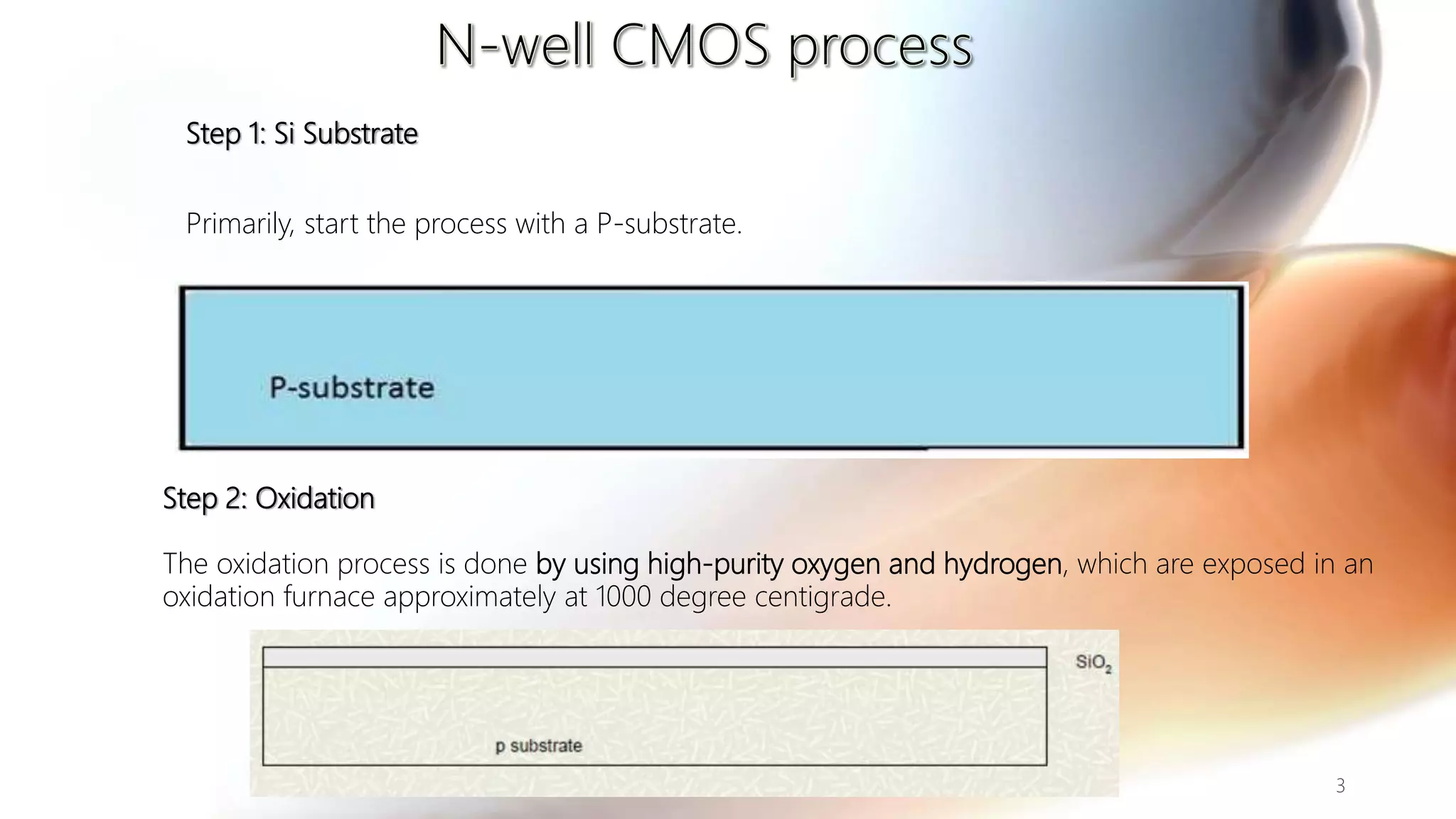
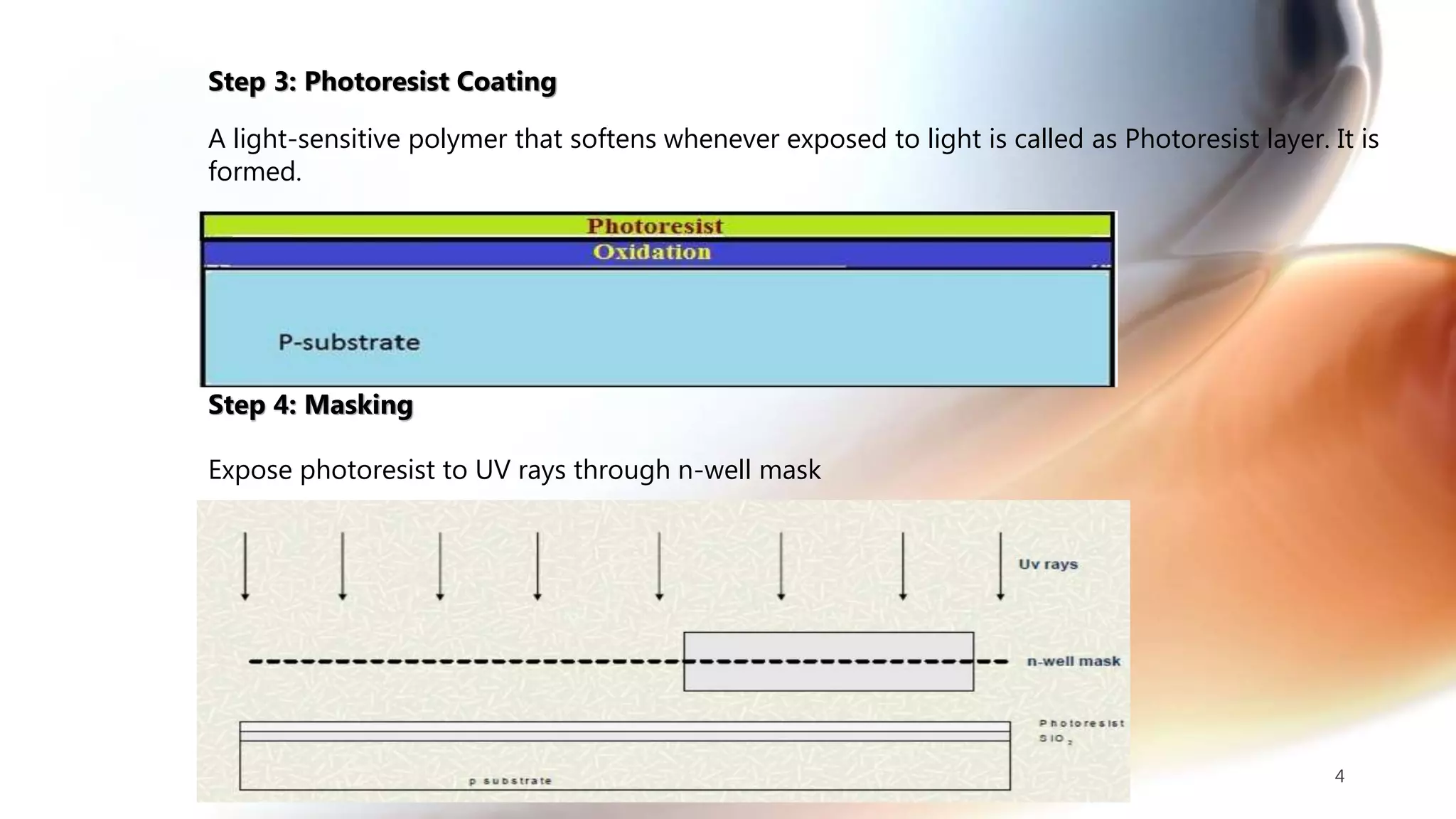
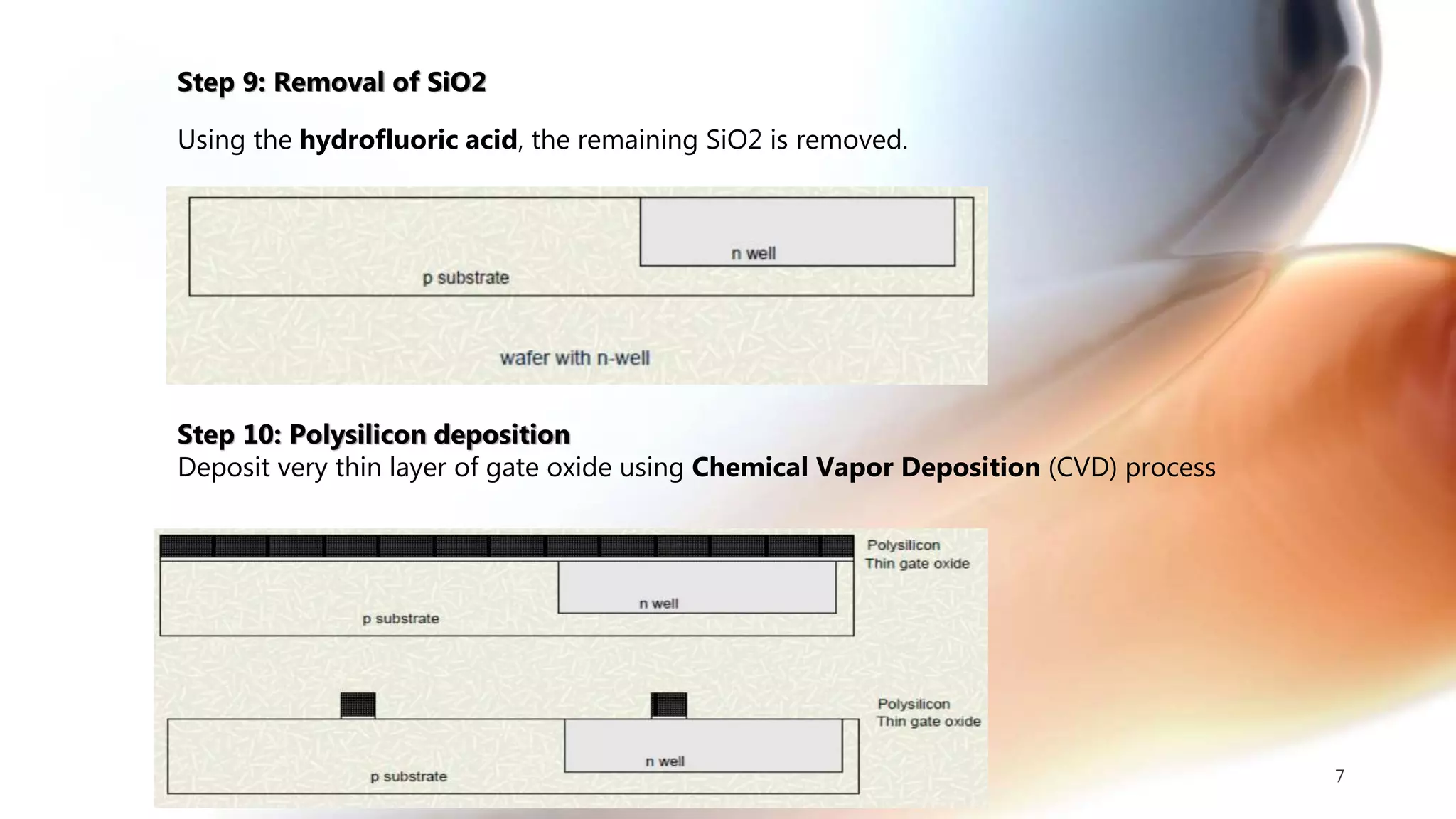
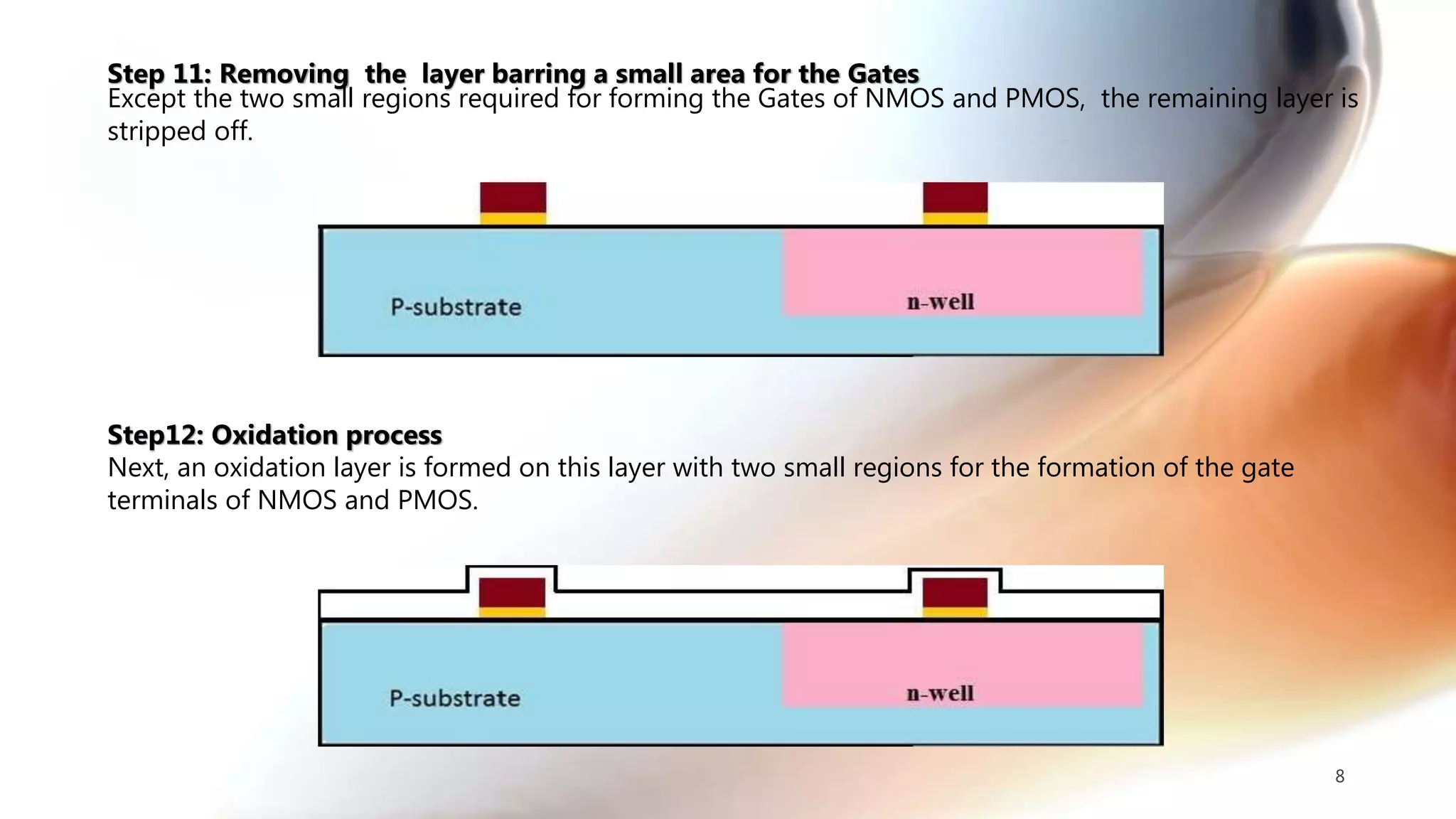
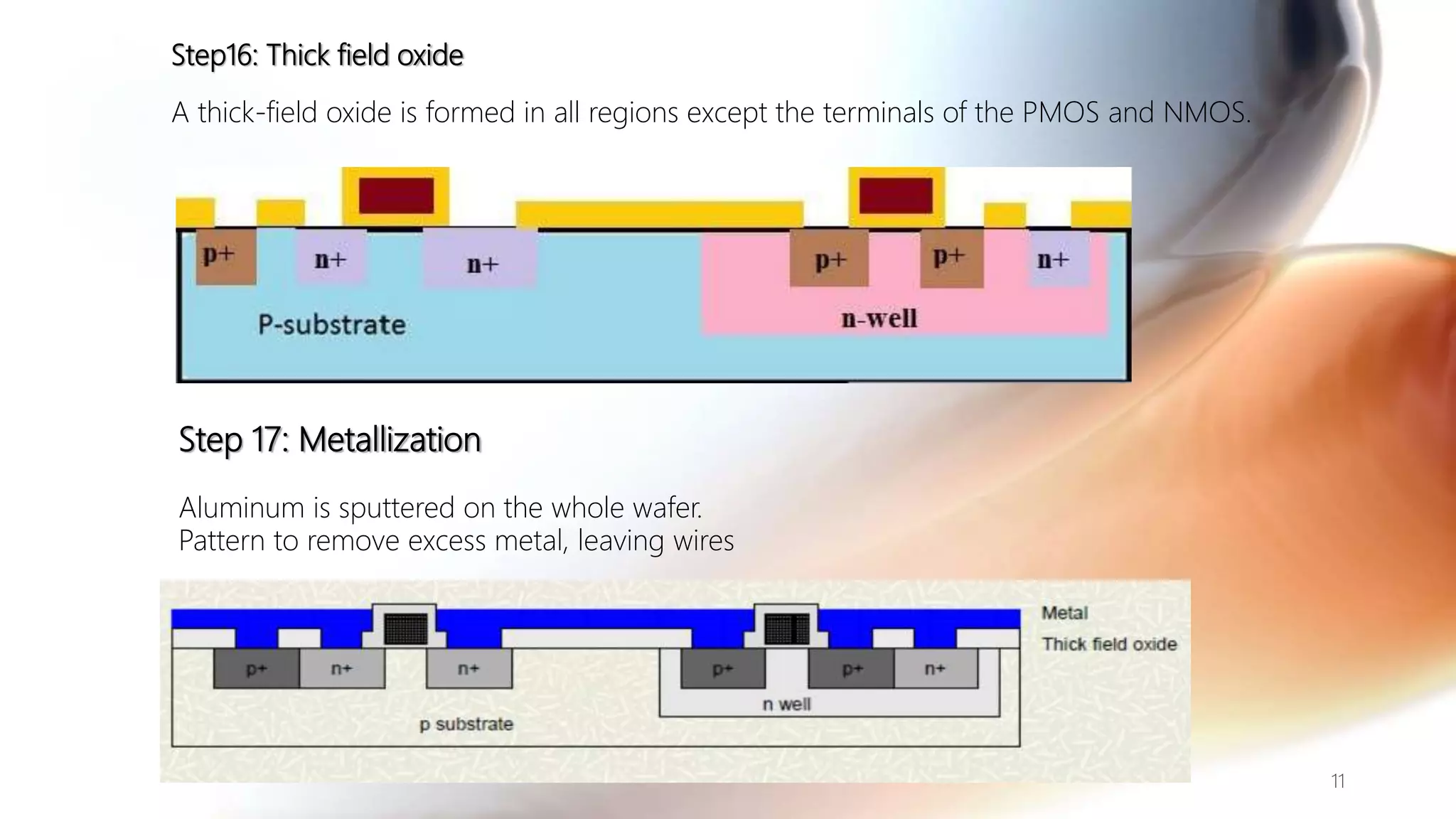
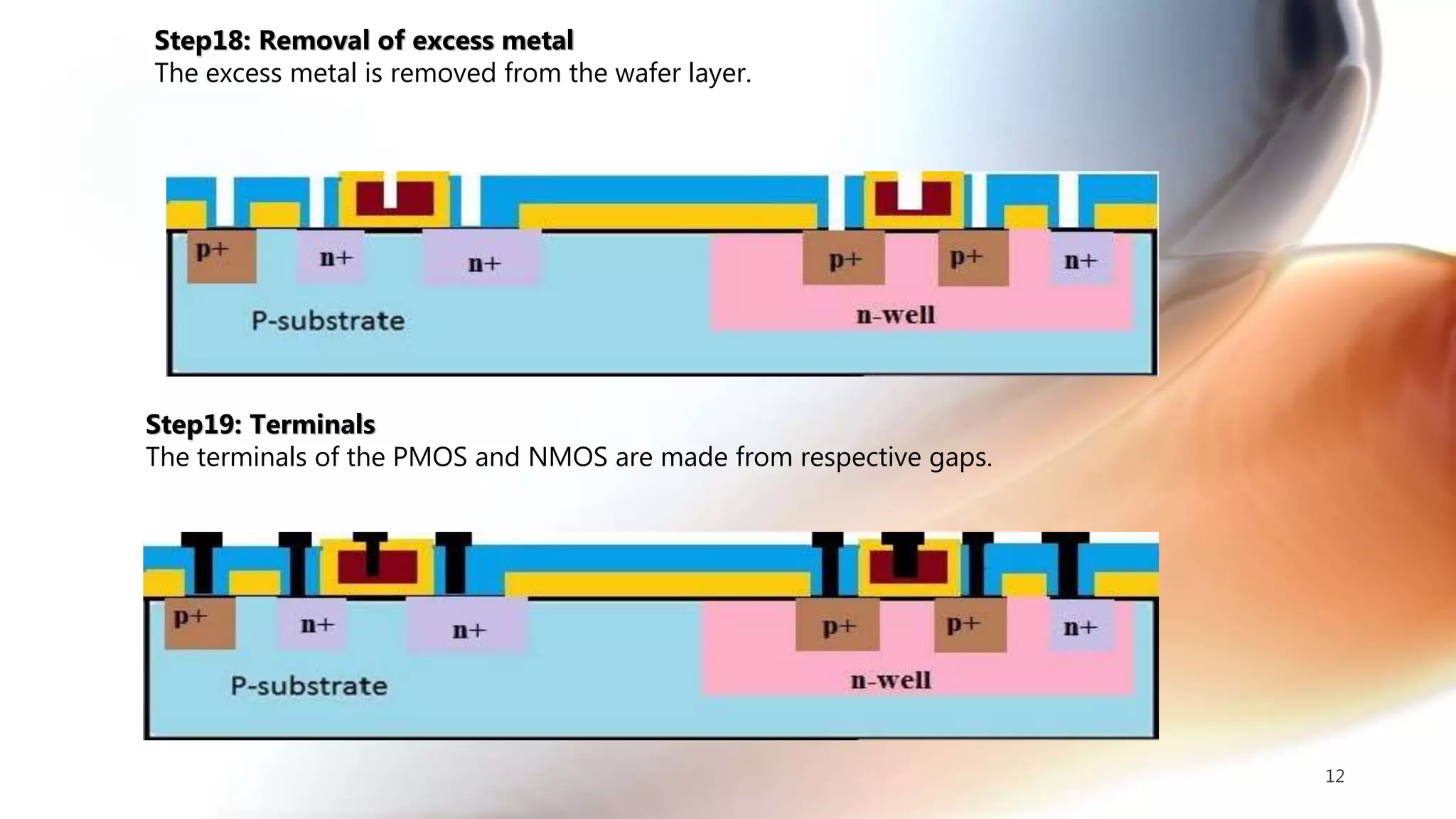
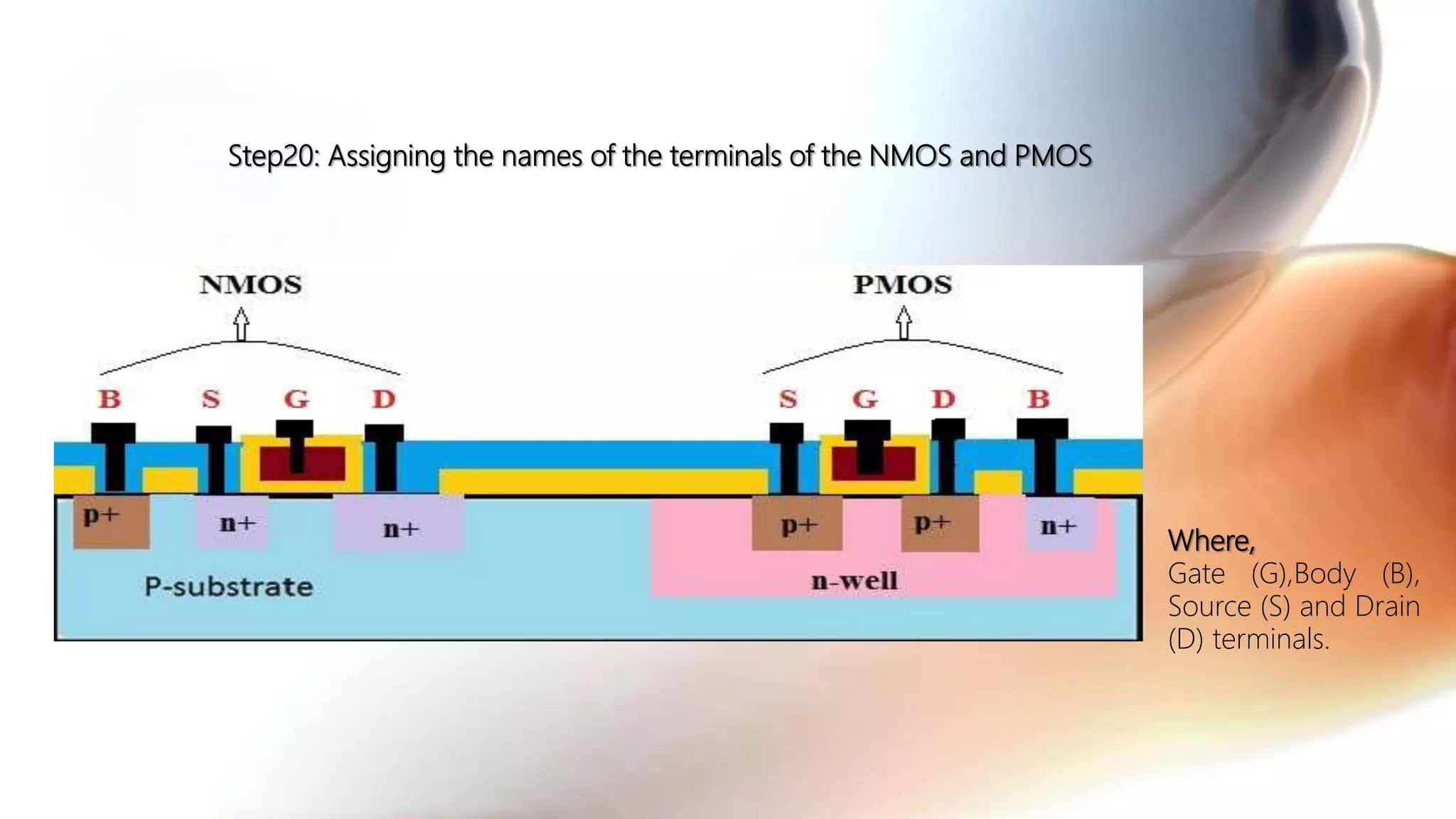
The document discusses the CMOS technology used for creating low power integrated circuits and outlines the steps involved in the n-well process of CMOS fabrication. It details each stage from substrate preparation to terminal formation, emphasizing processes like oxidation, photoresist application, diffusion, and metallization. The p-well process is briefly mentioned as a variation of the n-well process, differing primarily in substrate requirements.