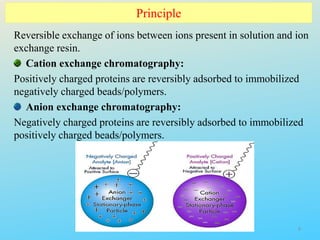
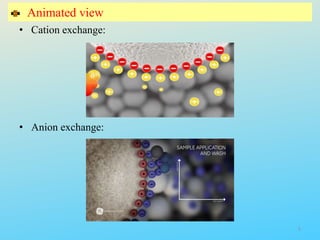
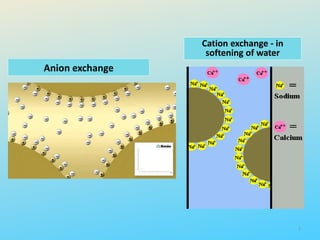
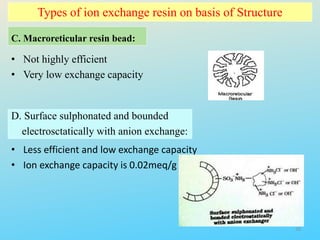
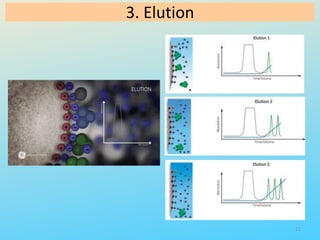
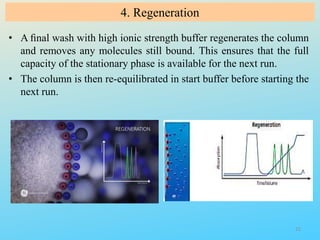
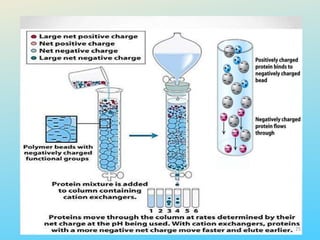
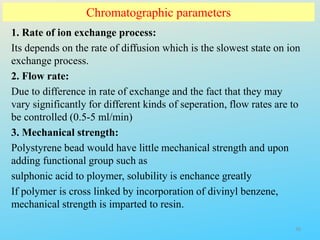
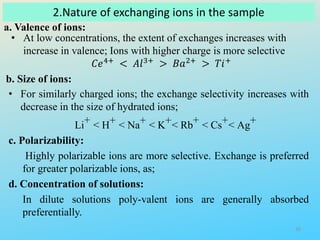
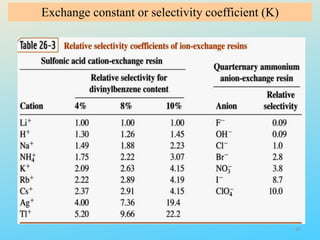
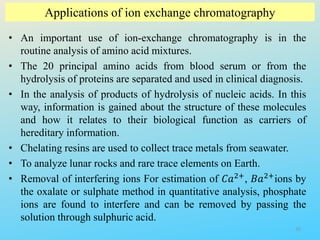
Ion exchange chromatography is a process that separates ions and polar molecules based on their charge using an ion exchange resin. There are two main types of ion exchange - cation exchange which uses a negatively charged resin to adsorb positively charged proteins, and anion exchange which uses a positively charged resin to adsorb negatively charged proteins. The process involves equilibrating the resin, applying the sample mixture, then eluting the bound molecules by altering conditions such as pH or ionic strength to cause differential elution. Ion exchange chromatography is useful for purifying proteins and other charged biomolecules.