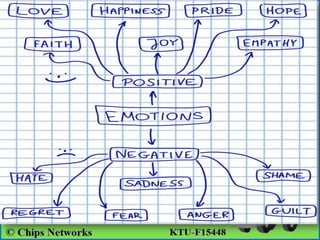
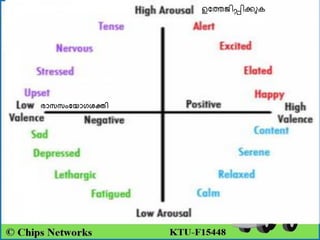
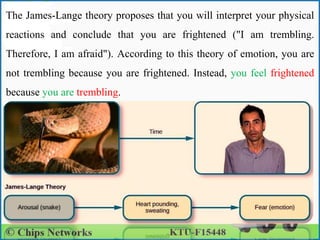
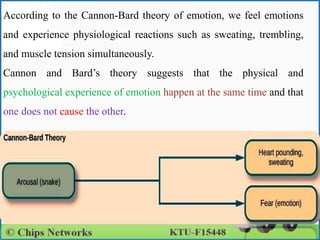
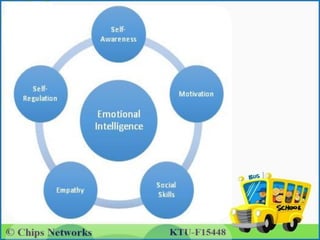
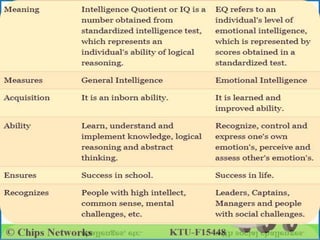
Emotion in psychology is a complex state that influences thought and behavior, being associated with various psychological phenomena. Key theories, including the James-Lange, Cannon-Bard, and Schachter-Singer theories, explain the physiological and cognitive aspects of emotional experiences. Emotional intelligence involves recognizing, managing, and applying emotions effectively, with five components defined by Daniel Goleman: self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills.