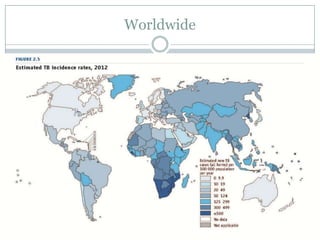
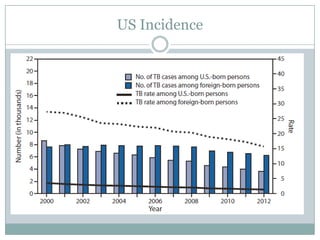
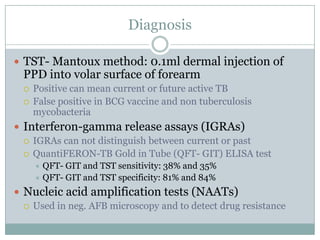
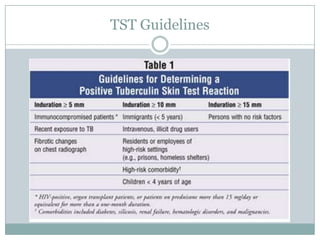
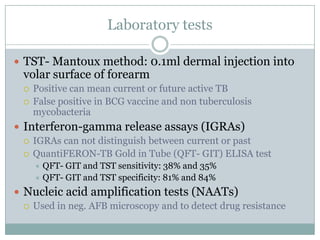
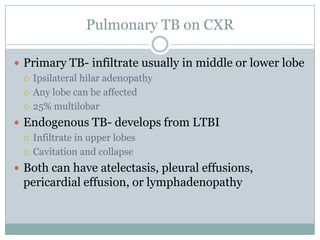
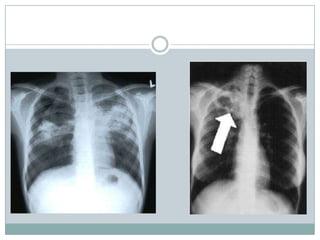
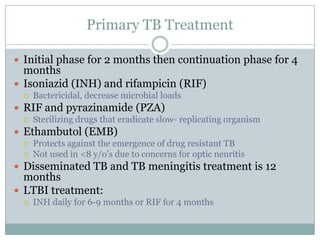
This document summarizes key information about pediatric tuberculosis (TB). It describes that TB is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and can manifest as latent or active disease. Active TB can be pulmonary or extrapulmonary. Worldwide, there are an estimated 8.7 million new TB cases annually, including 490,000 in children. Infants and young children are more susceptible to developing life-threatening forms of TB. Diagnosis involves tests such as tuberculin skin test (TST), chest x-ray, and sputum culture. Treatment consists of a multi-drug regimen including isoniazid and rifampin over 6-12 months depending on disease type.