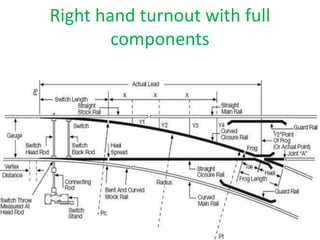
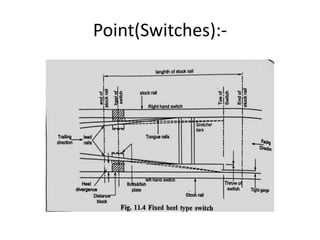
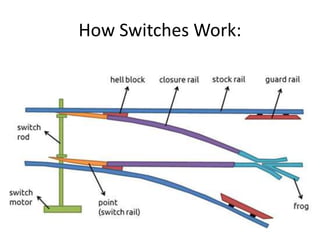
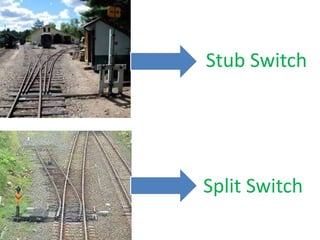
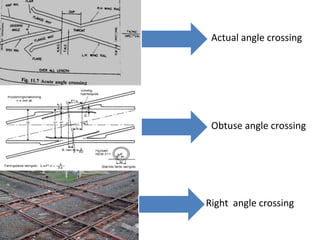
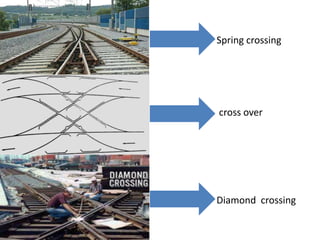
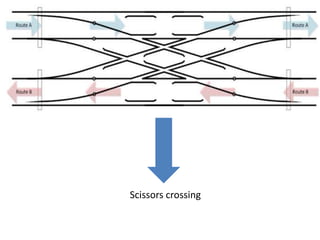
Points and crossings are railroad track components that allow trains to be diverted from one track to another. A point, or switch, is a movable section of rail that can be aligned to direct trains to the left or right. A crossing is a section of overlapping rails that allows trains to pass through an intersection. Together, points and crossings make up a turnout, which consists of a stock rail, tongue rail, heel block, and other parts to smoothly guide trains between tracks in either a left-hand or right-hand configuration.