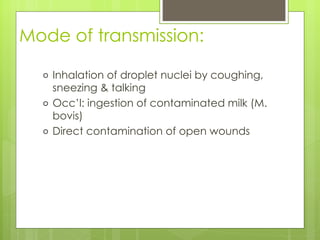
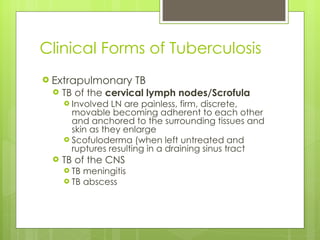
- Pulmonary tuberculosis is caused by infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis or Mycobacterium bovis bacteria. It is transmitted through inhalation of droplets from an infected person.
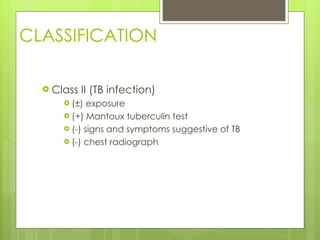
- Diagnosis involves the Mantoux tuberculin skin test, sputum smears and cultures, and chest x-rays. Treatment depends on whether a person has latent infection, active disease, or a history of previous treatment.
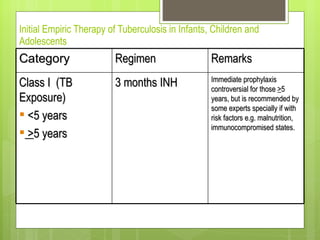
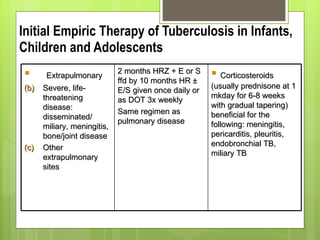
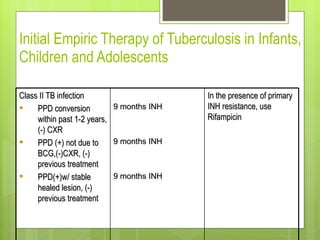
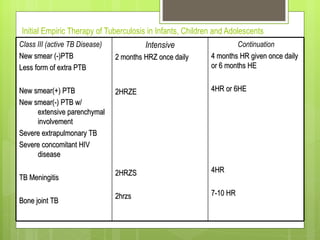
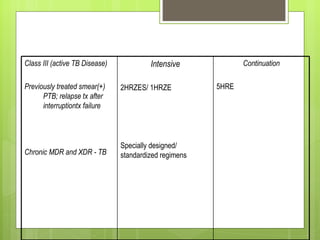
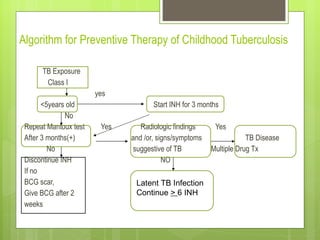
- For new cases of active pulmonary TB, treatment typically involves two months of four drugs followed by four months of two drugs. For latent infection, nine months of isoniazid is usually recommended. Preventive therapy aims to reduce the risk of developing active TB in the future.