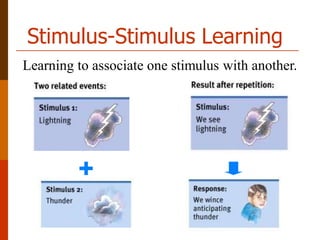
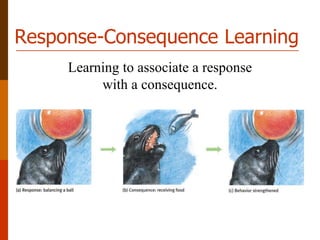
The document discusses different types of learning, including verbal learning, motor learning, concept learning, problem solving, serial learning, and paired-associate learning. It also discusses the learning process, how learning occurs through experience and the formation of associations, and different approaches to learning including behavioral, cognitive, stimulus-stimulus learning, and response-consequence learning. Major theories discussed include behaviorism, which views learning as the acquisition of behaviors through environmental interaction and conditioning, and cognitive approaches, which see learning as involving conscious information processing and problem solving.