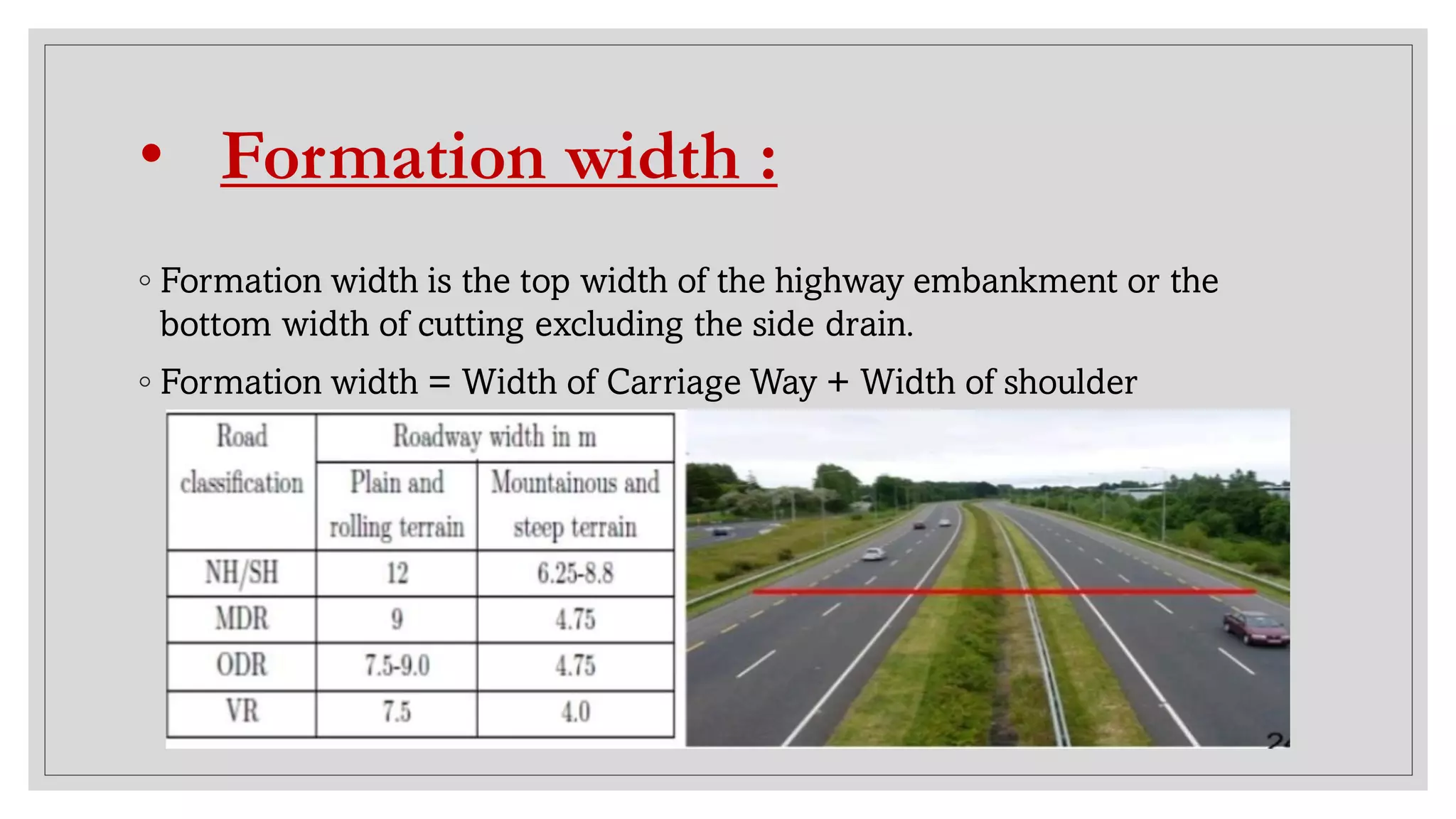
This document provides an overview of transportation engineering. It defines transportation engineering as a branch of civil engineering involved in planning, designing, operating, and maintaining transportation systems such as roadways, railways, airways and waterways. It then describes different modes of transportation including various types of roads, railways, airports and waterways. For each mode, it discusses their classification, components, advantages and disadvantages. The document aims to introduce the key concepts in transportation engineering.