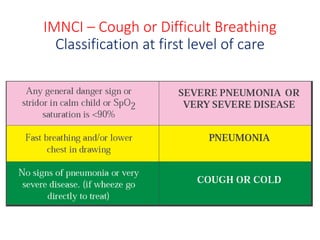
Pneumonia in children can be caused by viral or bacterial infections that lead to lung inflammation and fluid-filled alveoli. It is a common cause of death in children under 5 years old. Common bacteria that cause pneumonia include Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Staphylococcus aureus. Clinically, pneumonia can be diagnosed by symptoms like fast breathing, chest indrawing, and coarse lung sounds. Chest x-rays can reveal lung infiltrates. Treatment involves antibiotics, oxygen, and managing symptoms. Vaccines help prevent acute respiratory infections that can lead to pneumonia.