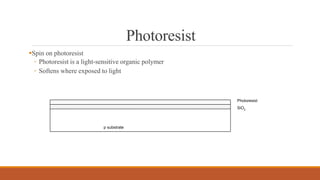
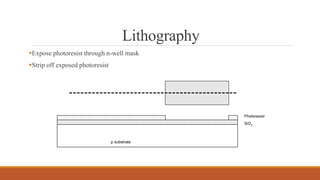
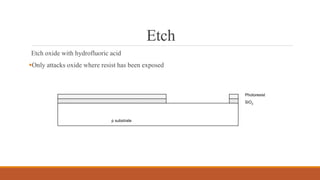
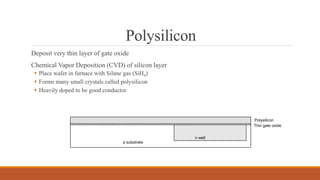
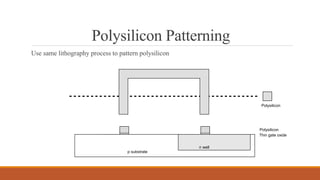
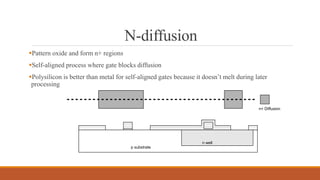
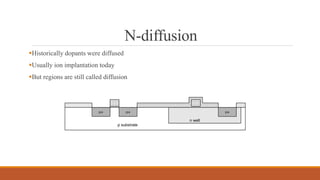
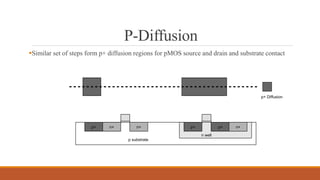
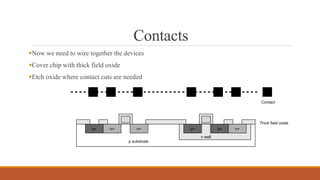
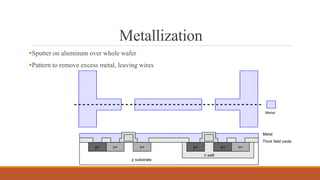
The document summarizes the basic steps in CMOS fabrication: (1) dopants are diffused or implanted into a silicon wafer to form n-well and p-substrate regions; (2) a gate oxide and polysilicon layer are deposited and patterned to form transistors; (3) n+ and p+ diffusion regions are implanted or diffused to form sources, drains and contacts; (4) a metallization process deposits aluminum wires to connect the transistors together into circuits. The process involves repeatedly depositing materials and using lithography to pattern layers from the bottom up on the silicon wafer.