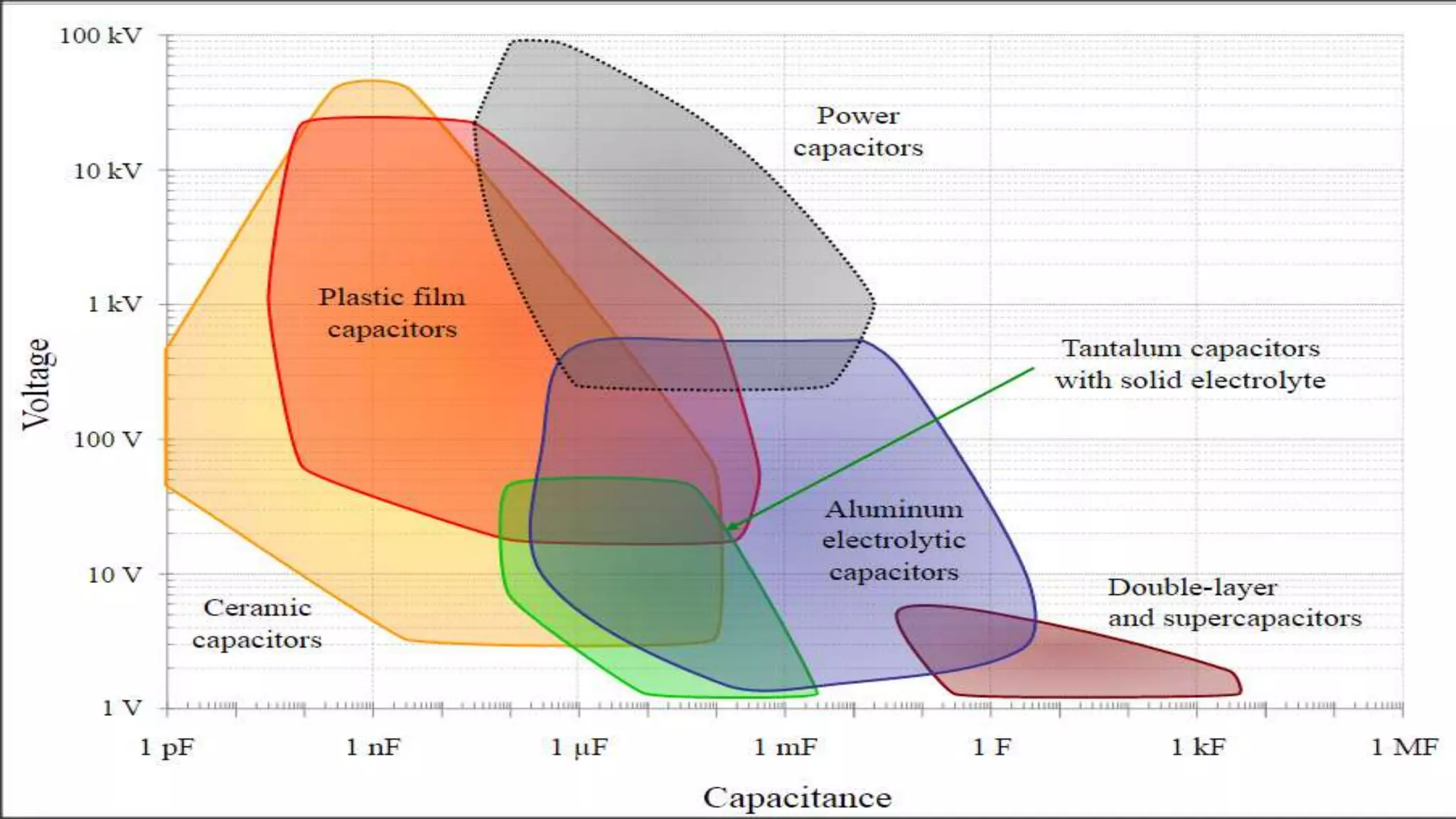
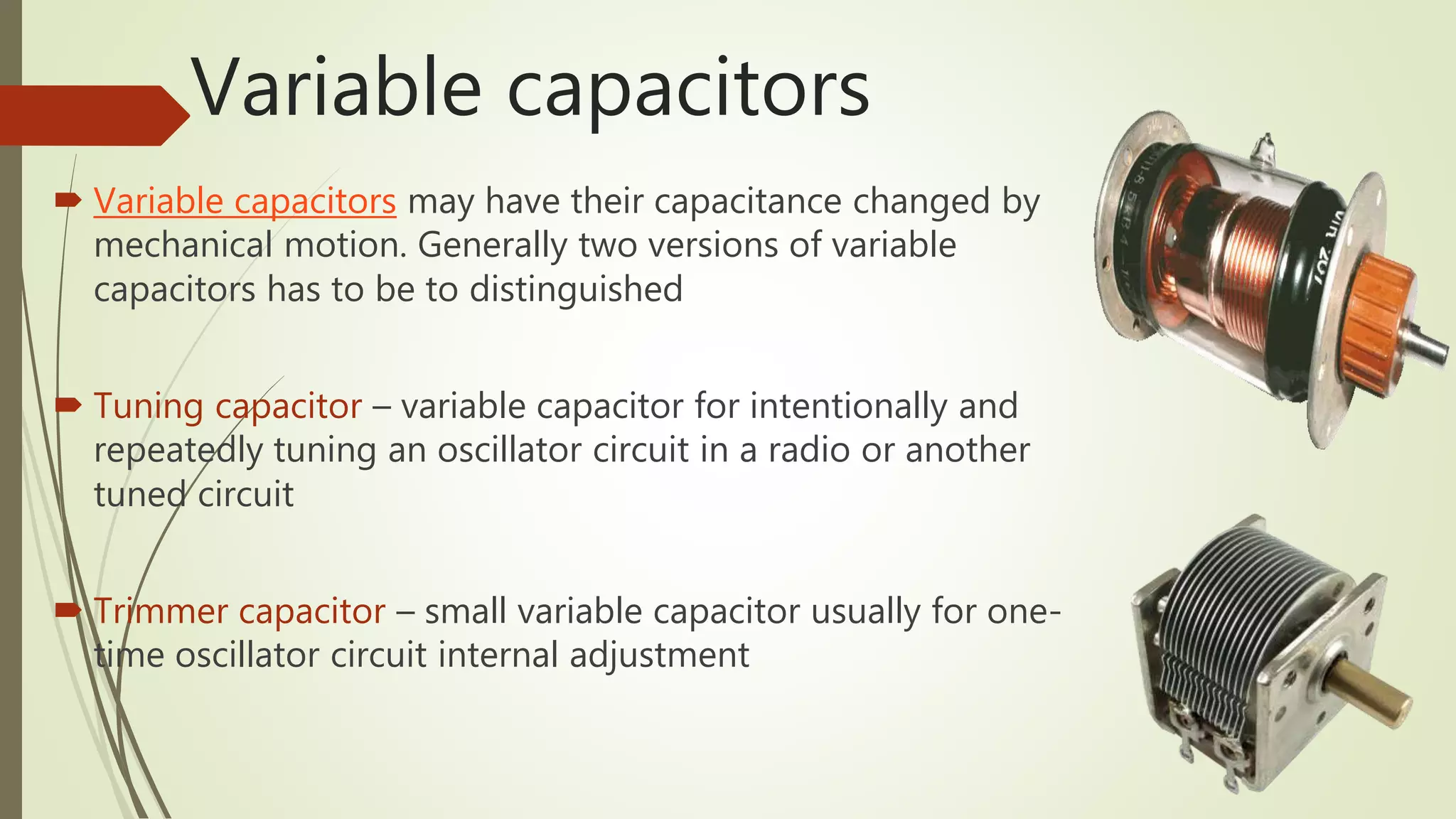
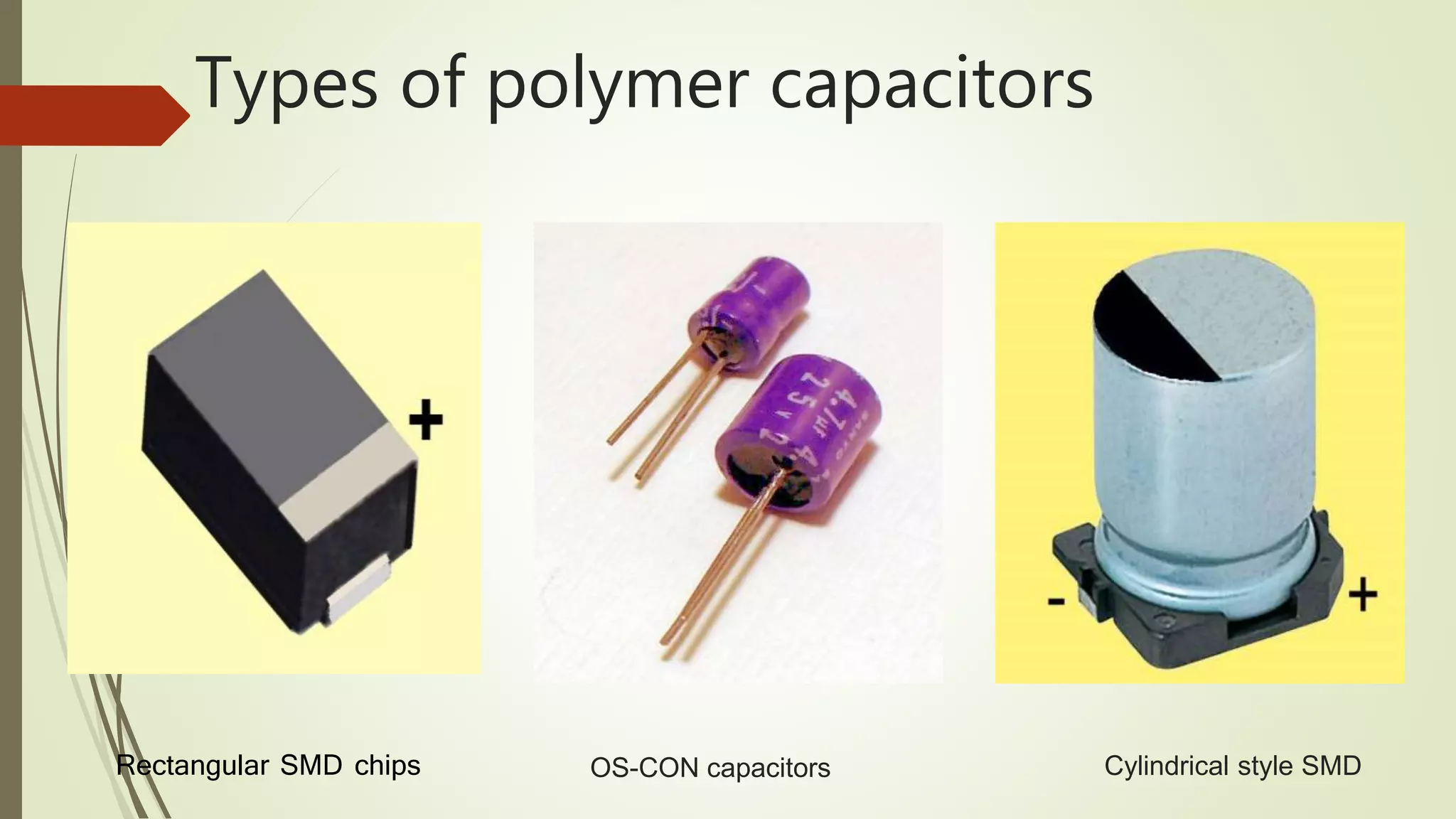
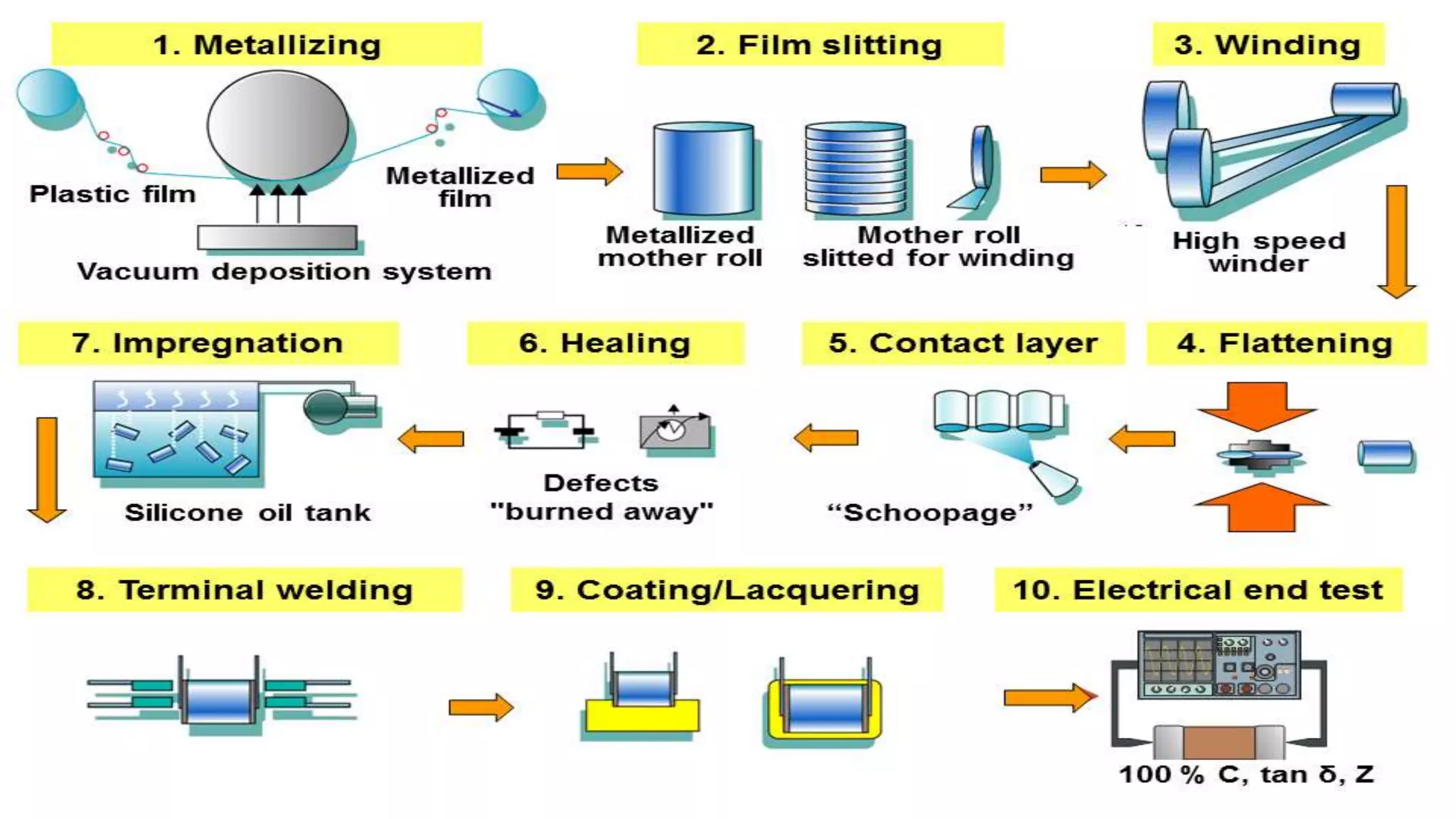
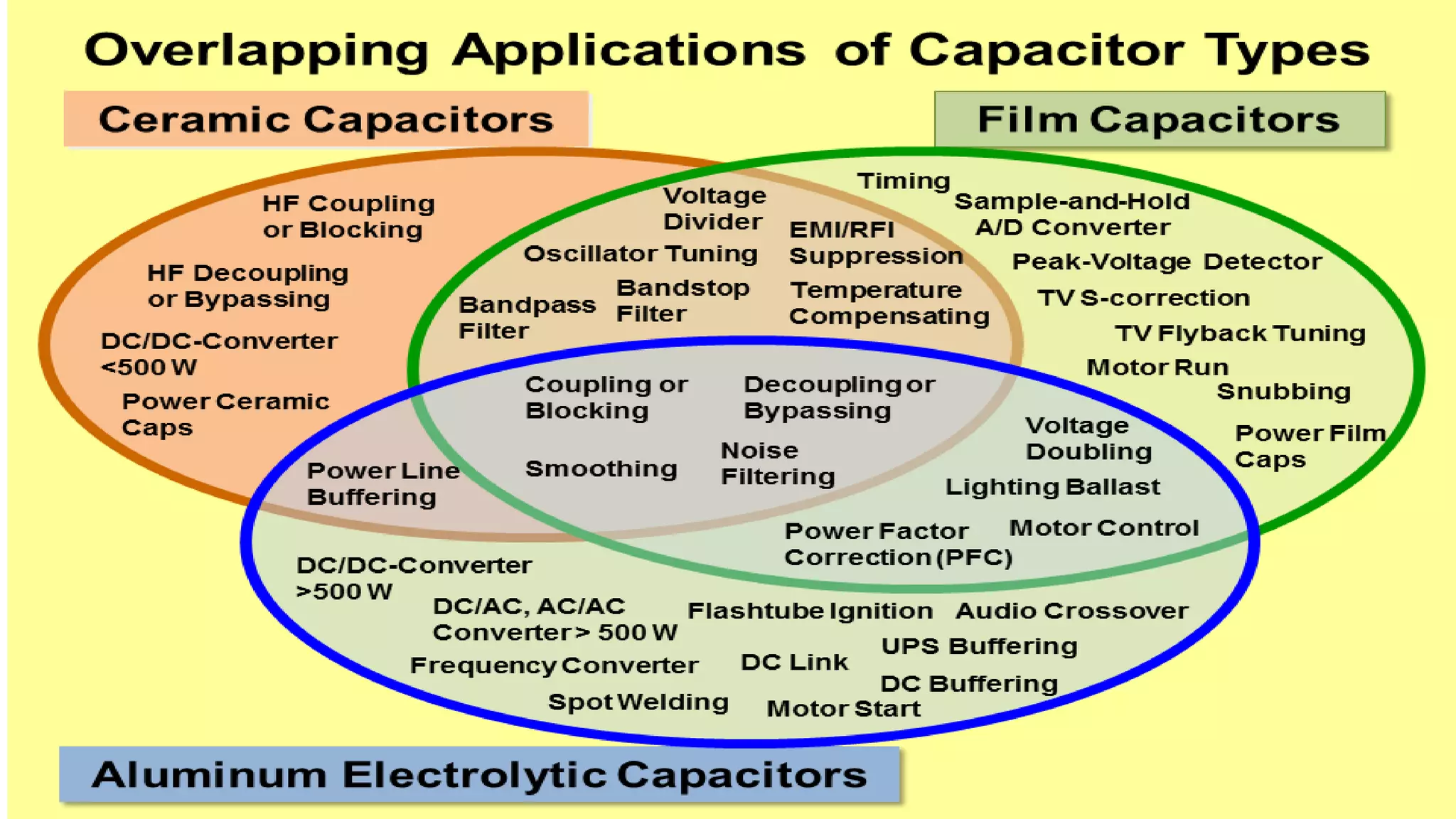
The document provides an overview of various types of capacitors, including non-polarized, polarized, ceramic, electrolytic, supercapacitors, variable capacitors, polymer capacitors, film power capacitors, and film capacitors, detailing their constructions and applications. Capacitors are essential components in electrical circuits, employing different materials and designs to store electric energy. The document categorizes each type based on its properties and uses in electronic devices.