Embed presentation
Downloaded 191 times


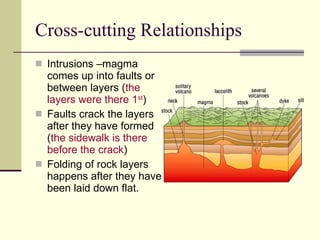




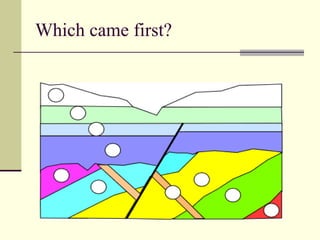
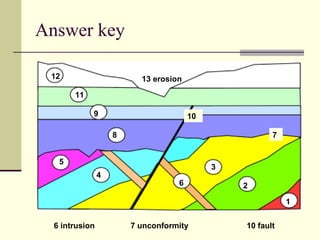
This document discusses principles of relative dating used to determine the sequence of geological events and the age of rock layers. It describes three key rules: 1) the law of superposition stating that younger layers are above older layers, 2) uniformitarianism stating that geological processes today are the same as in the past, and 3) cross-cutting relationships showing intrusions and faults occurred after existing rock layers. It also defines three types of unconformities - angular, disconformity, and nonconformity - which indicate gaps in the geologic record due to erosion.








