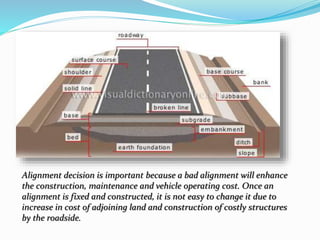
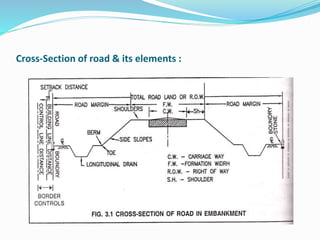
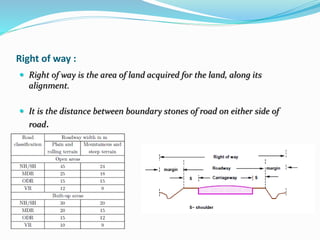
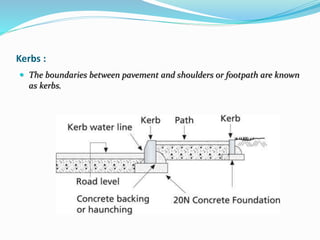
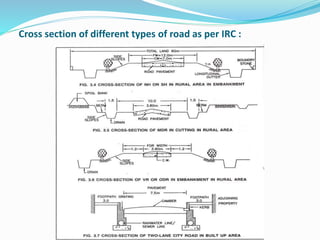
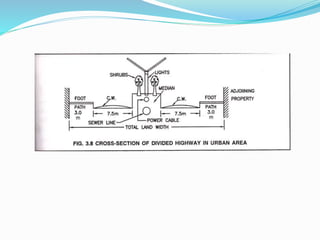
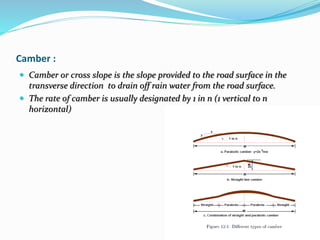
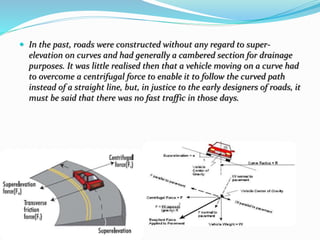
The document presents an overview of highway geometric design, emphasizing its importance in ensuring driver comfort, efficiency, and safety while minimizing accidents. Key factors affecting geometric design include design speed, topography, and environmental aspects, with considerations for road alignment, cross-section elements, and pavement design. Additional topics covered include various types of alignments, road components like carriage way and shoulders, as well as drainage and camber for effective water management.