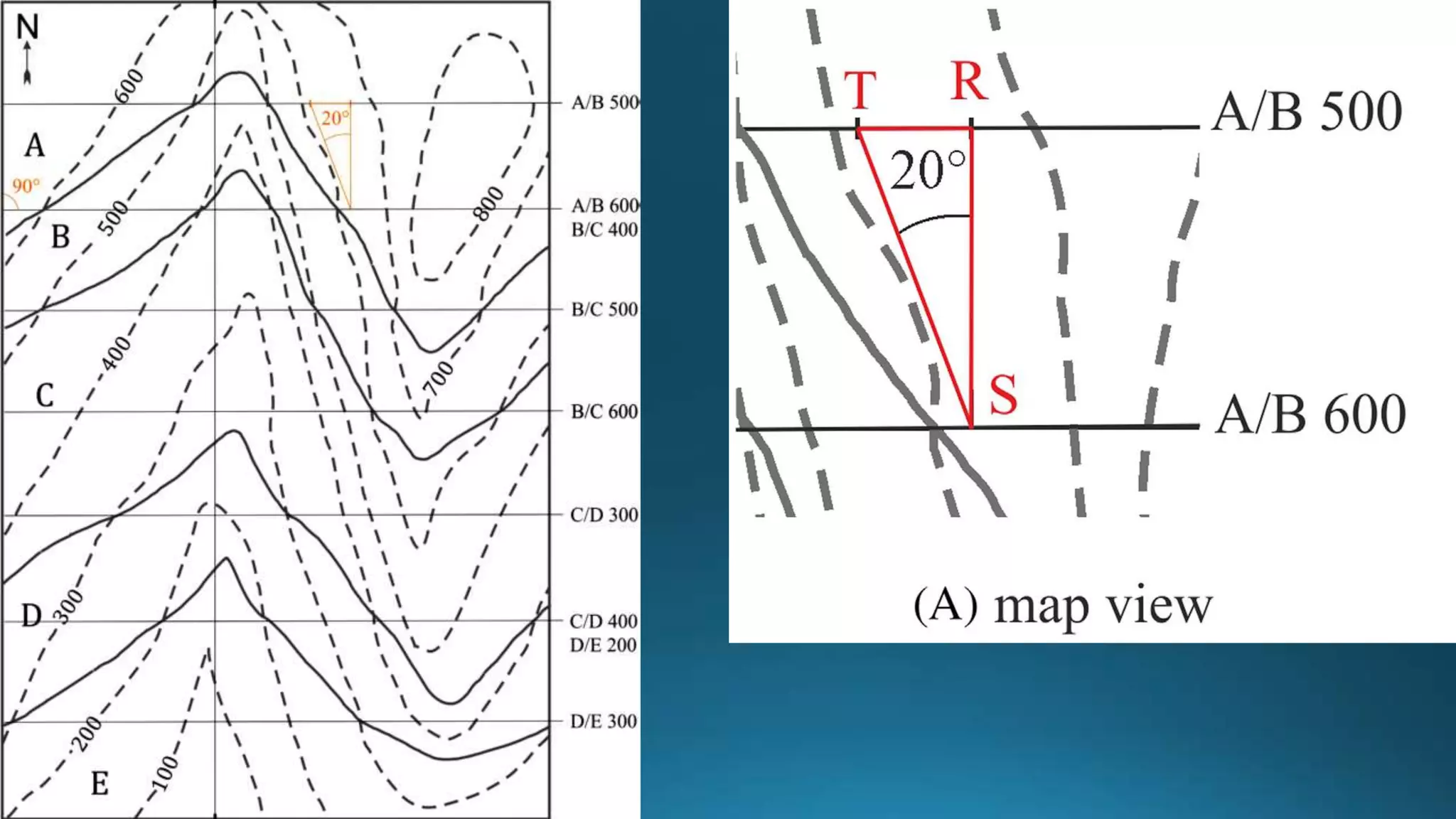
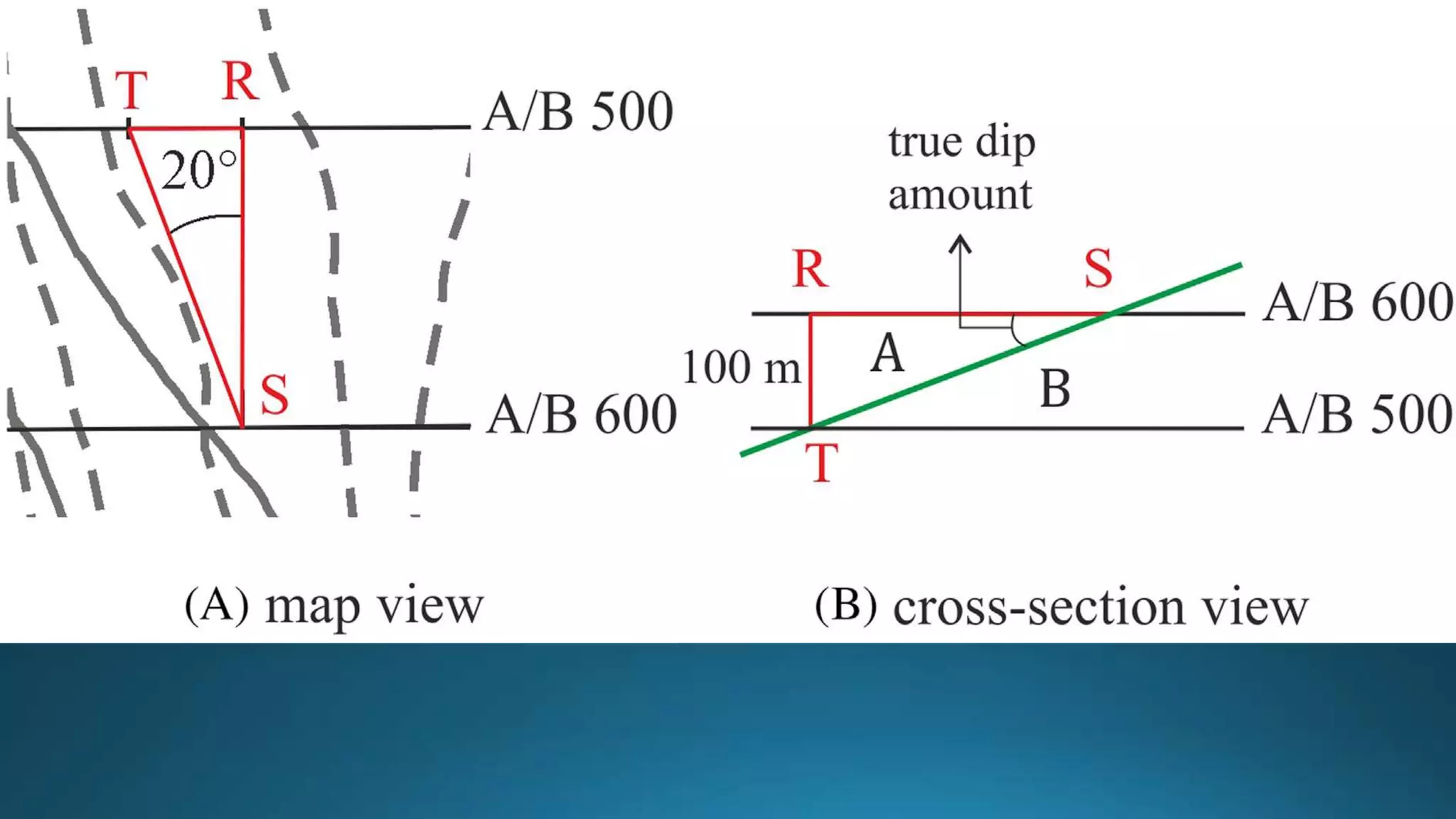
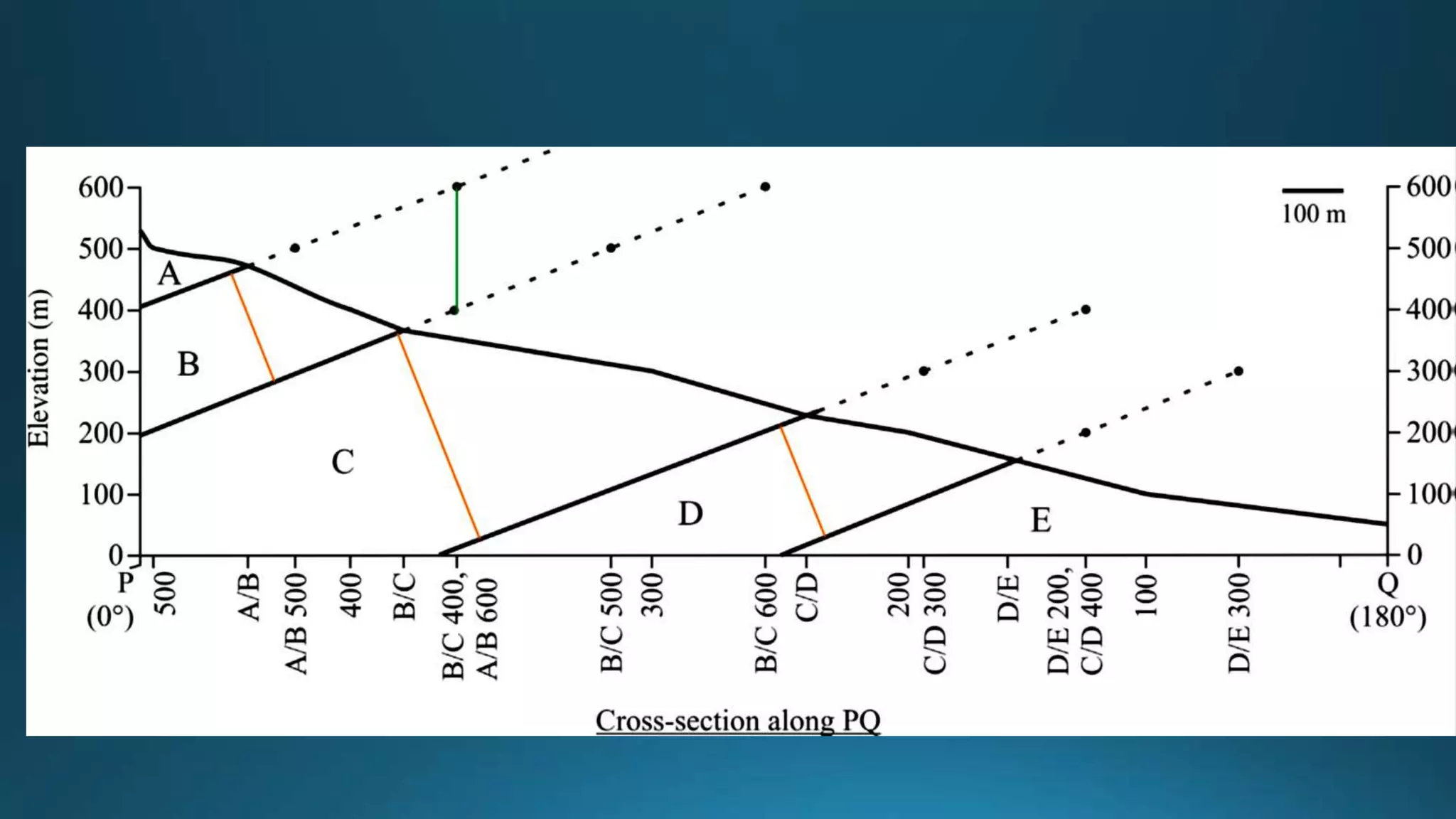
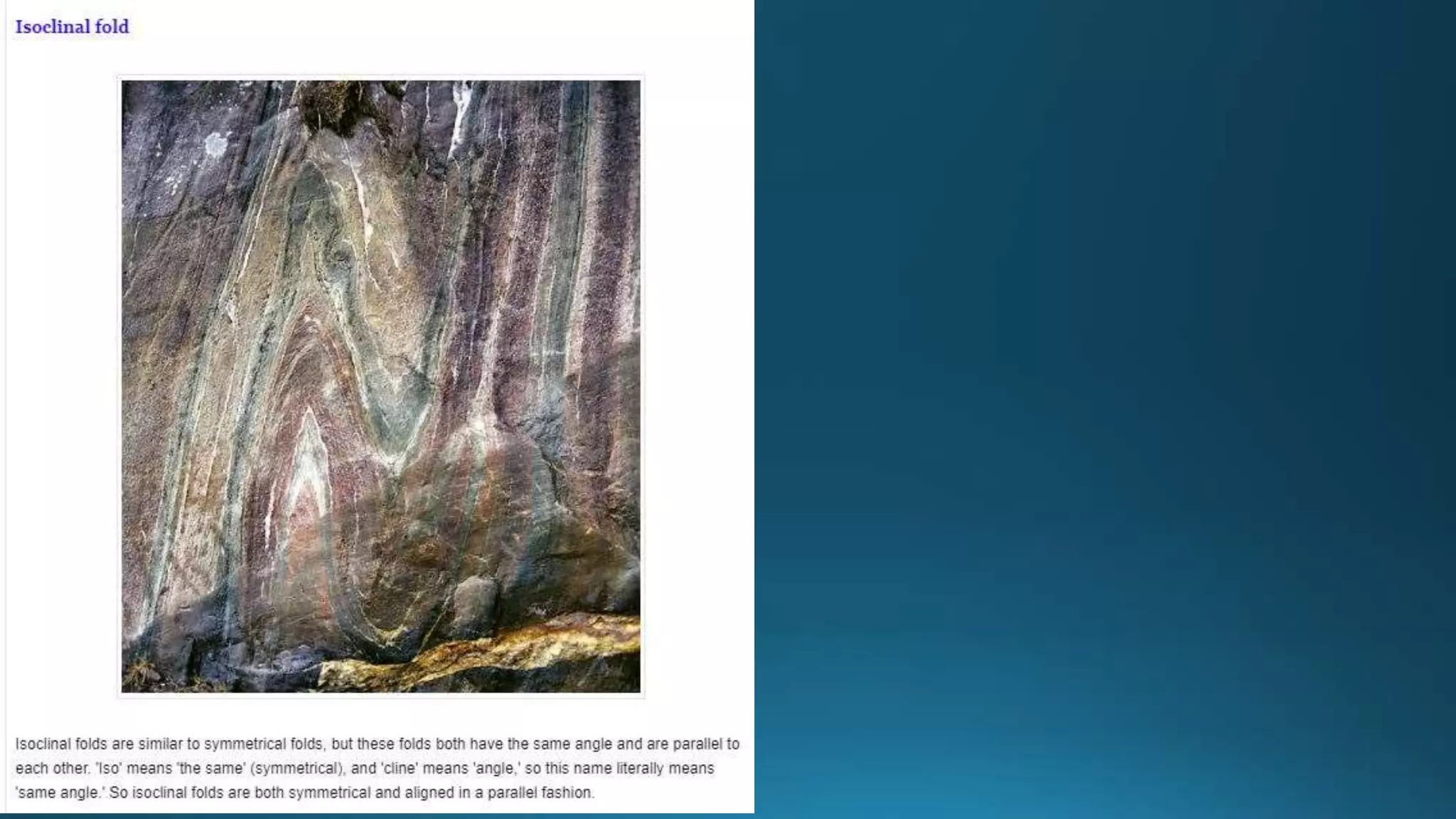
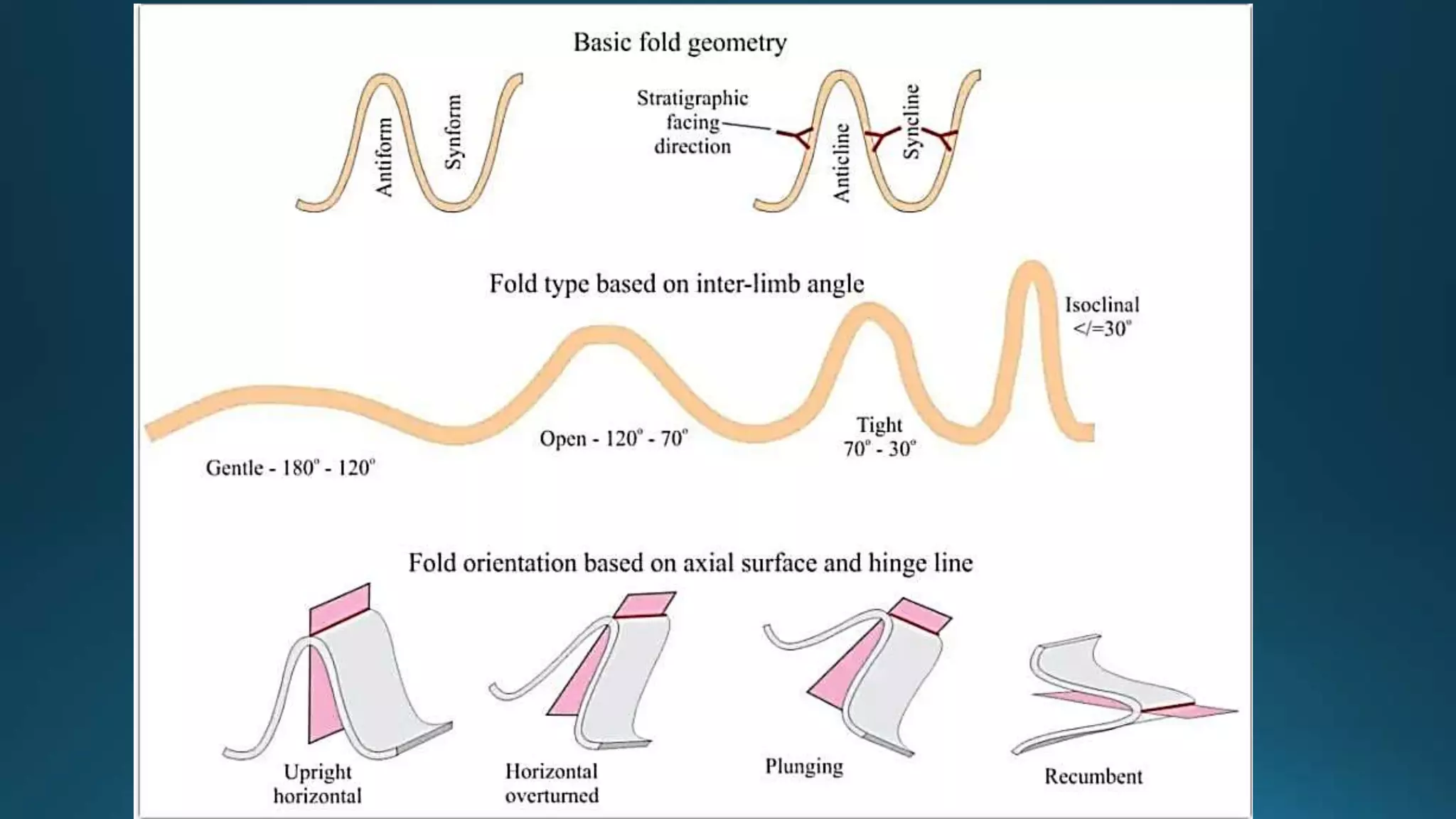
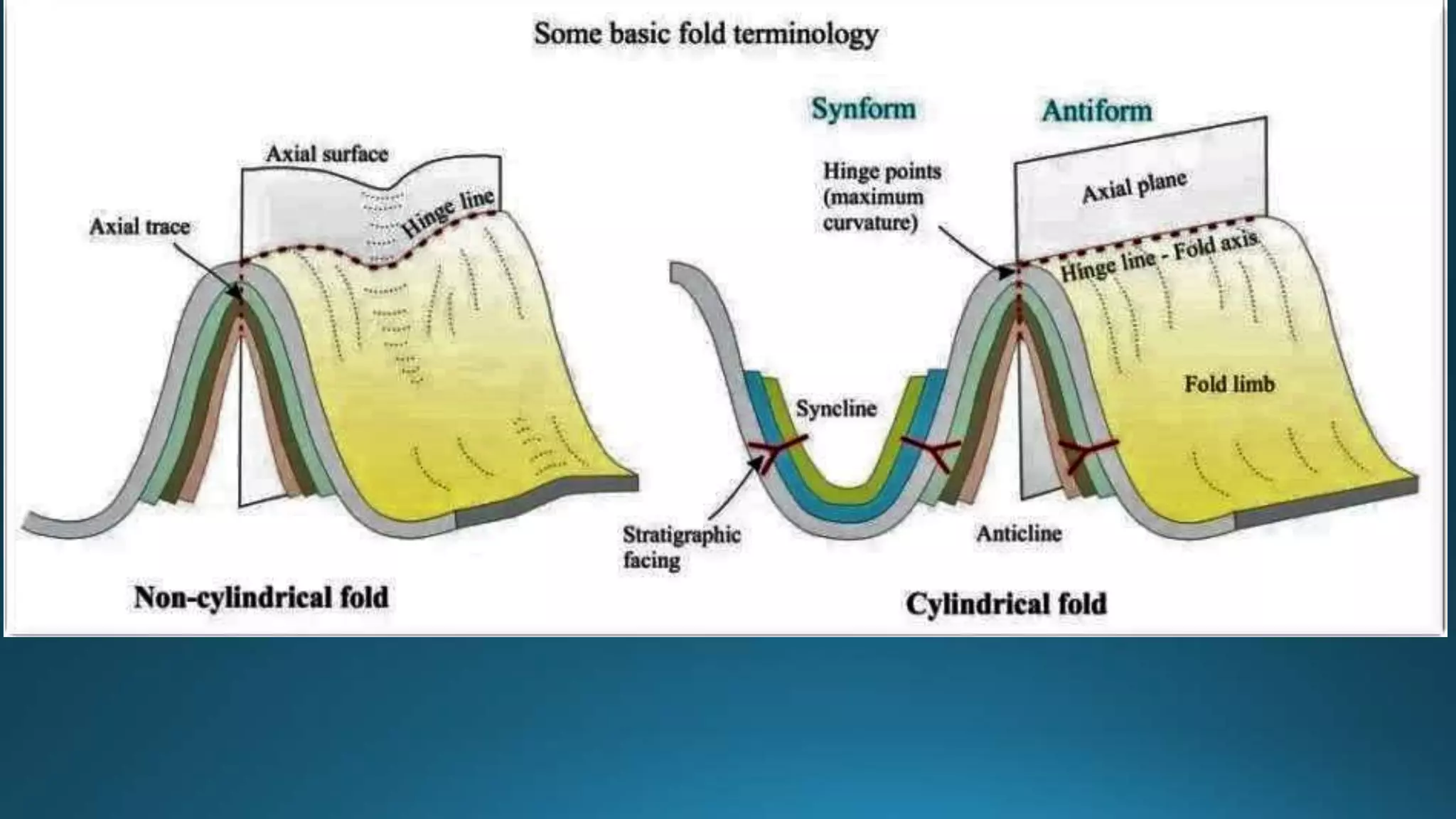
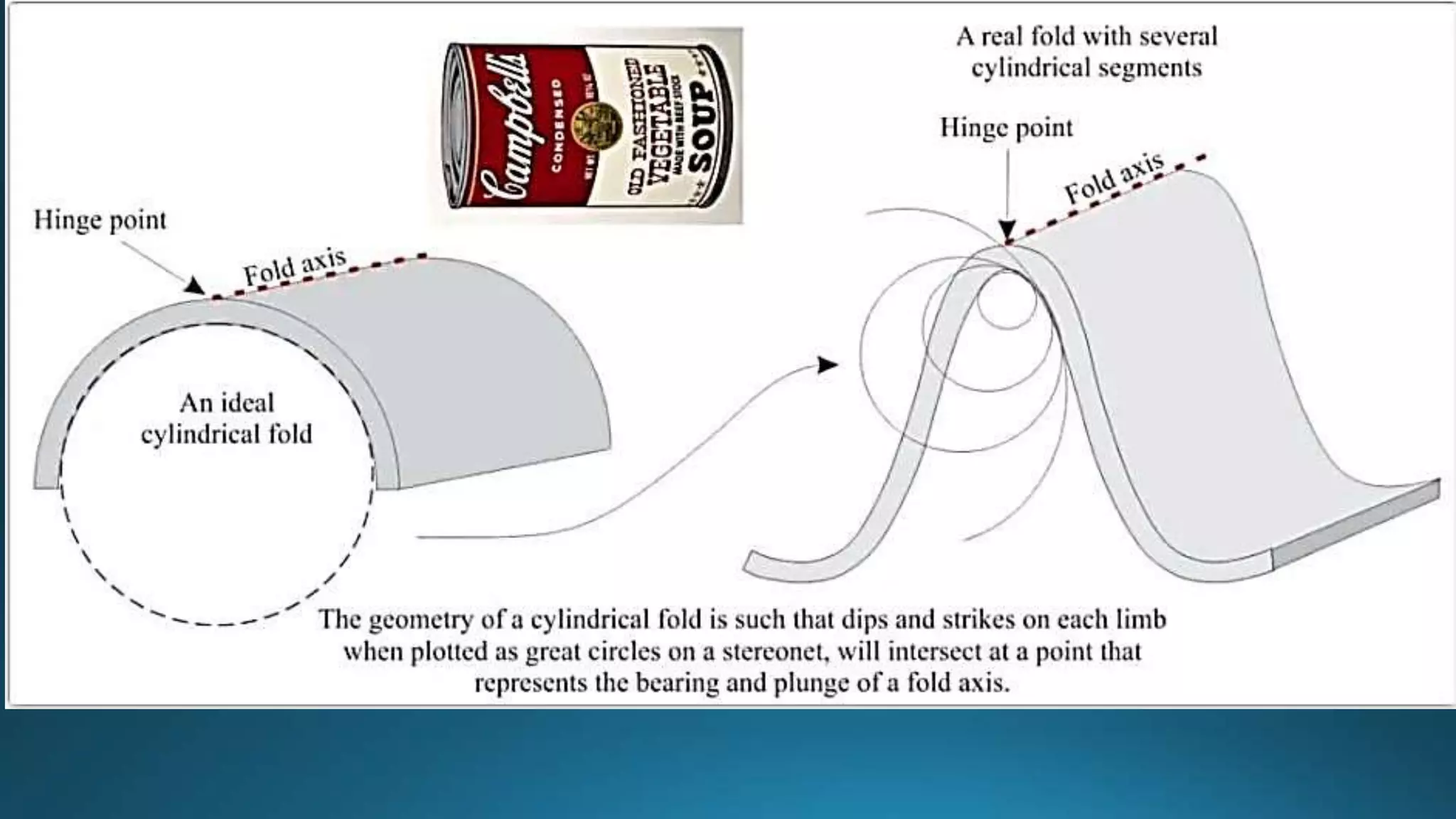
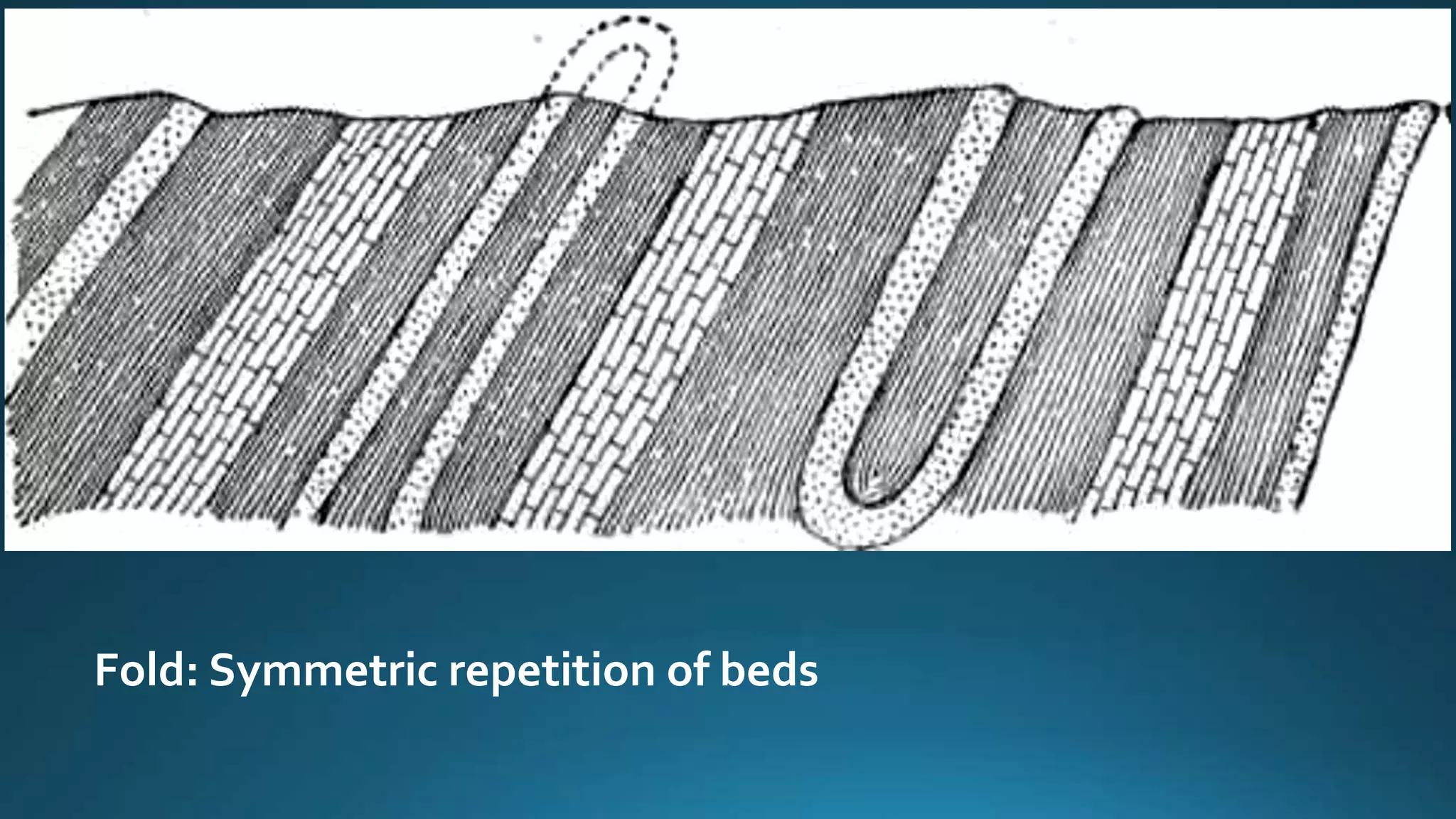
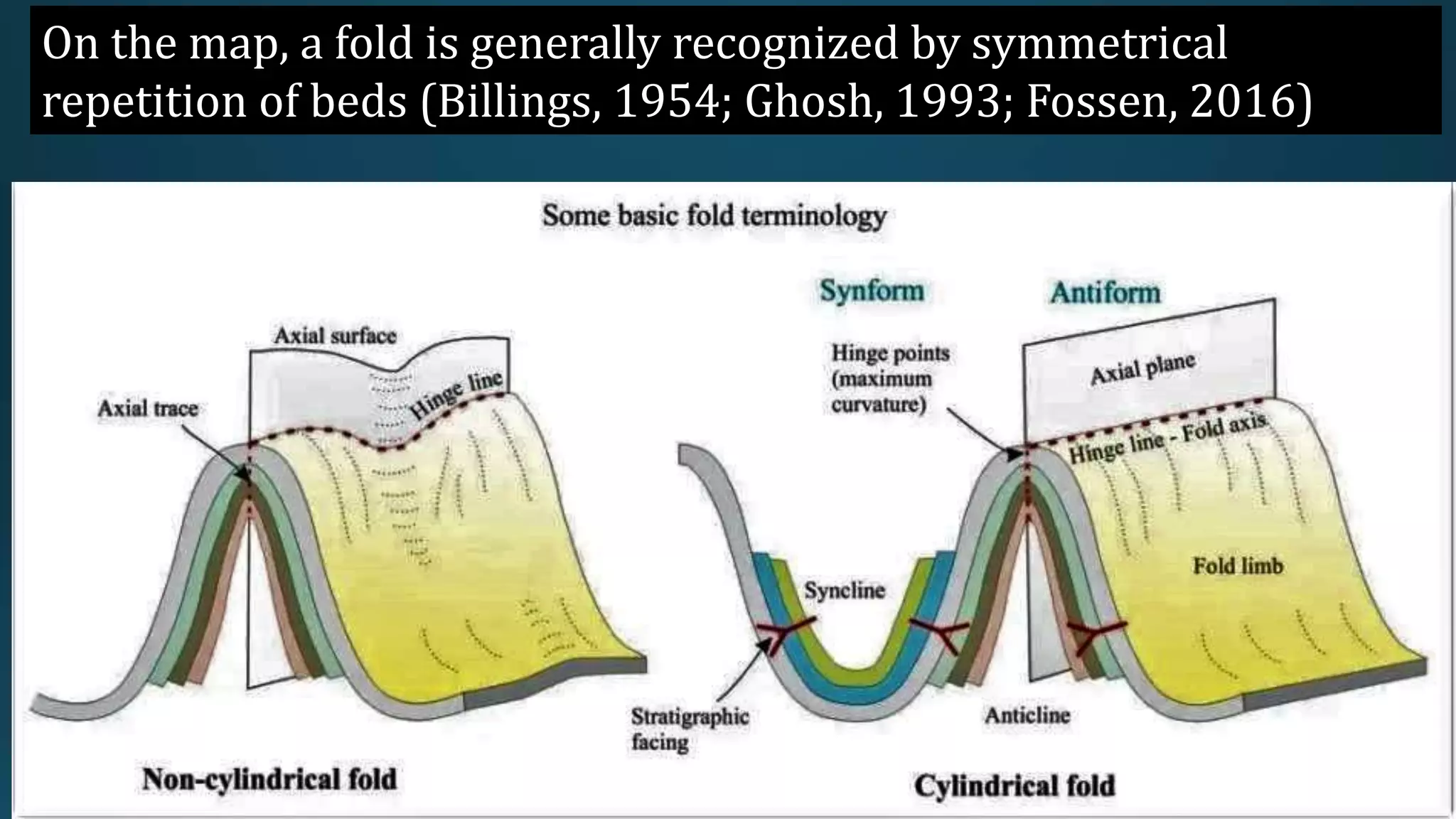
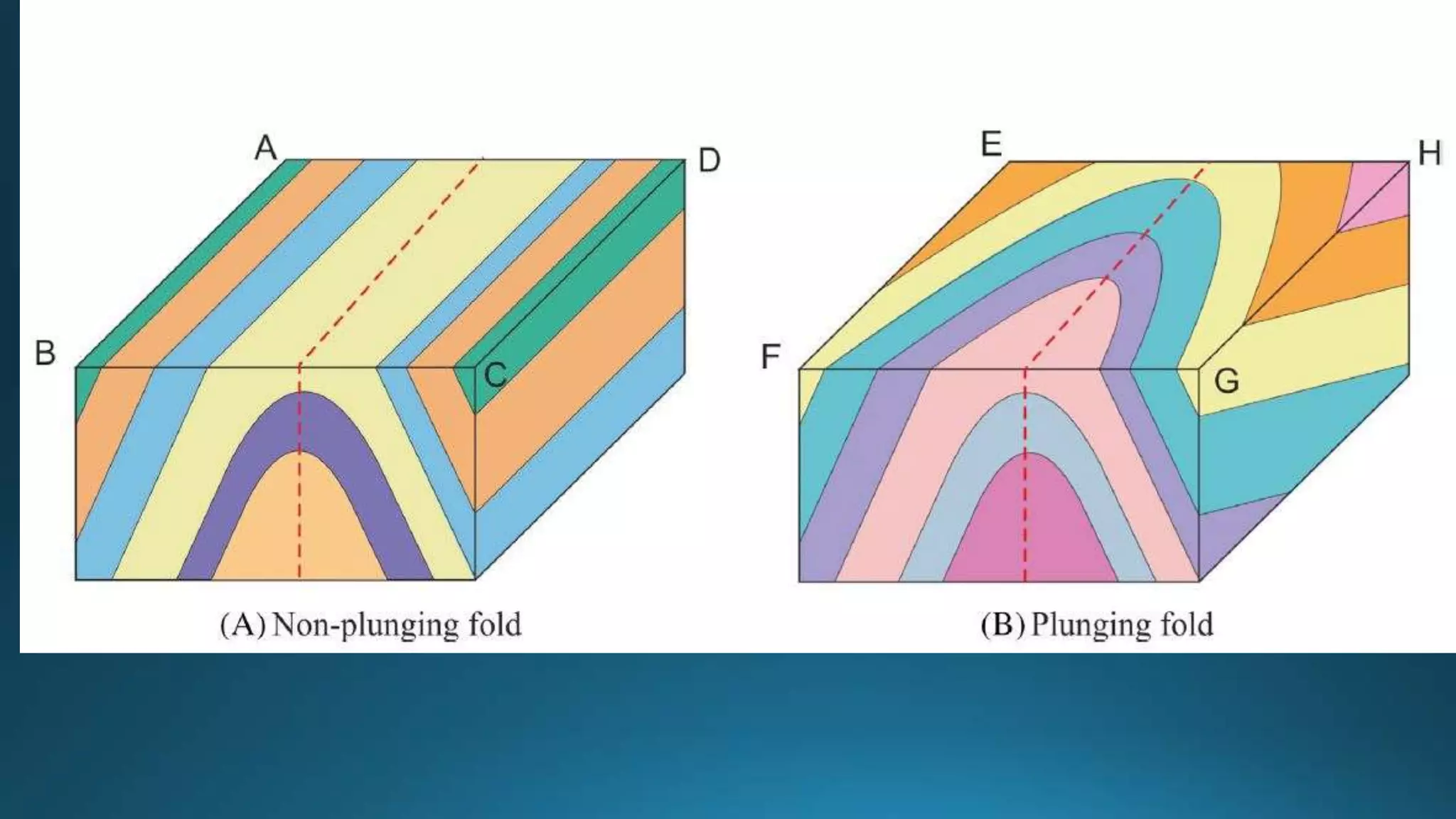
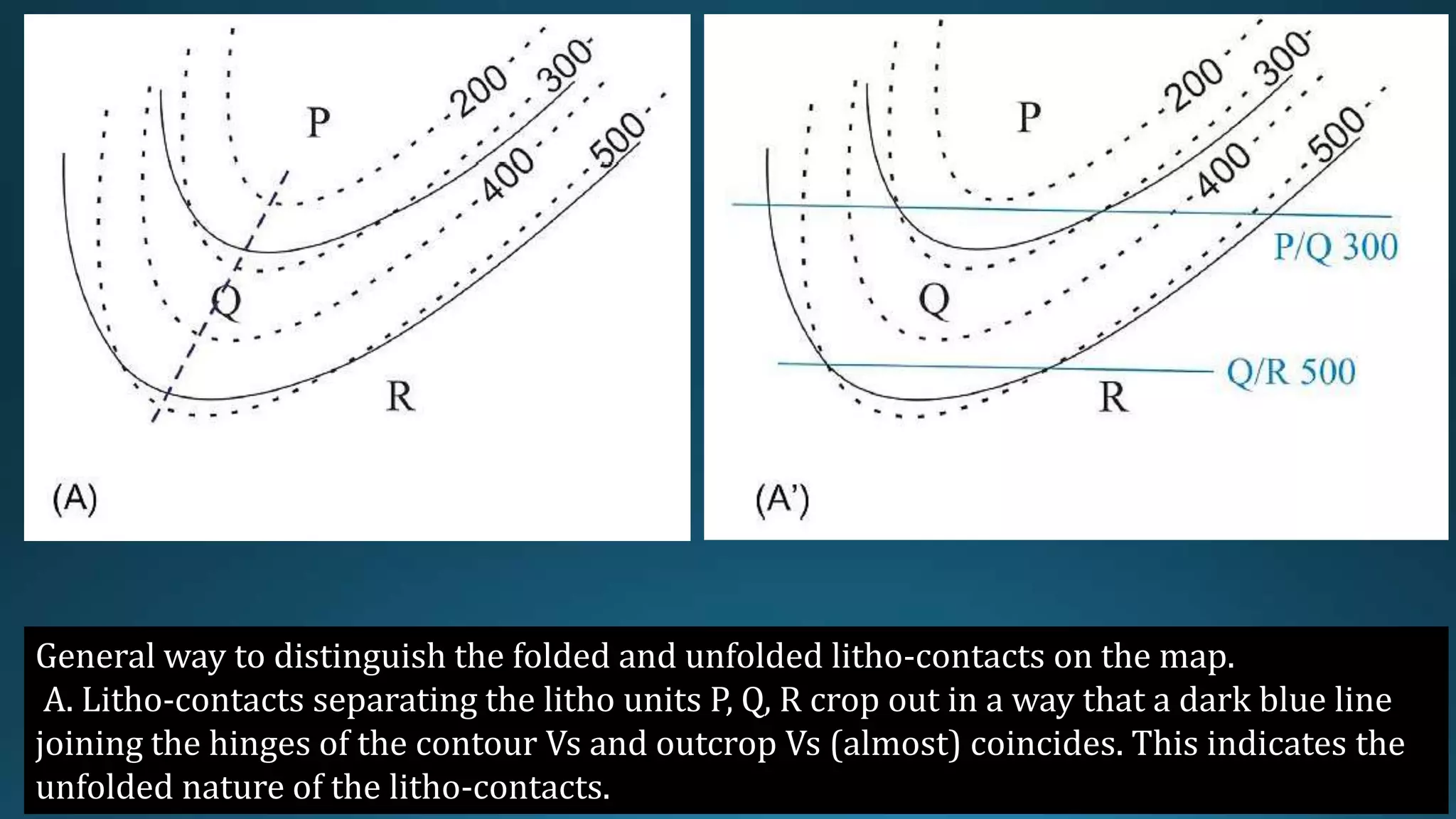
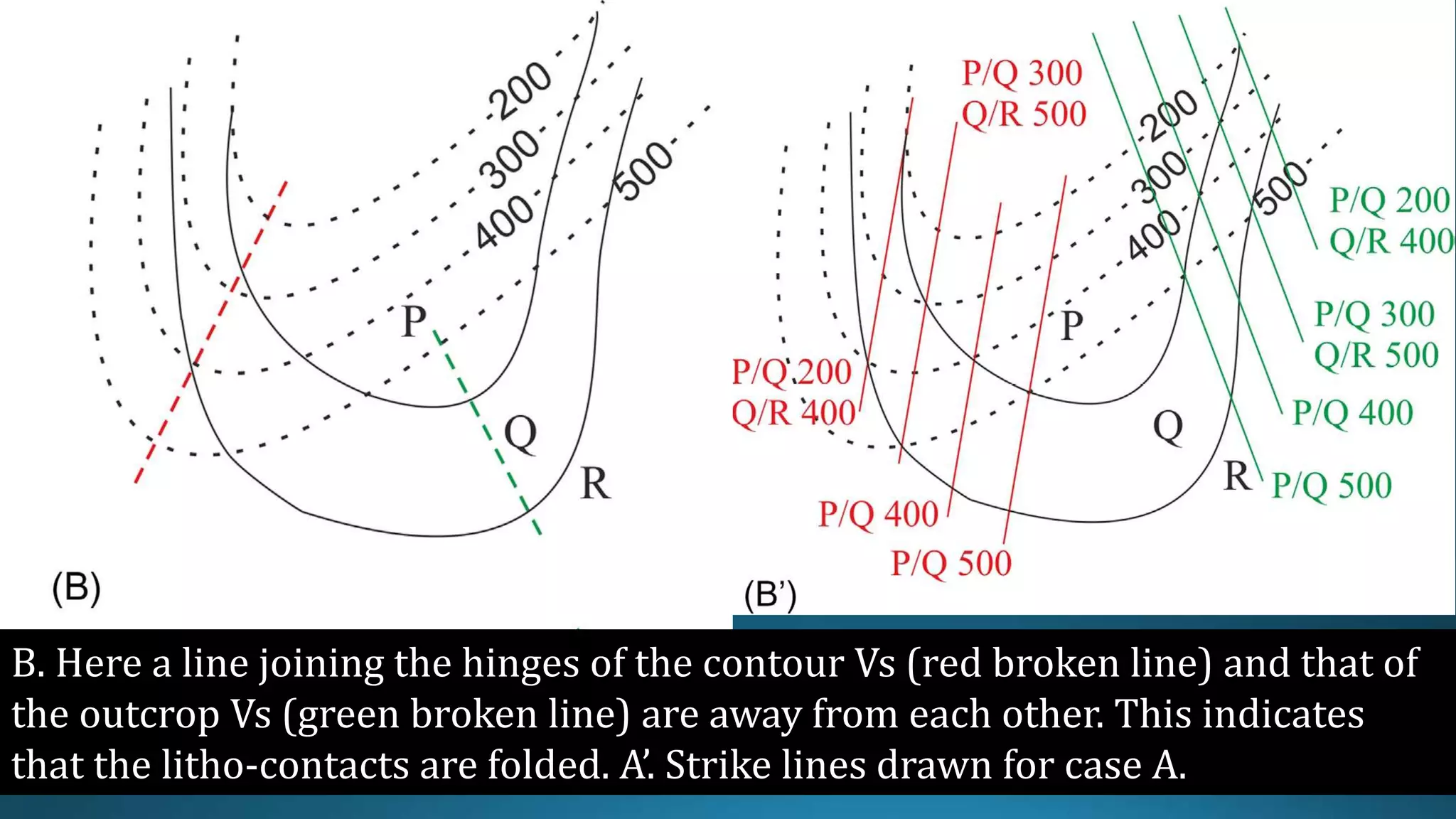
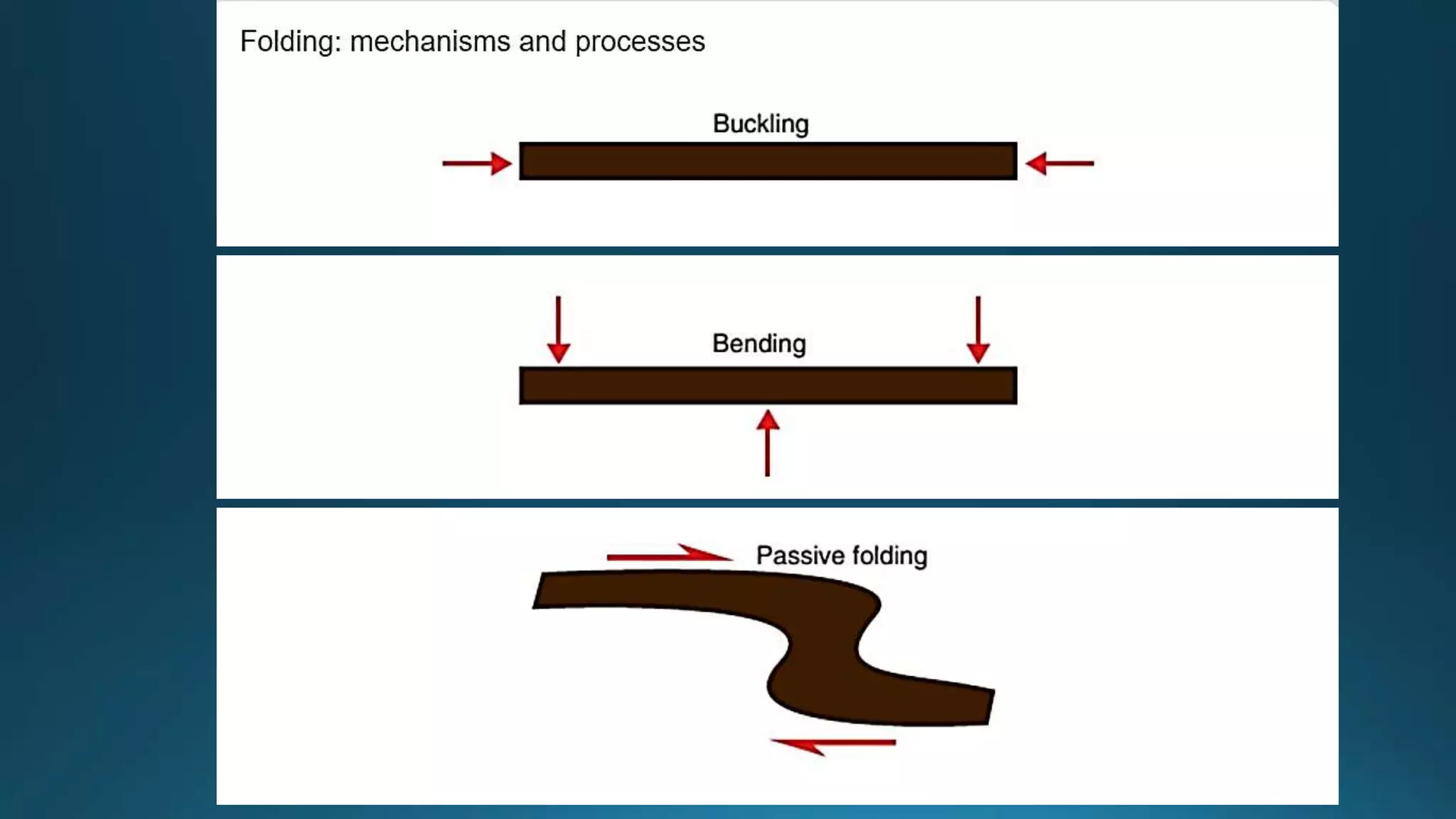
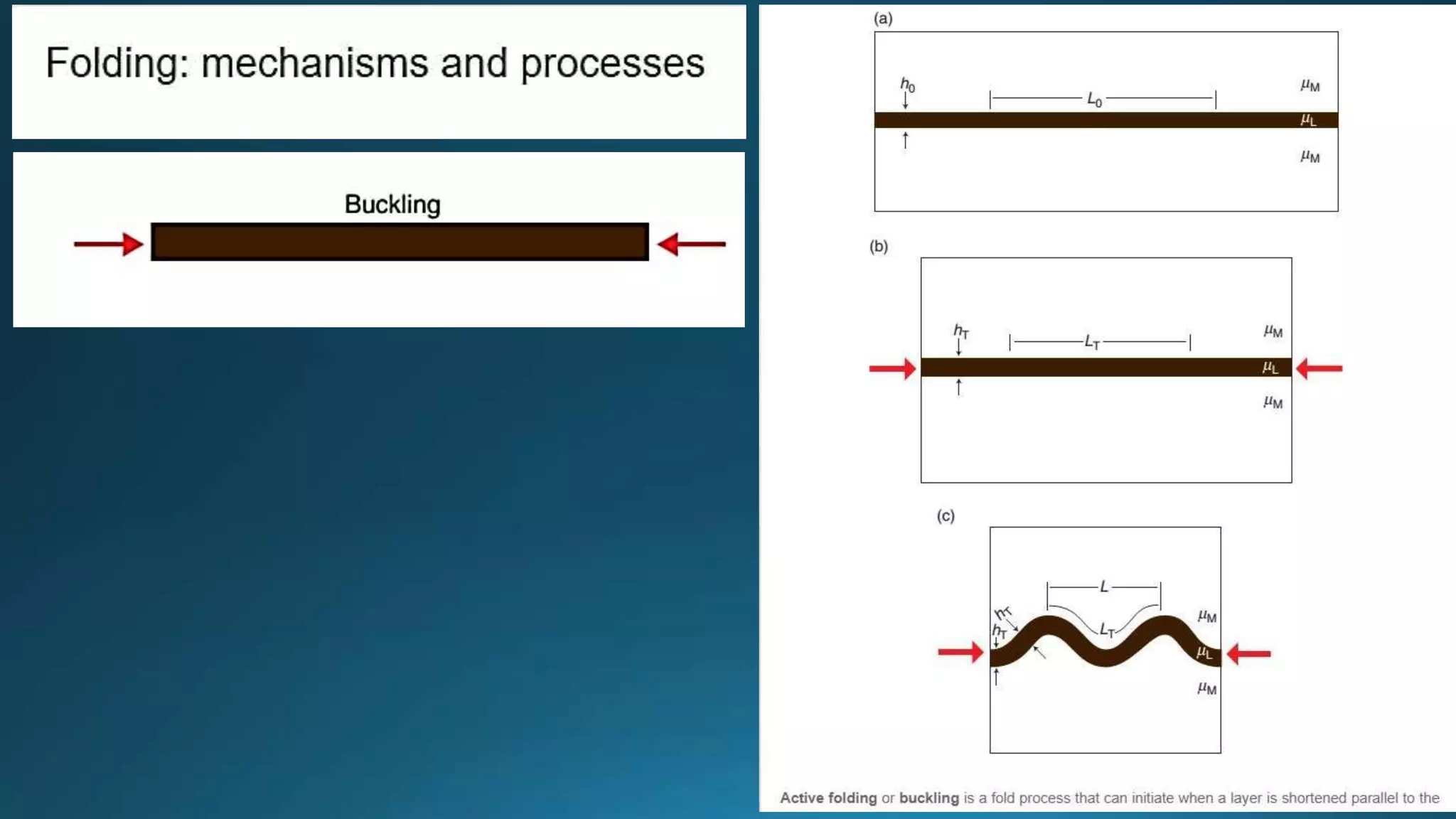
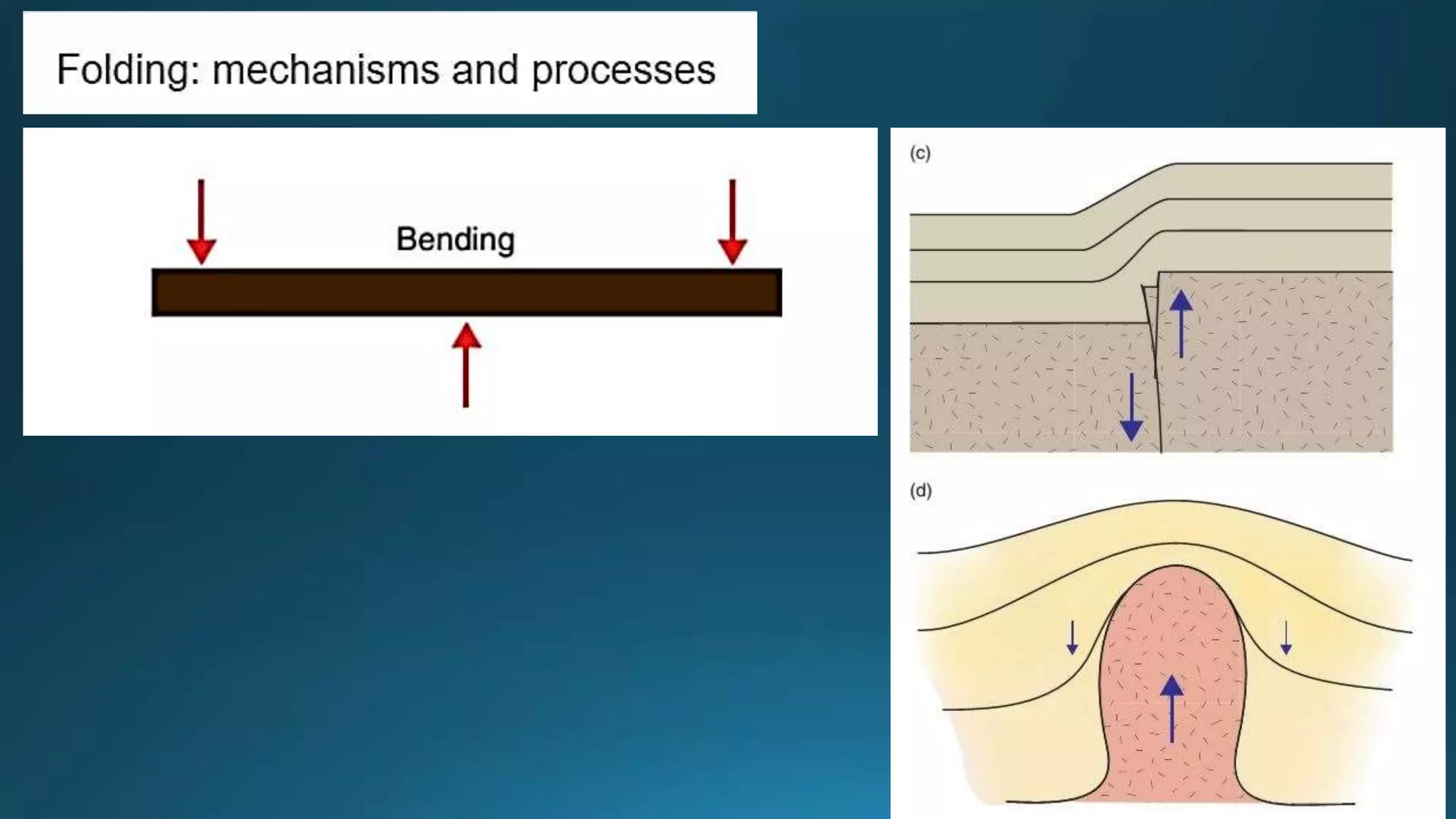
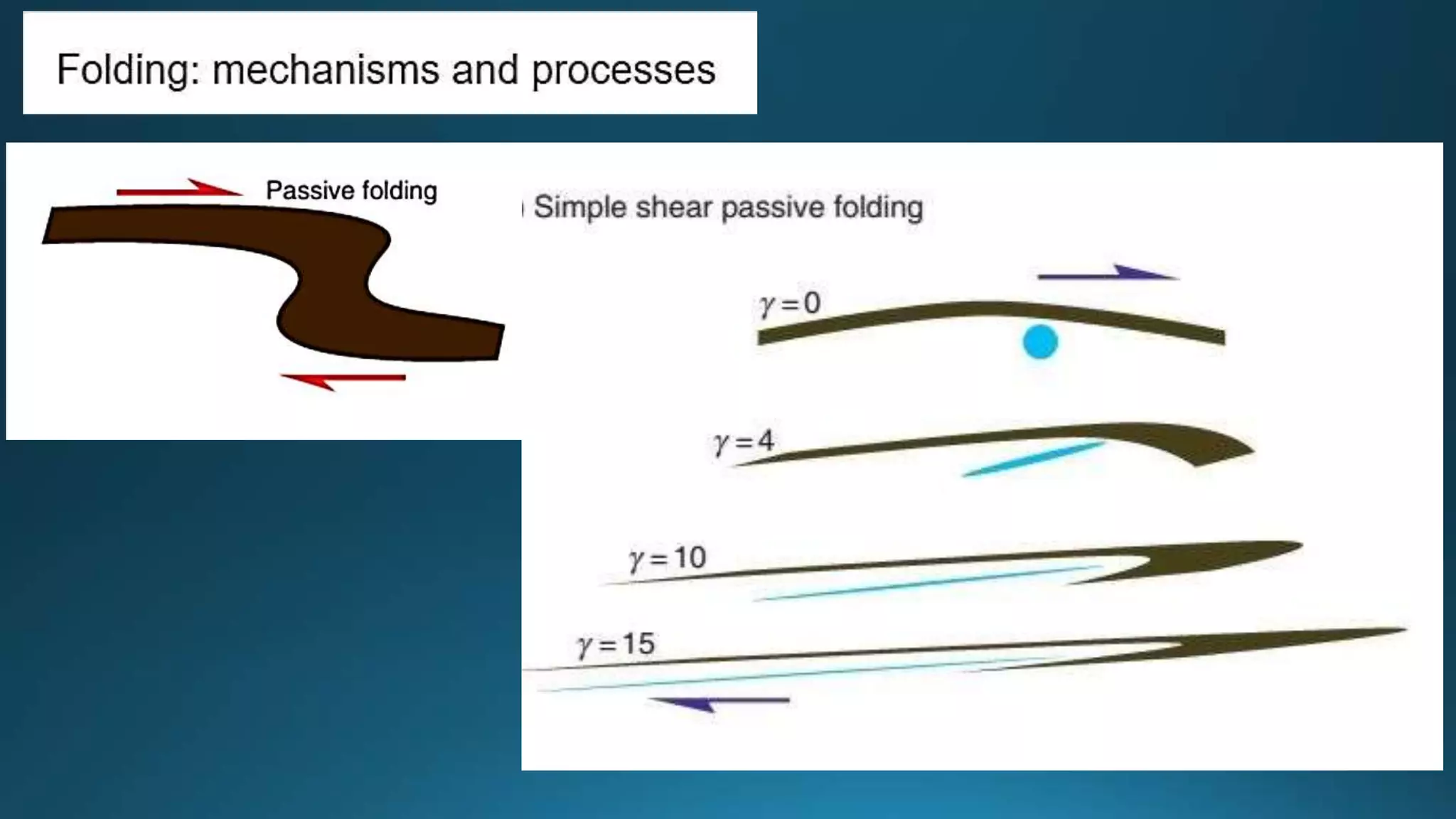
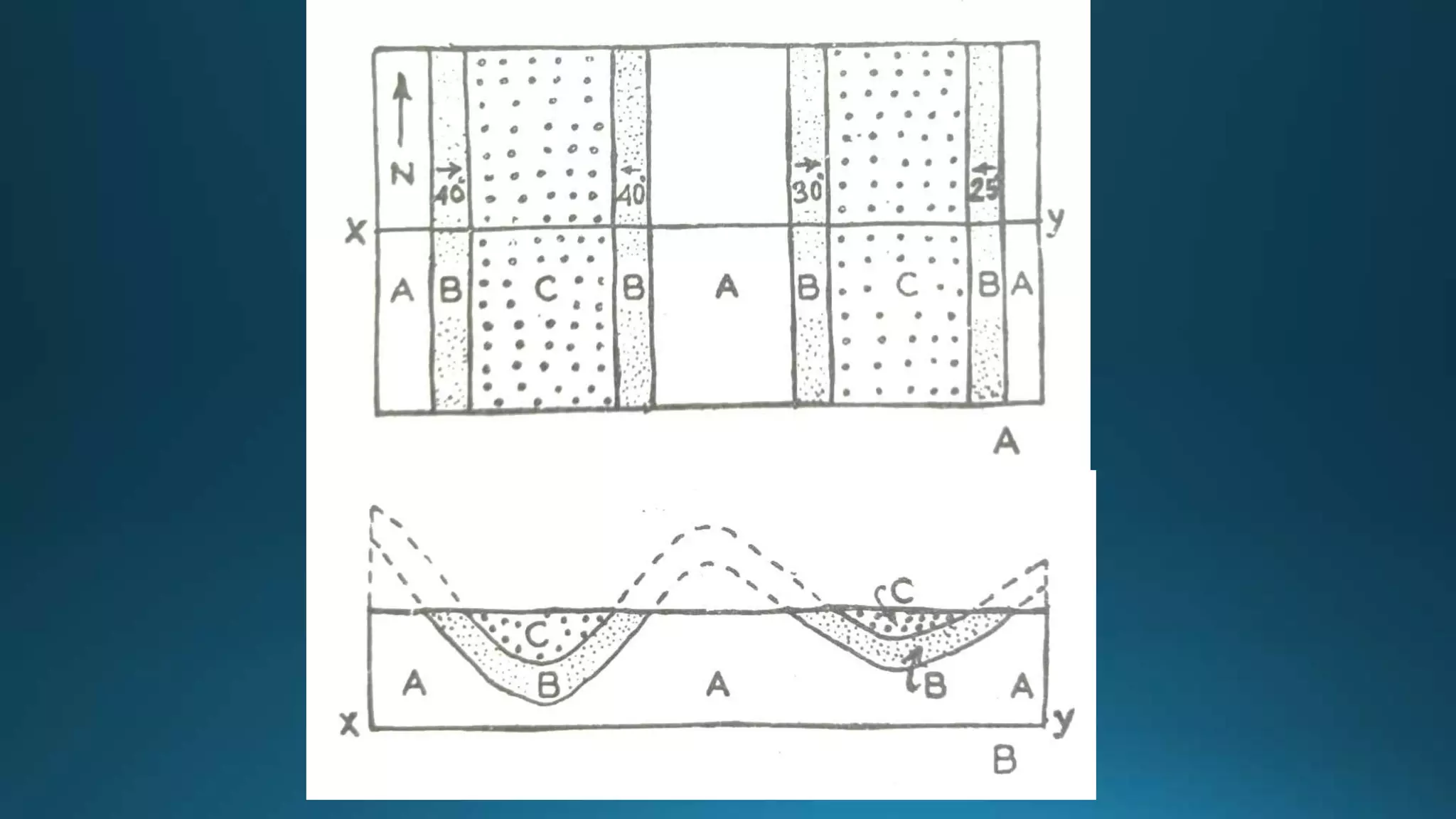
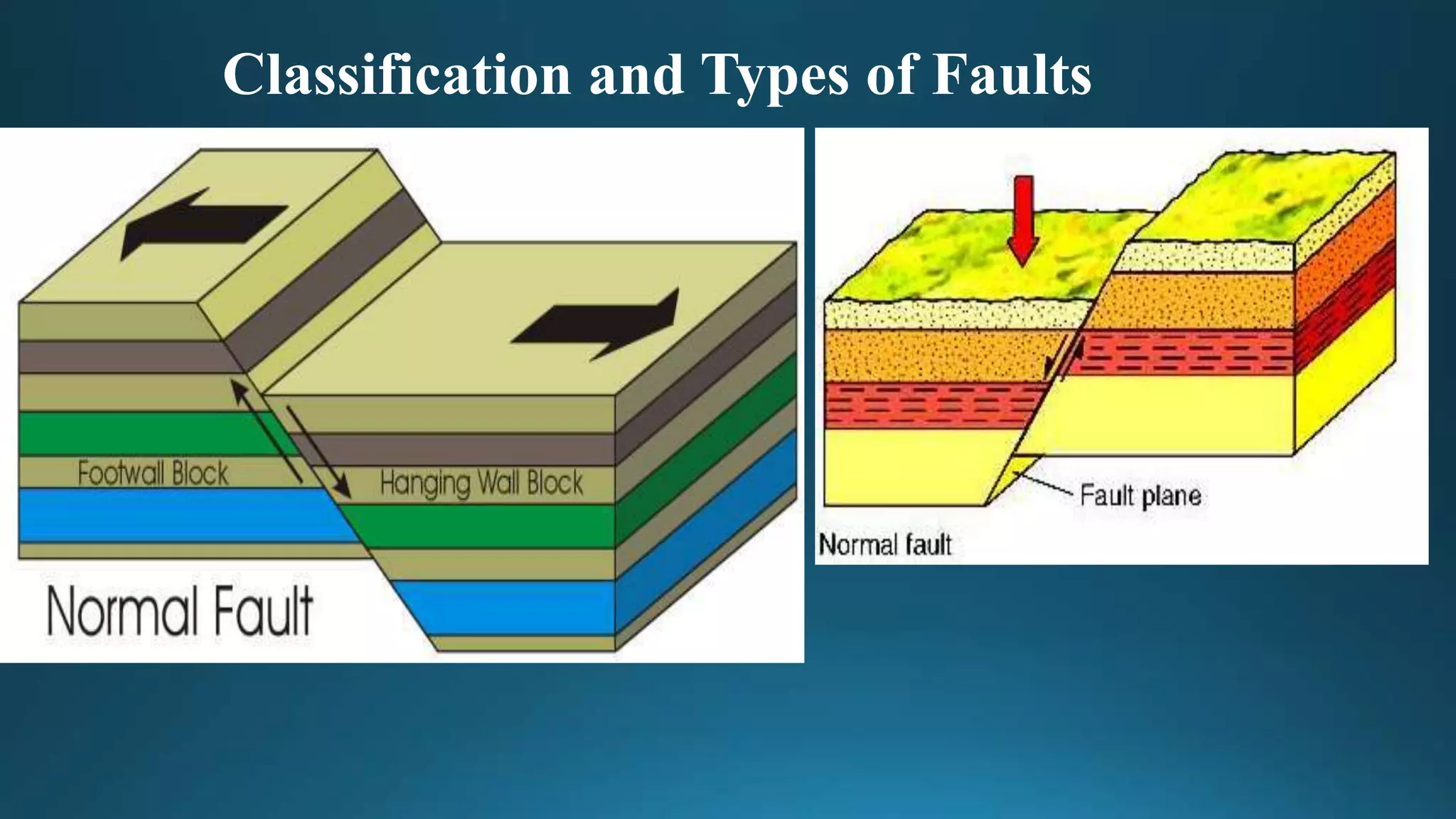
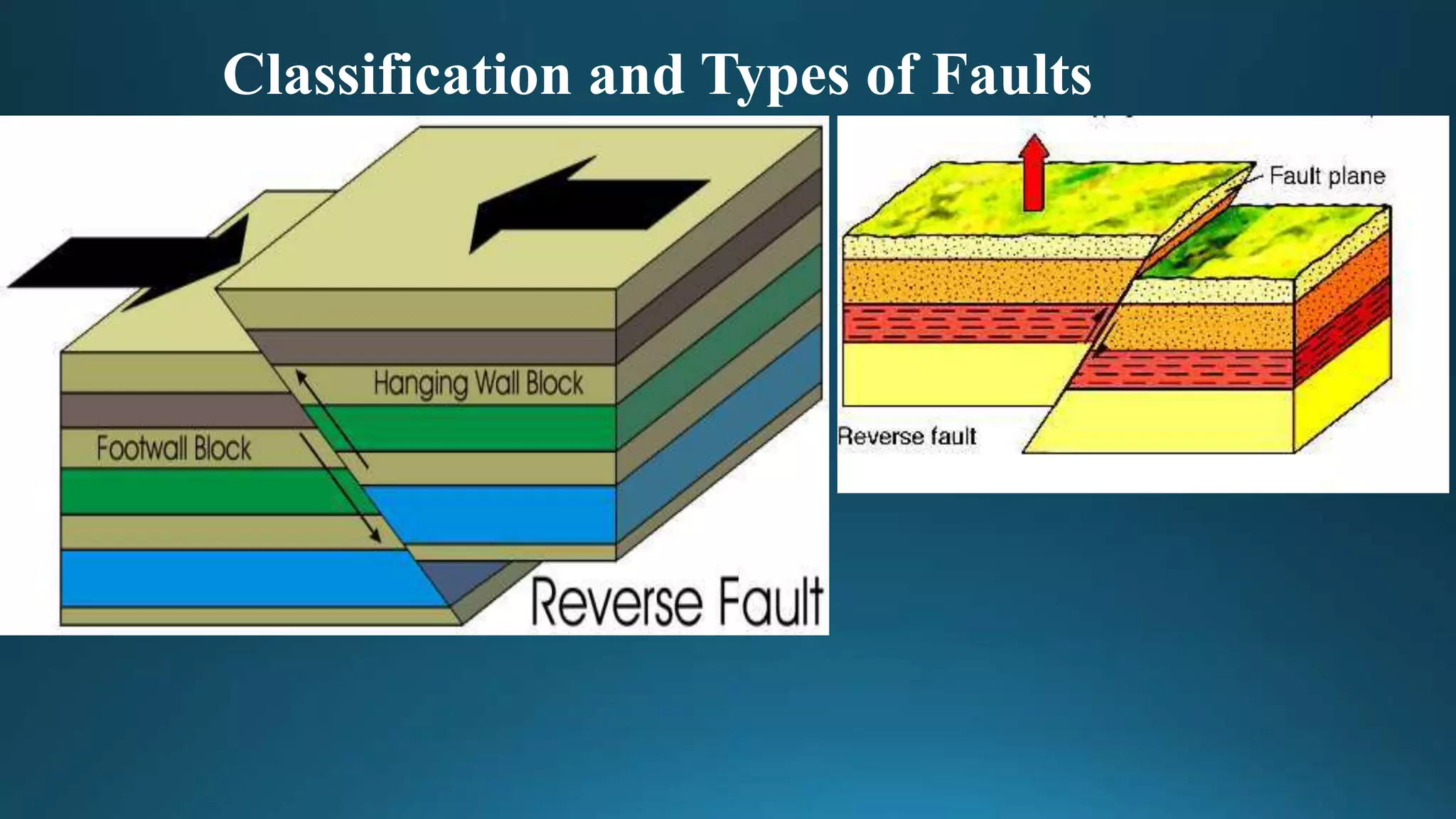
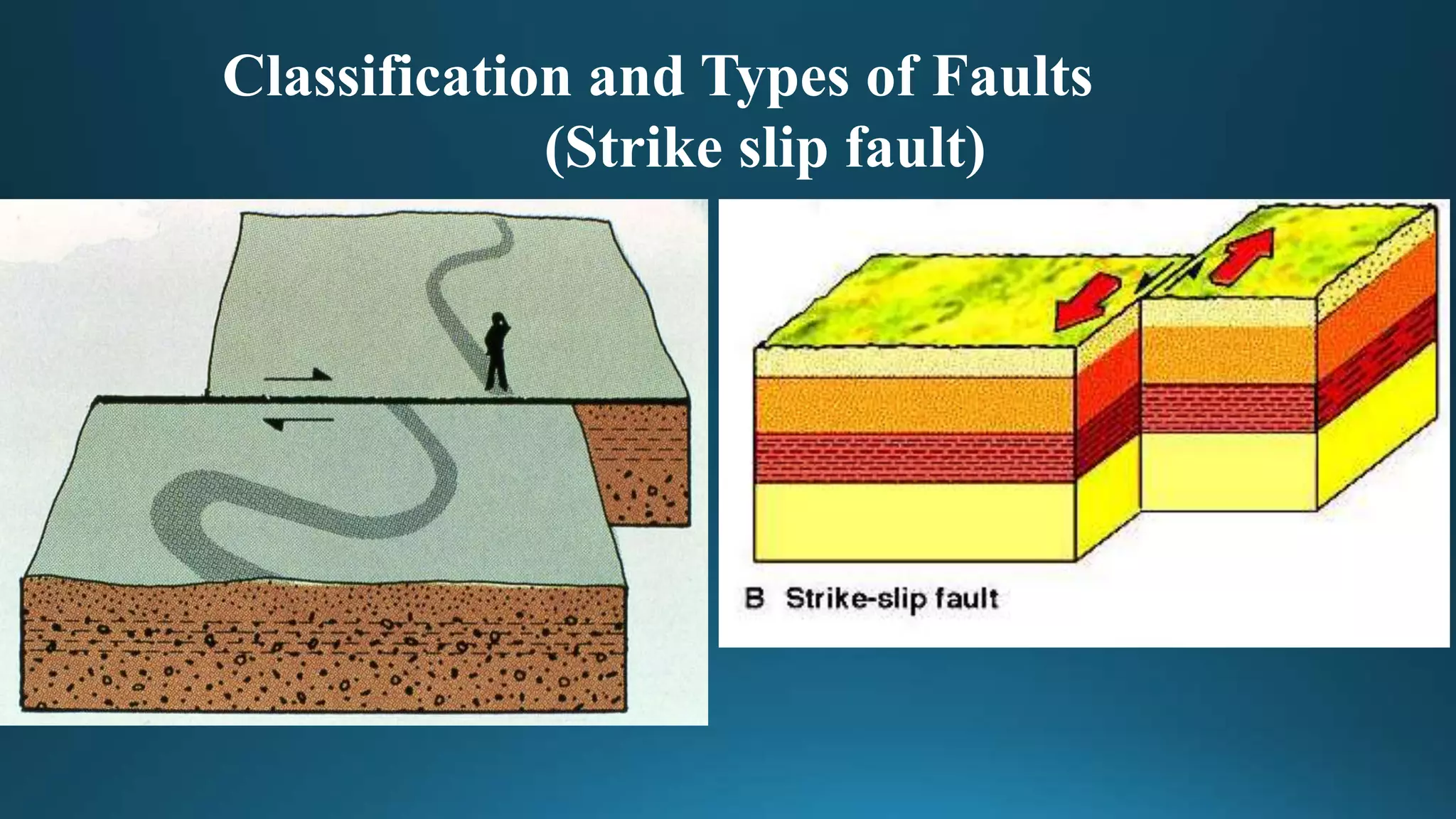
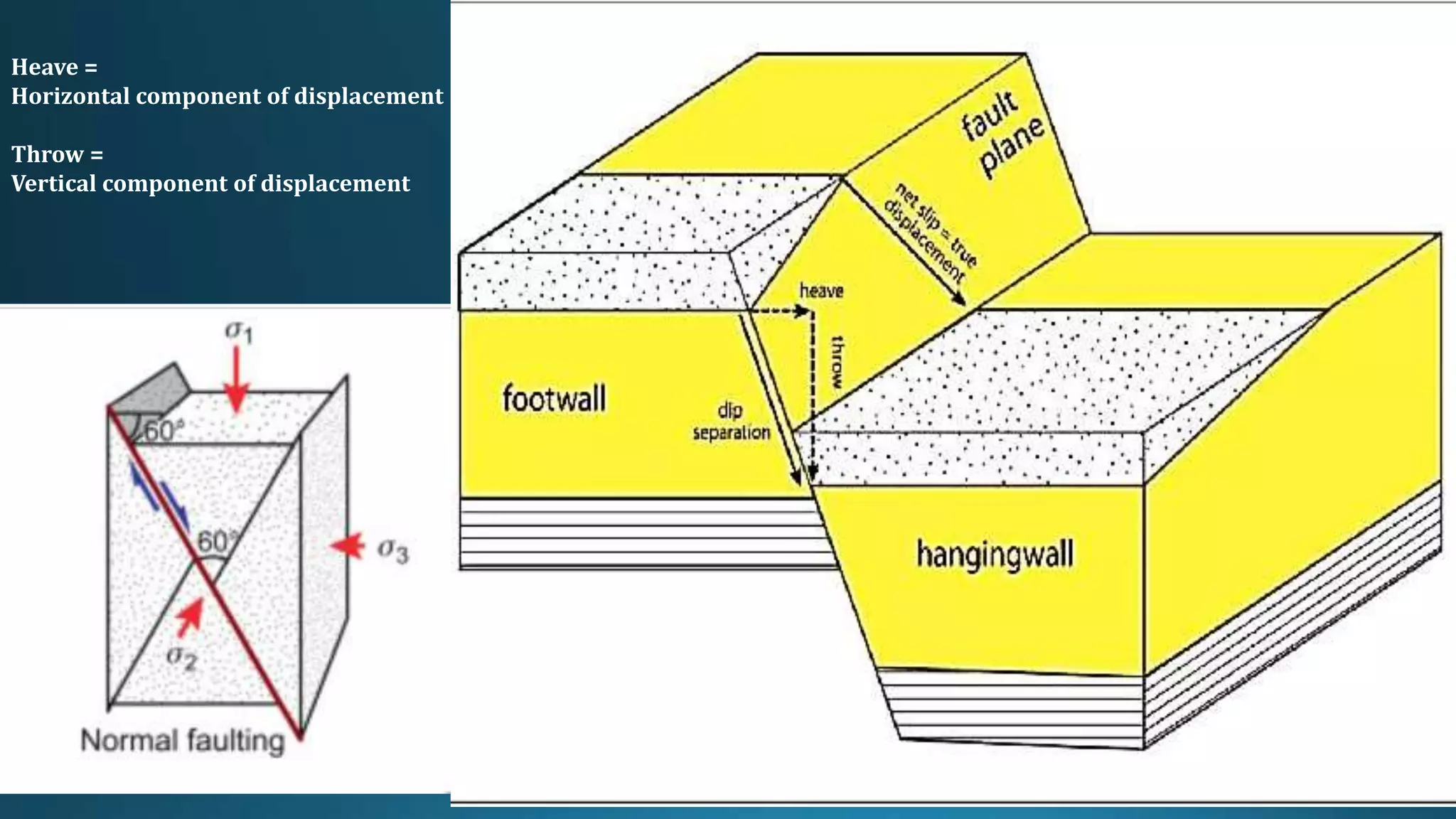
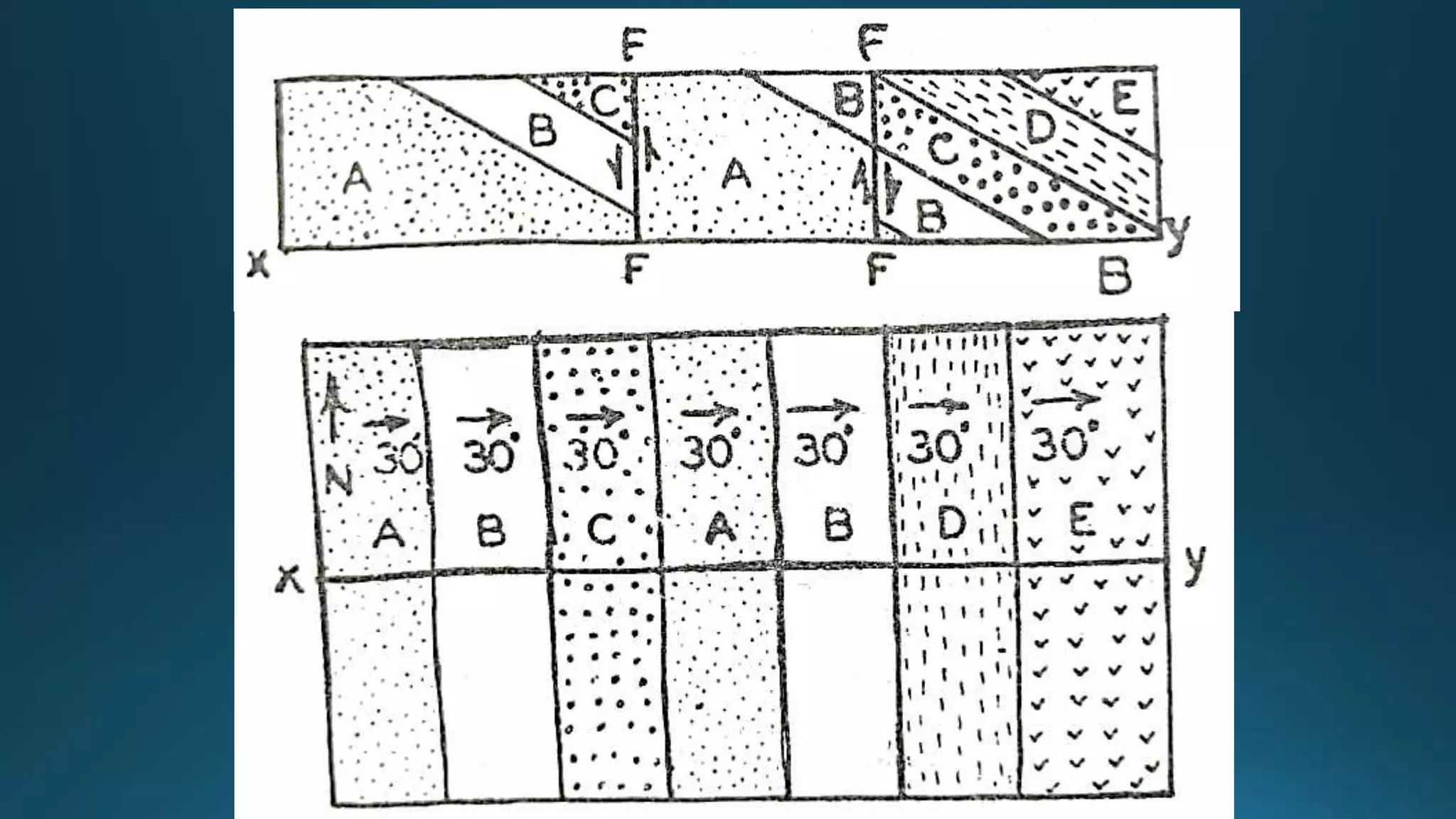
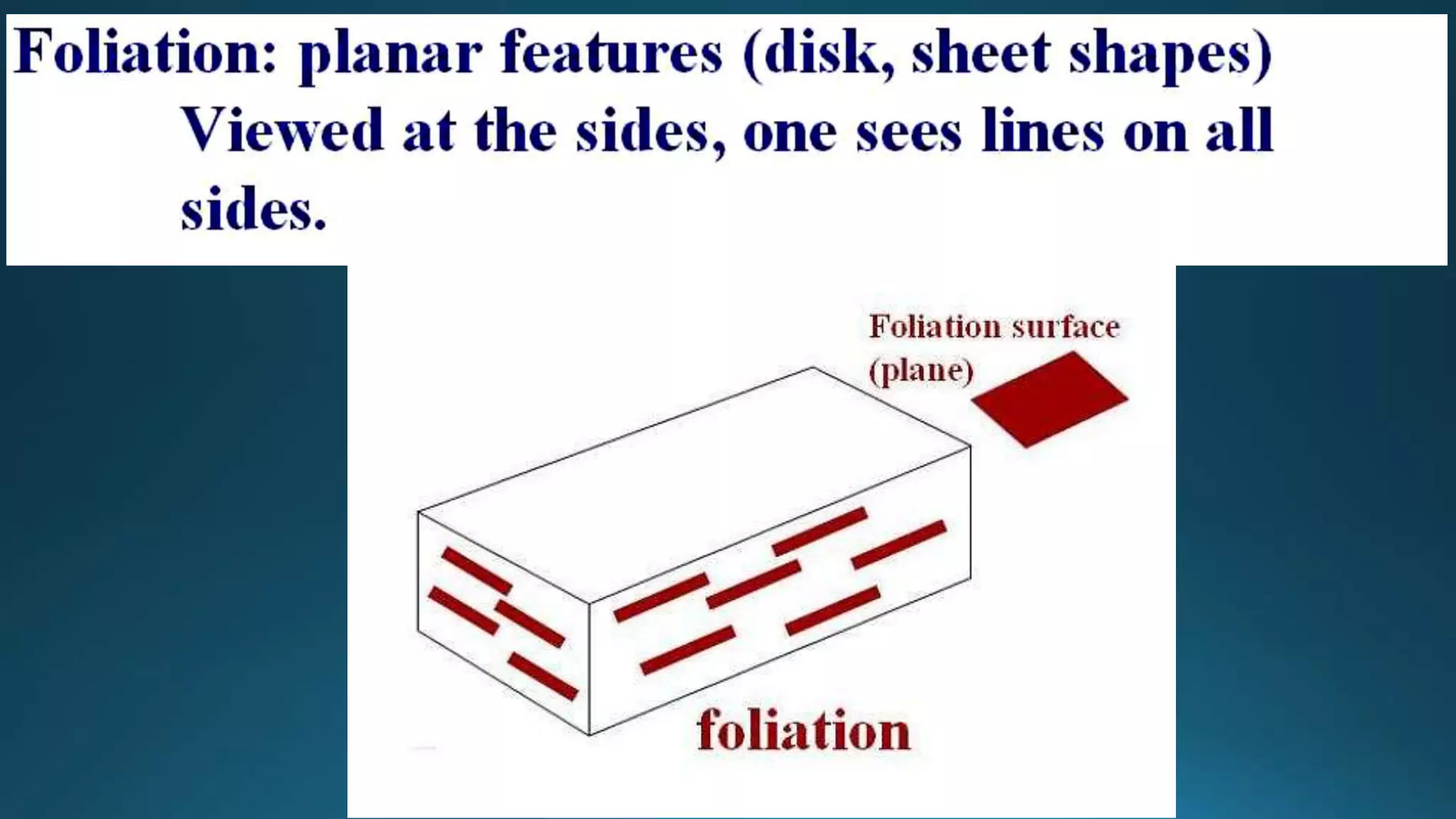
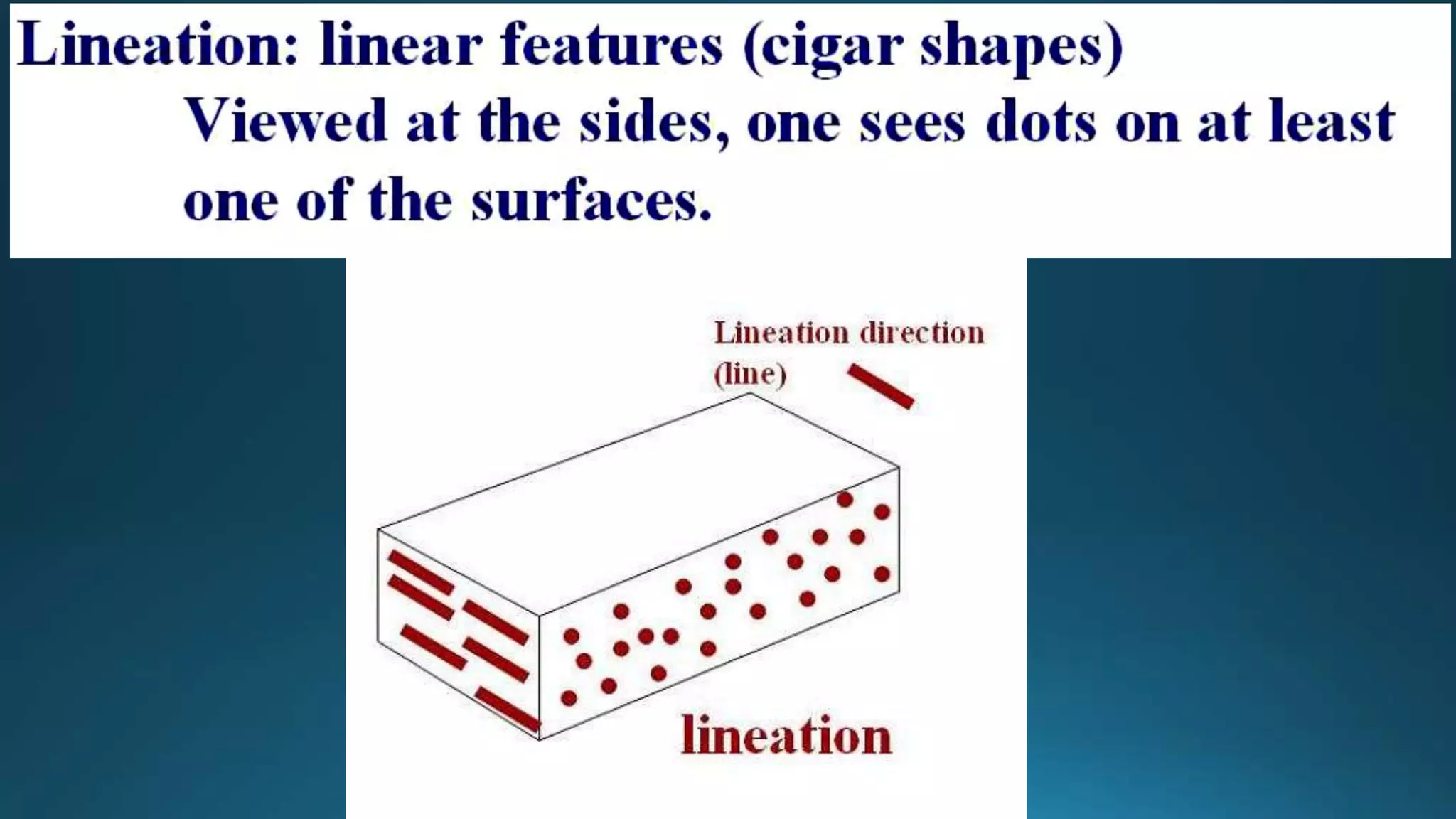
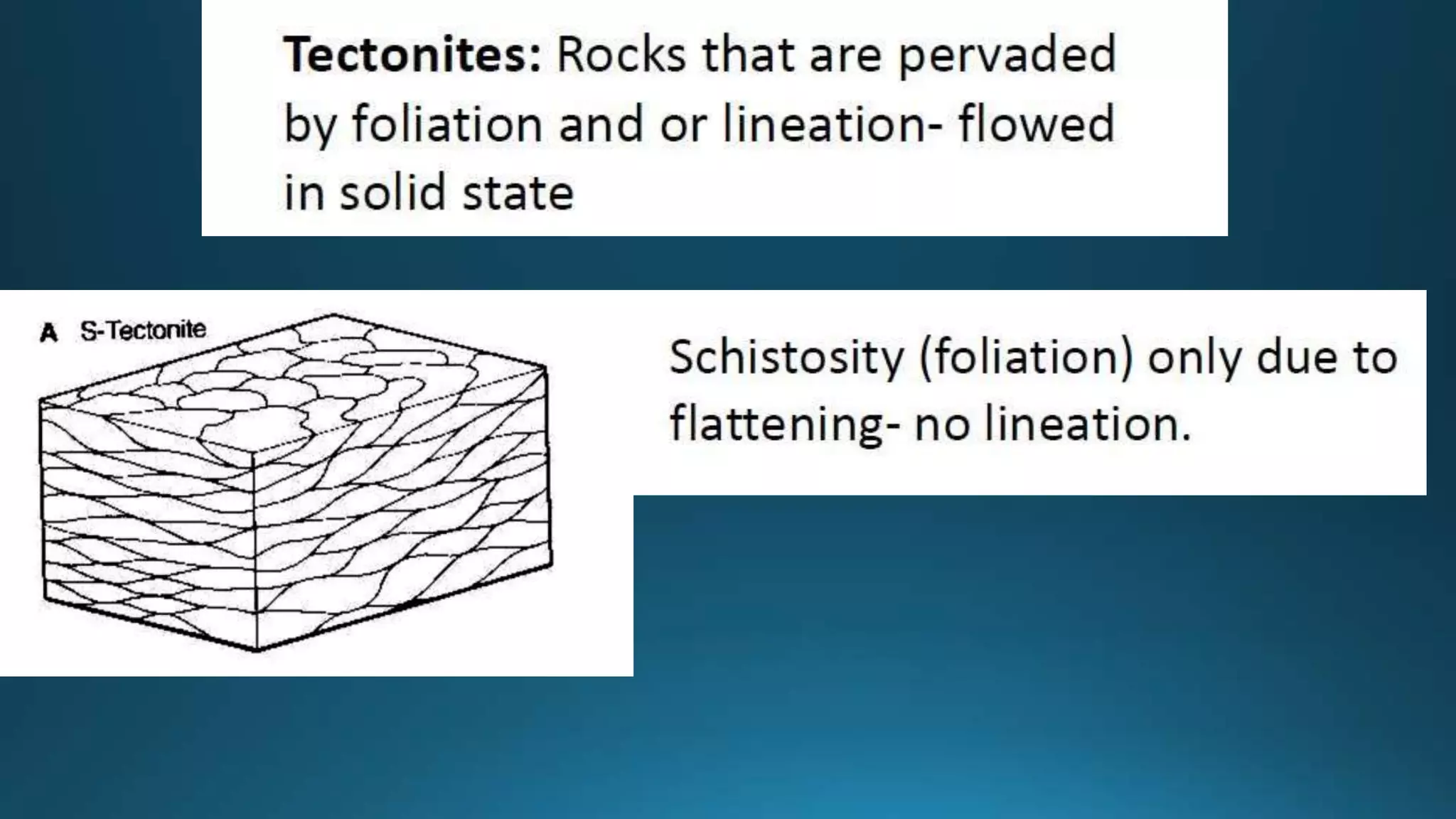
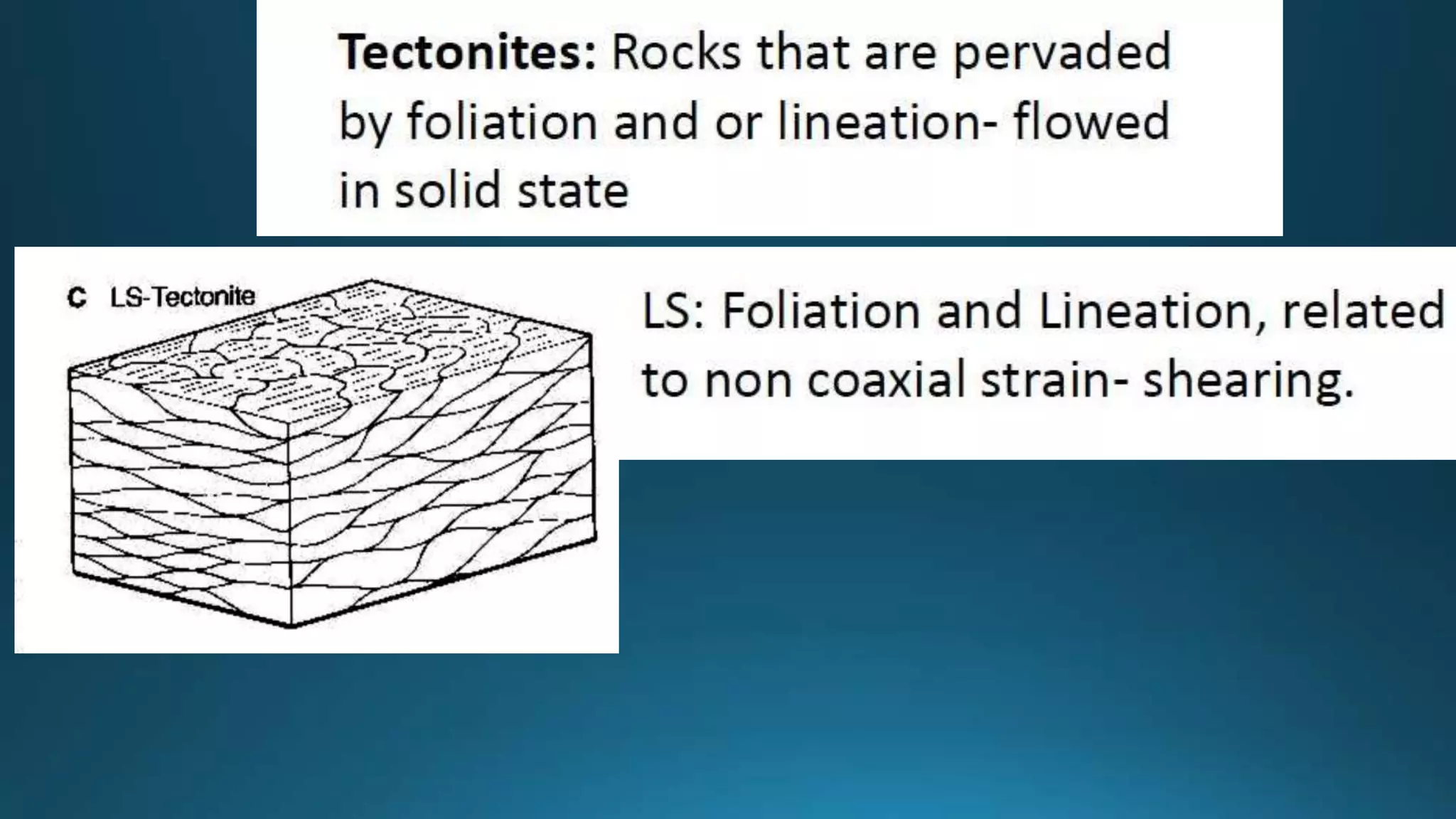
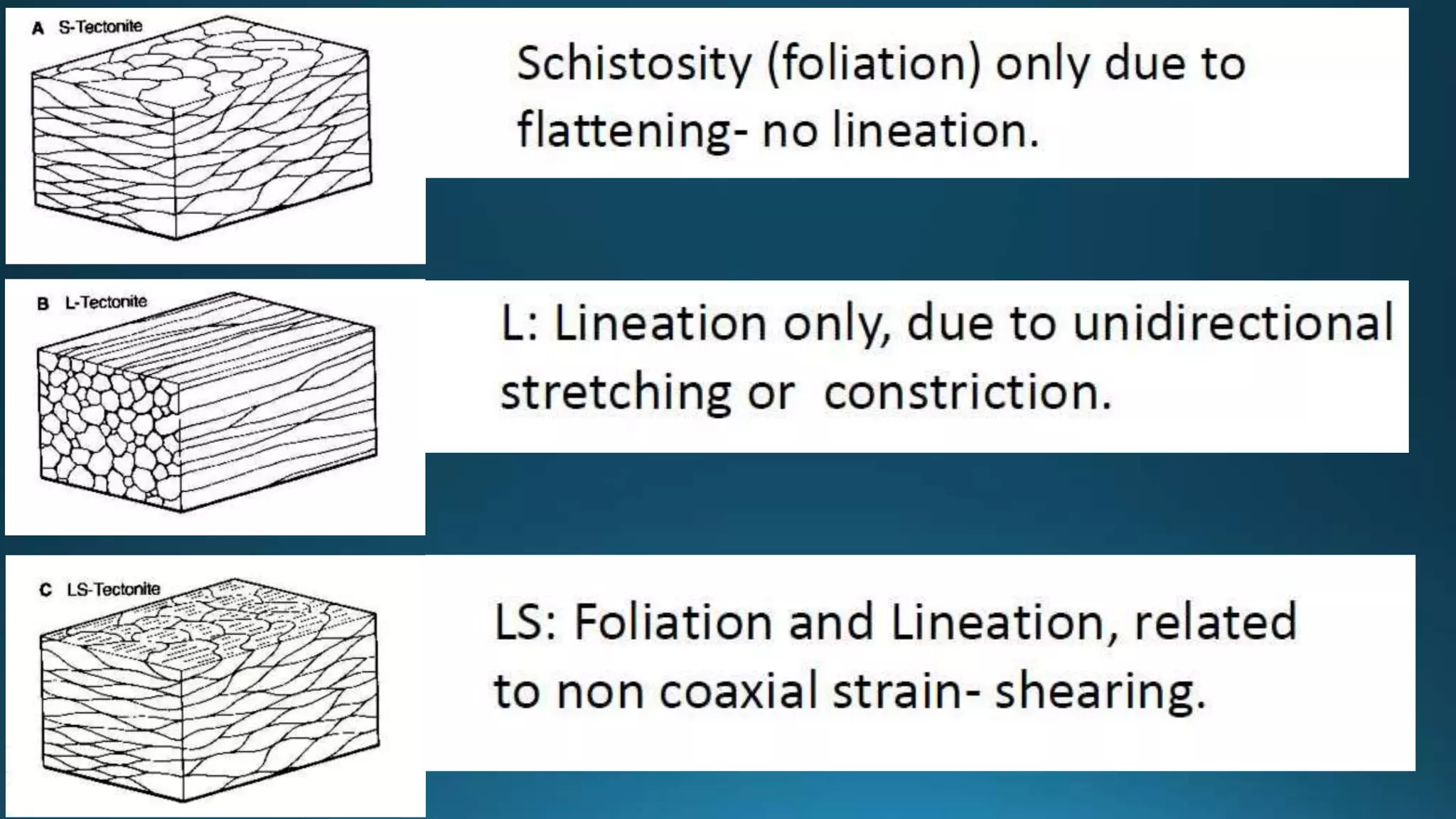
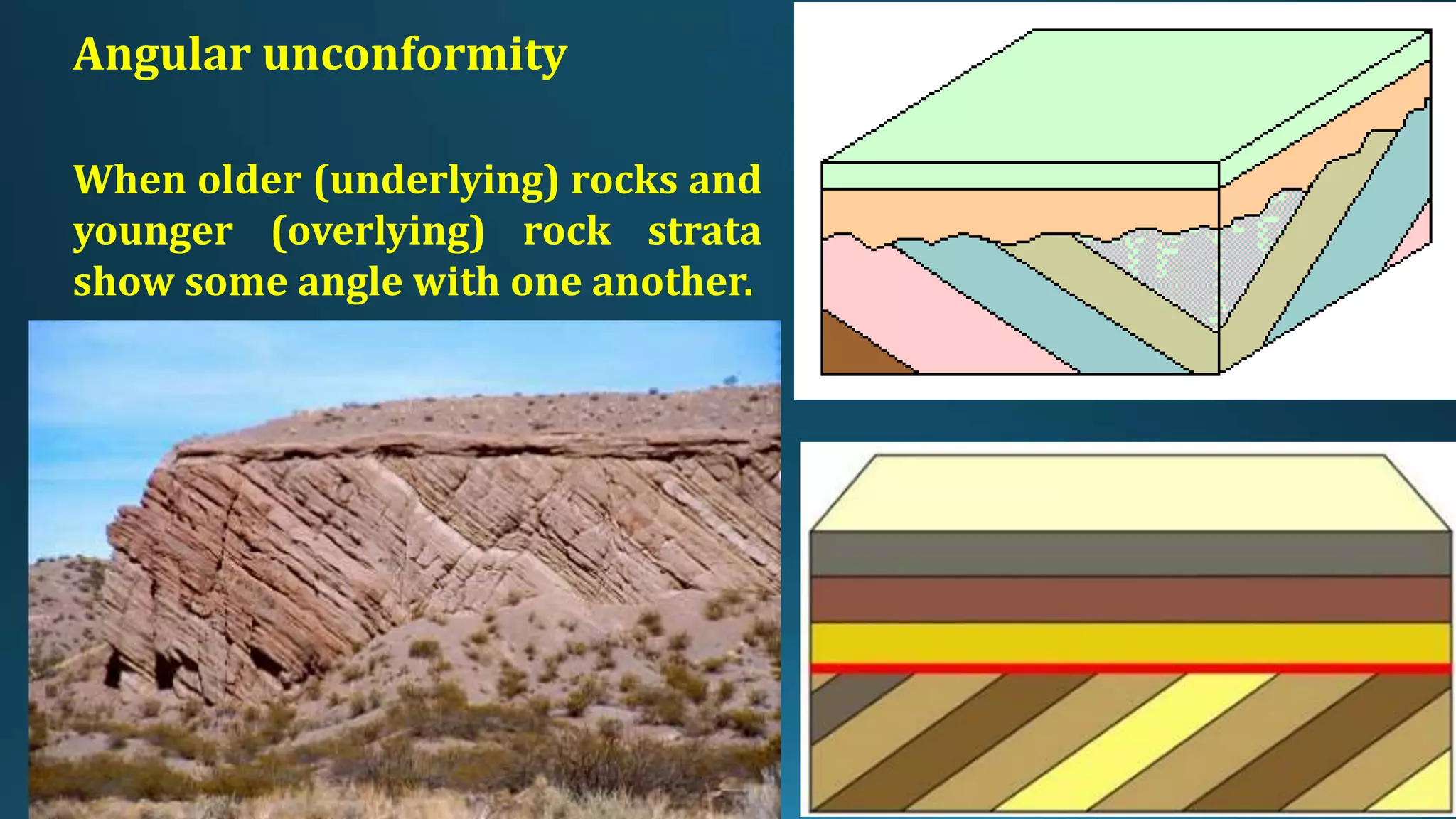
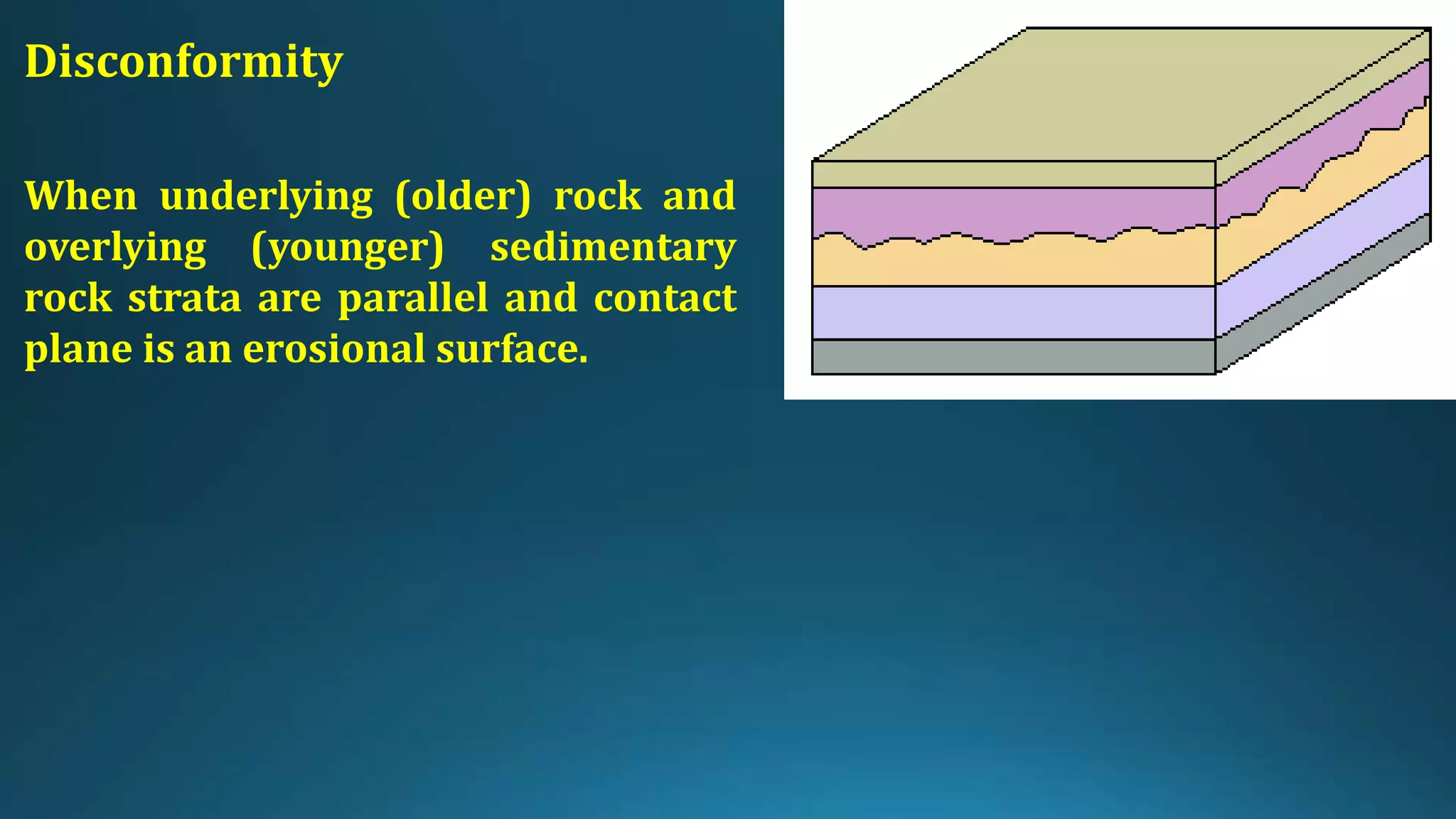
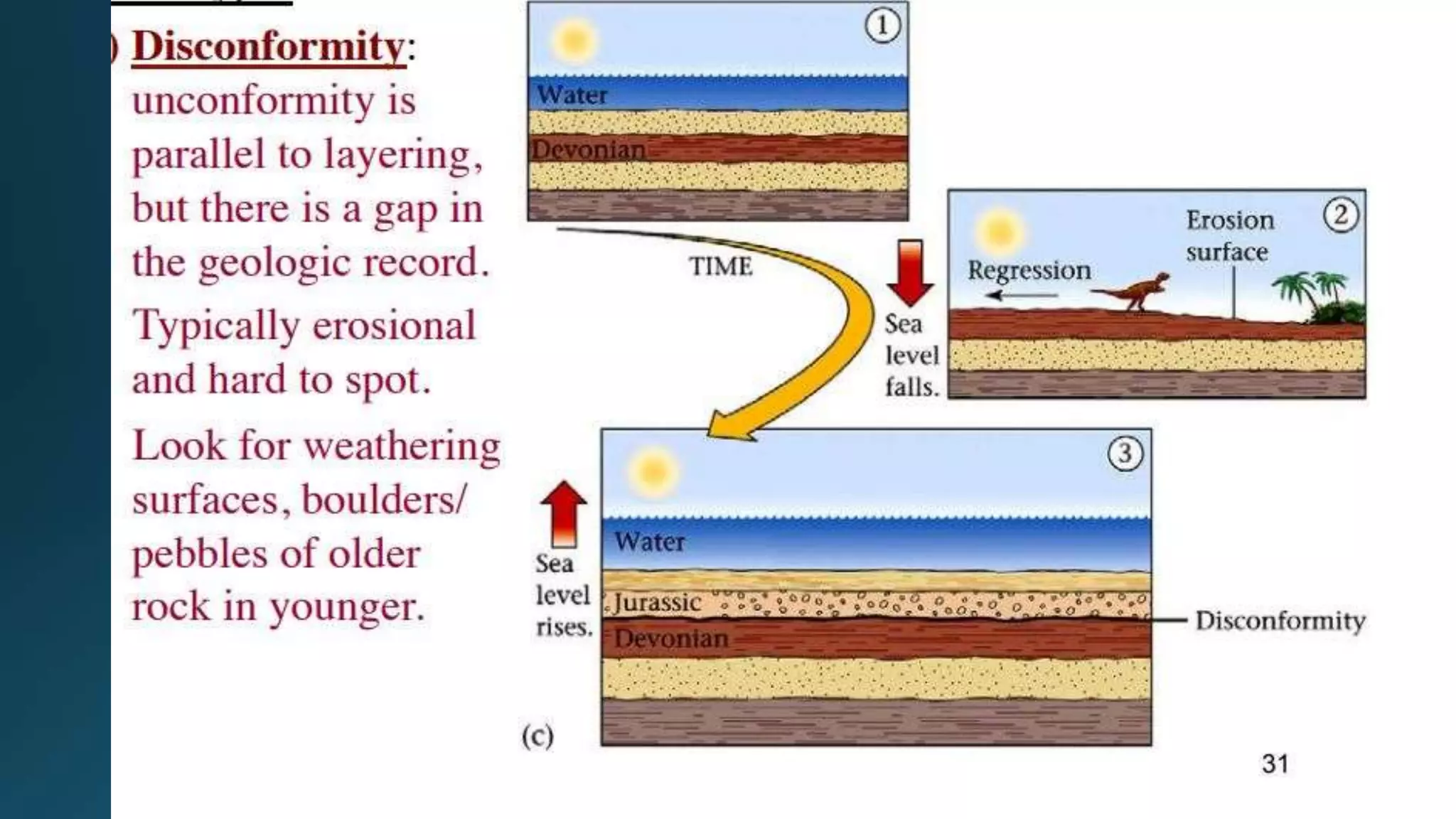
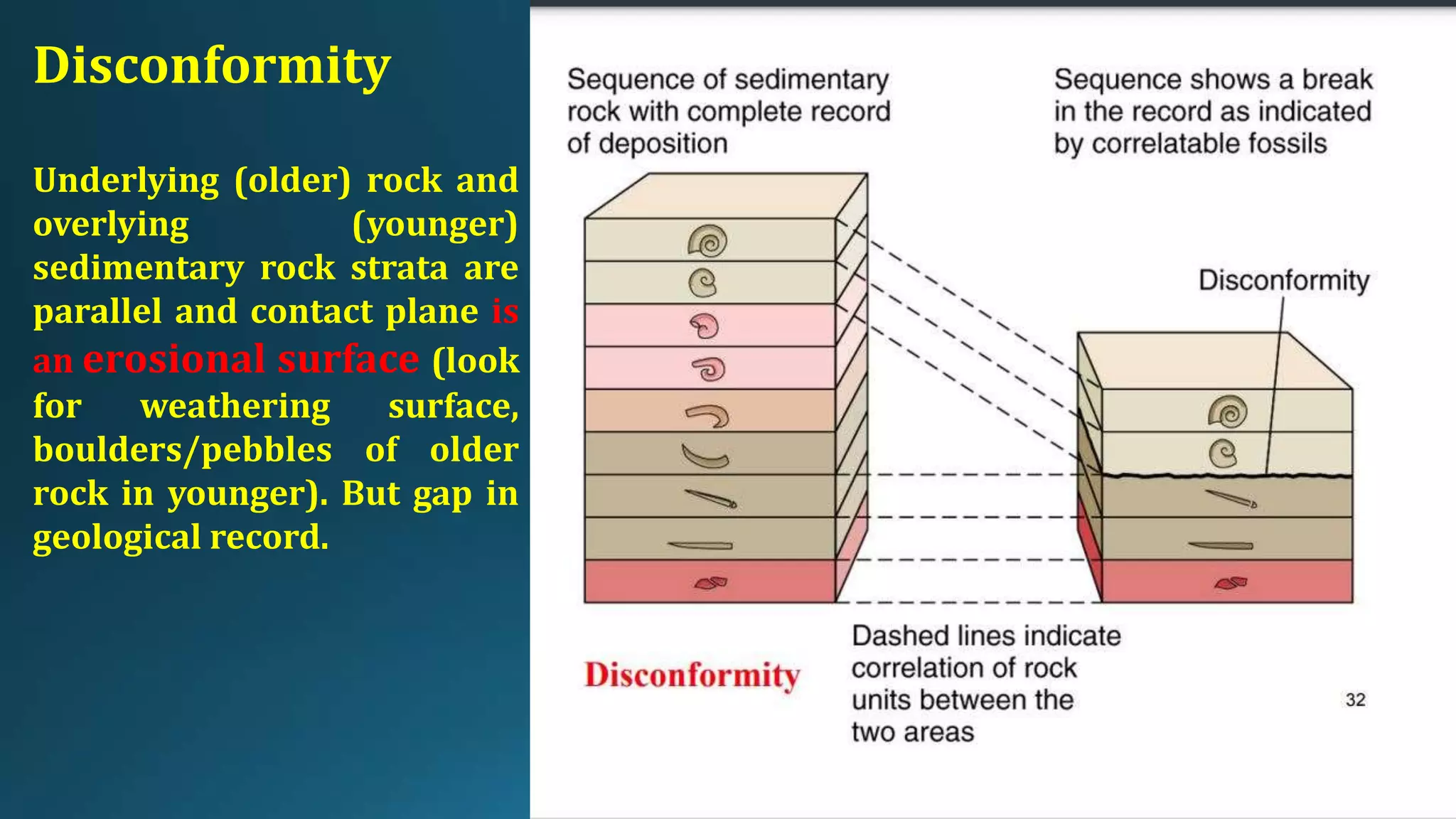
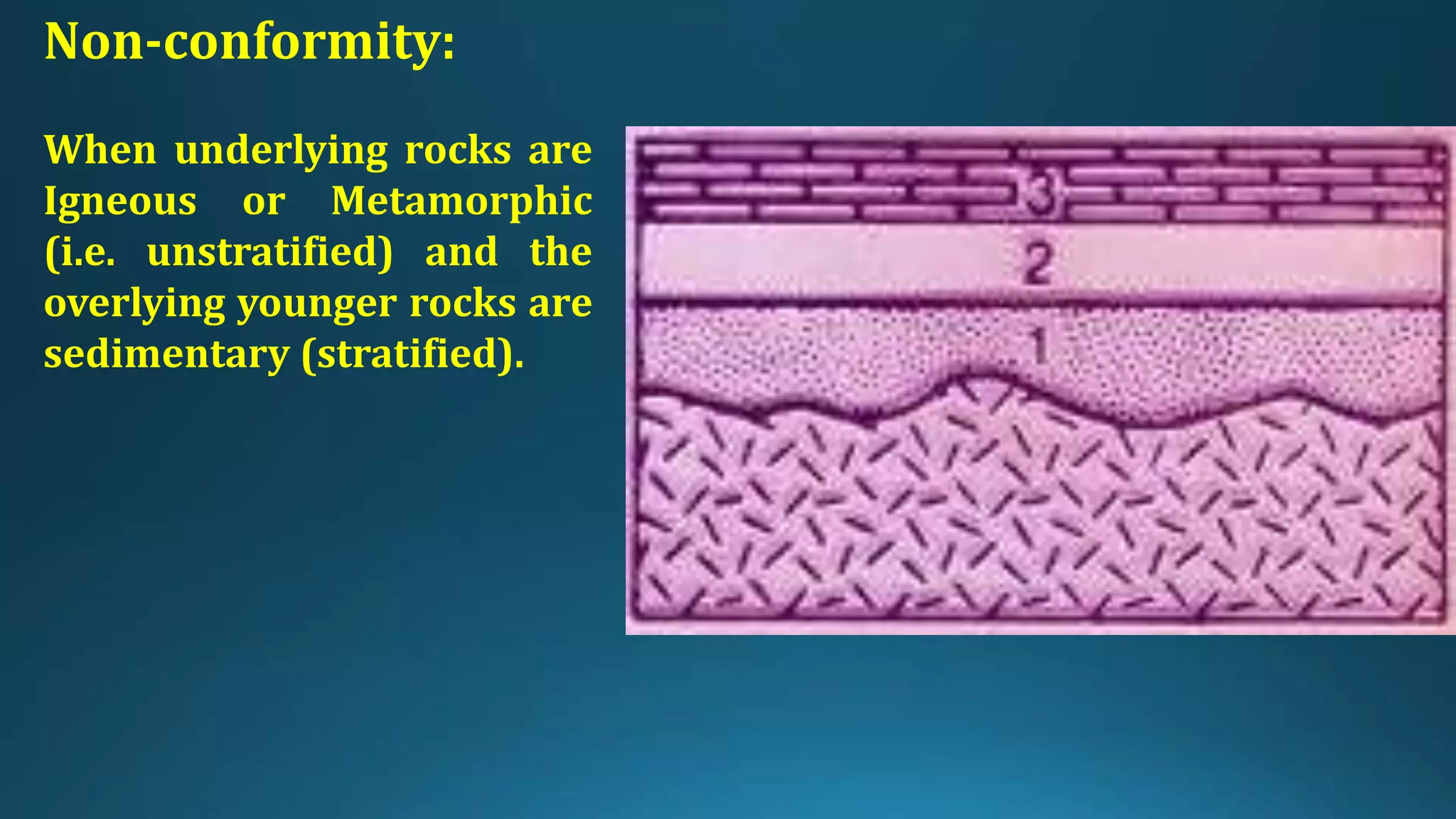
1) Geological structures such as folds, faults, joints and unconformities form in rocks due to tectonic plate forces and deformation of the earth's crust.
2) These structures can change the physical properties of rocks, making them more or less suitable for civil engineering projects. For example, sedimentary rocks with an upstream dip are more suitable for dam sites than the same rocks with a downstream dip.
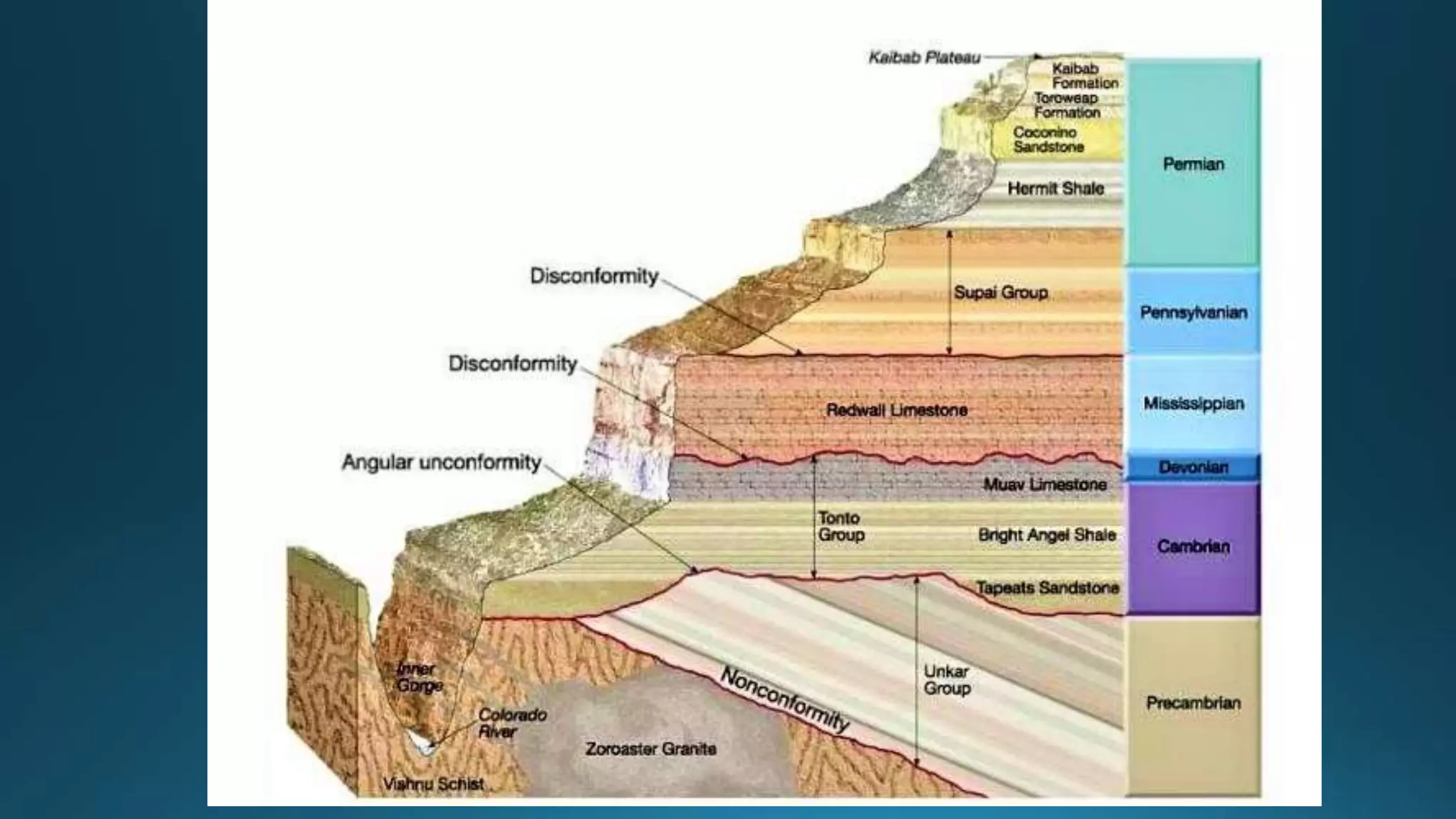
3) Folds, faults, unconformities and other structures are investigated in detail when evaluating sites for major construction due to the weaknesses and hazards they may pose.