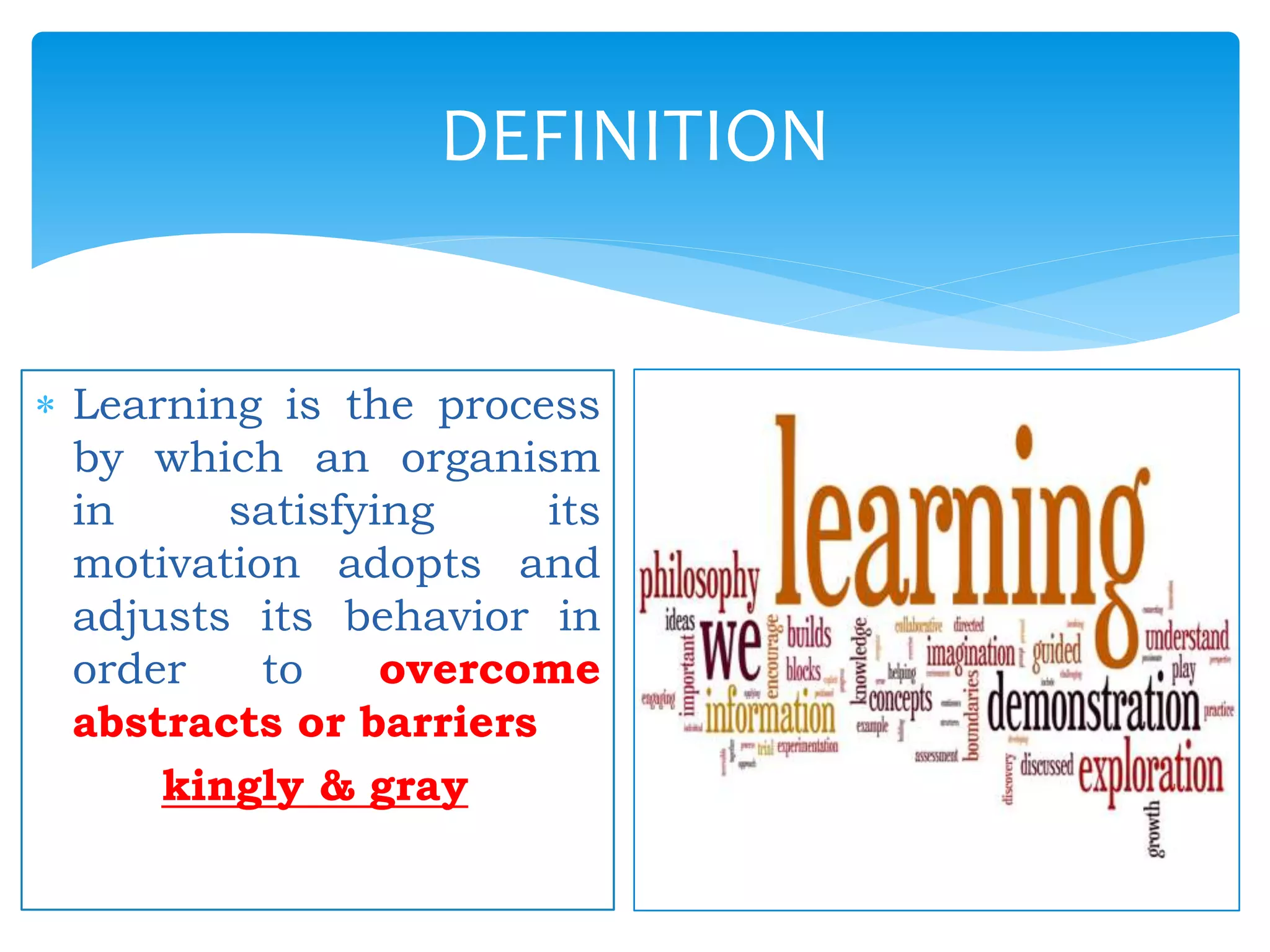
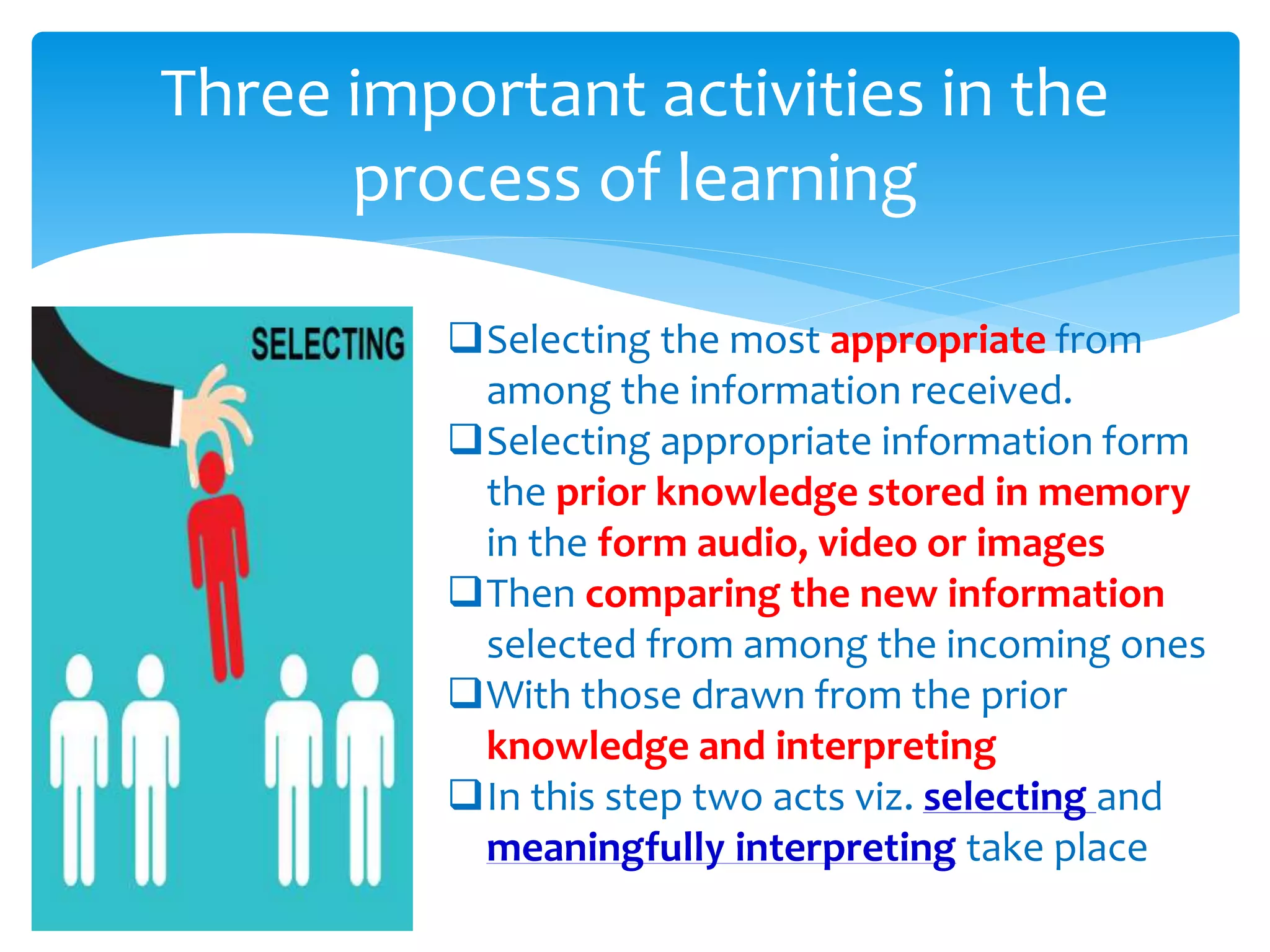
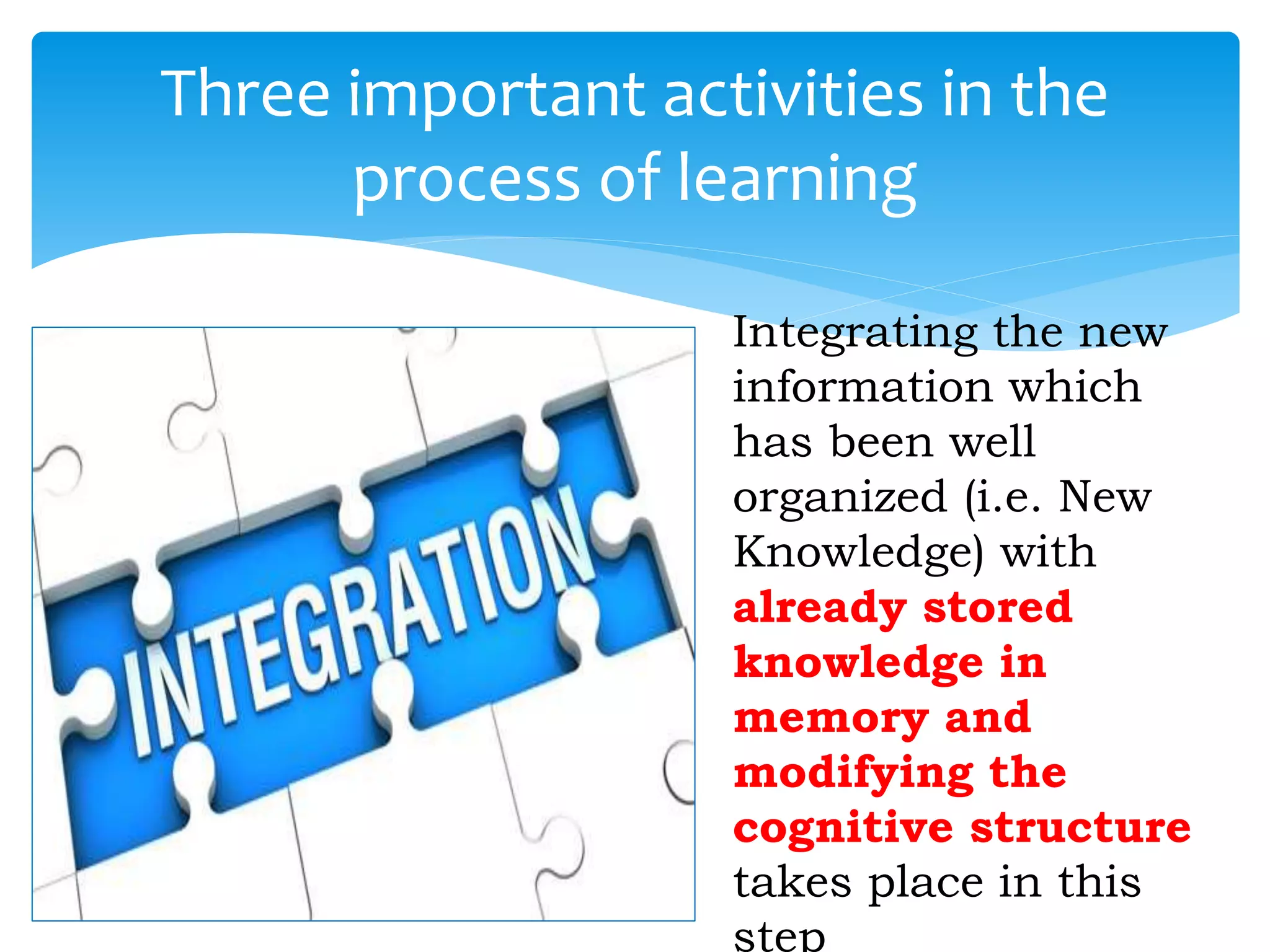
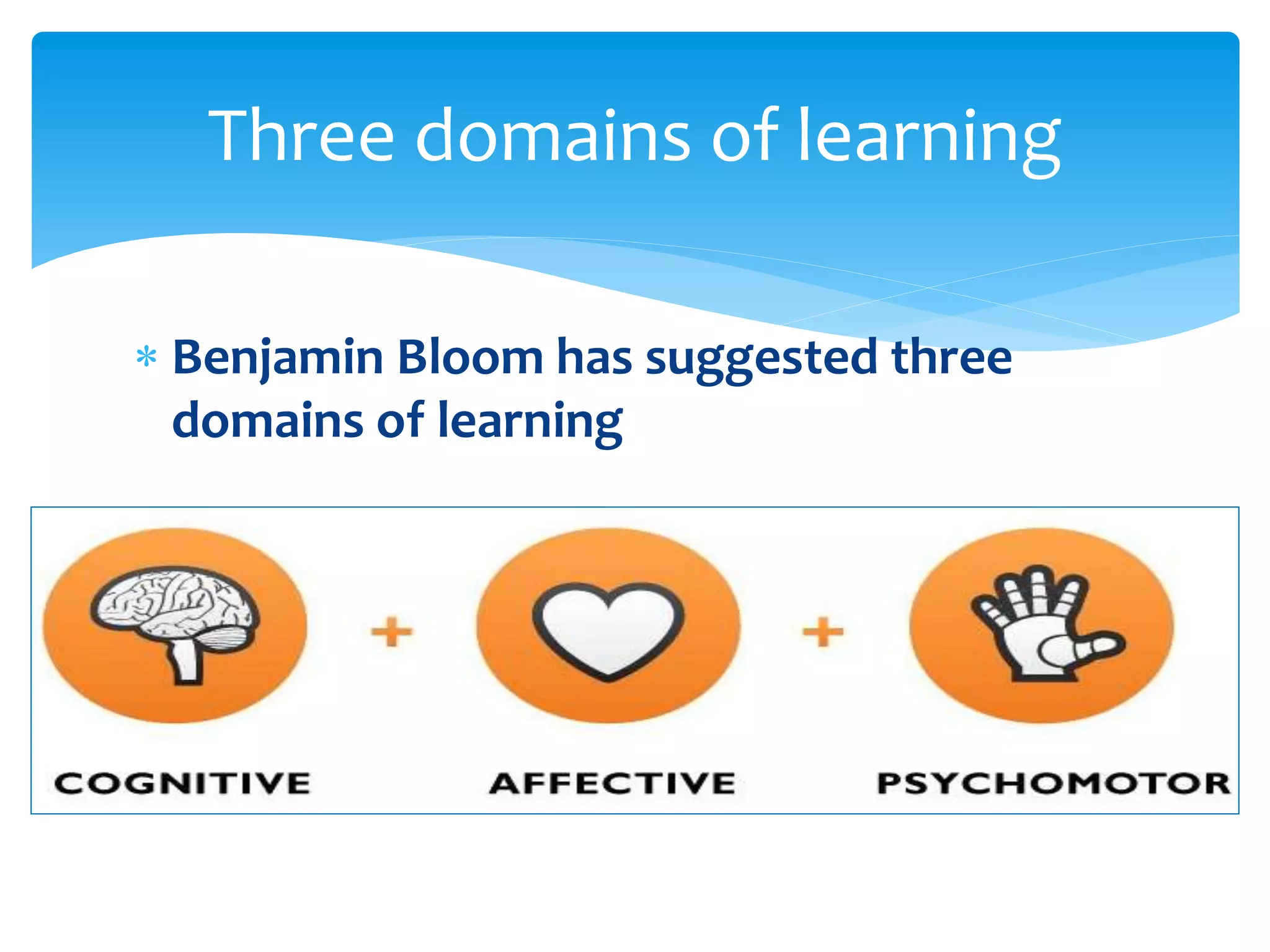
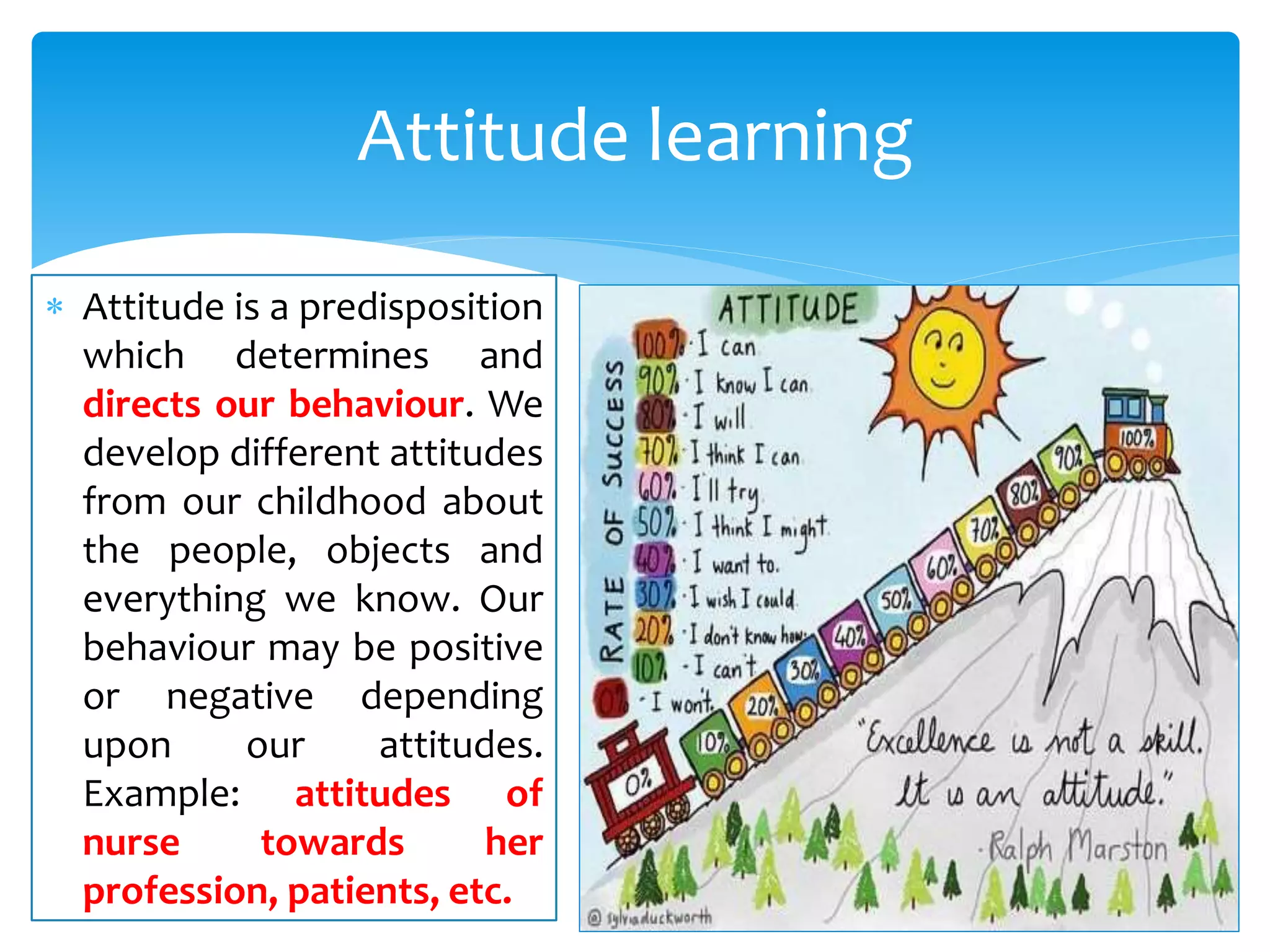
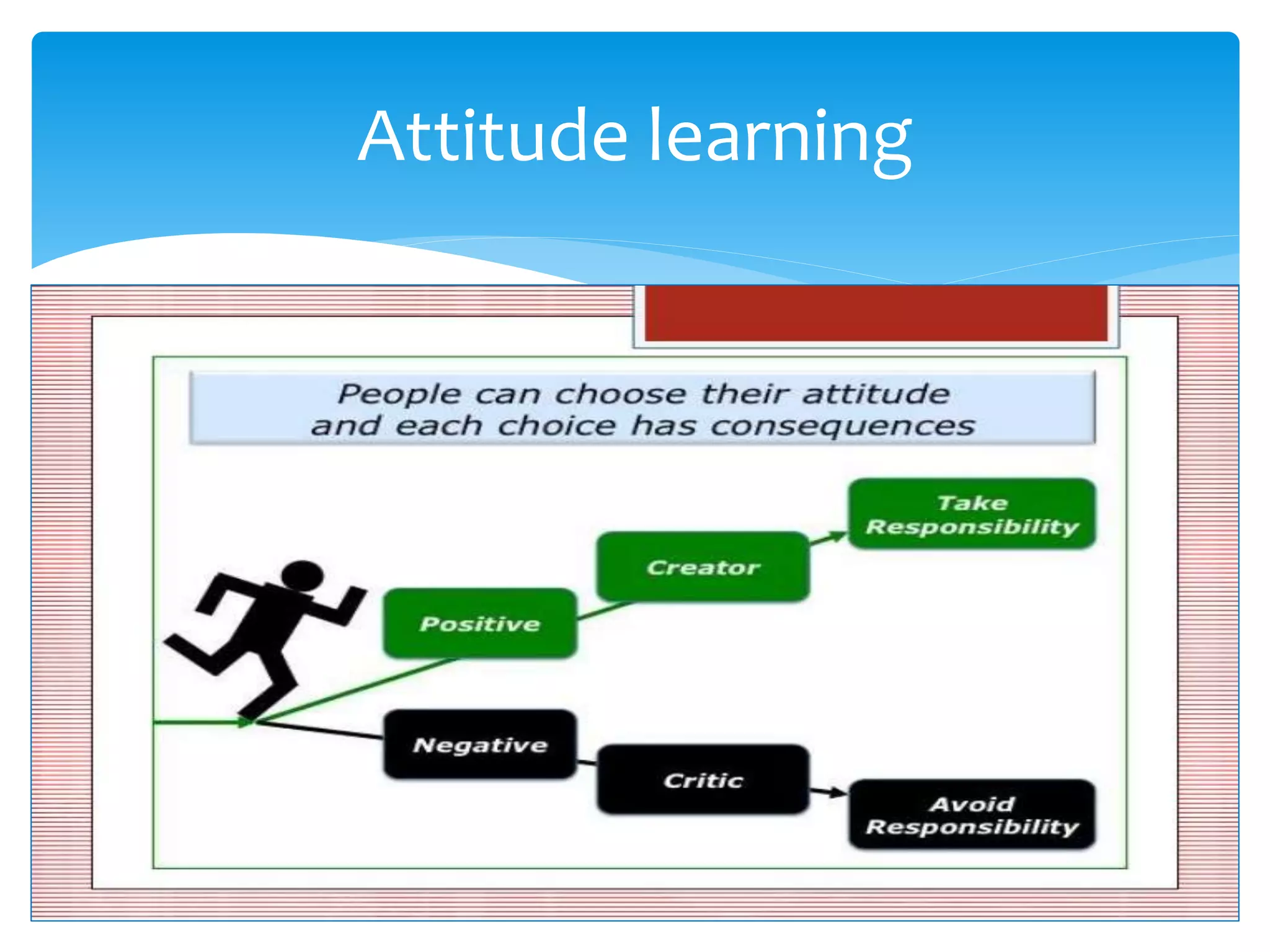
The document summarizes the key aspects of the nature of the learning process according to various theorists. It discusses learning as an active social process according to Vygotsky, McMahon, and Kukla. It also outlines five principles of learning, three important activities in the learning process (selecting, organizing, and integrating information), and three domains of learning (cognitive, affective, psychomotor). Different types of learning are defined, including motor learning, verbal learning, concept learning, and attitude learning.