1) Transportation engineering involves applying scientific principles to plan, design, operate, and manage transportation facilities to provide for the safe, rapid, comfortable, convenient, economical, and environmentally compatible movement of people and goods.
2) Early transportation committees in India, like the Jayakar Committee, recommended establishing funds and organizations to support transportation development, leading to the creation of the Central Road Fund, Indian Road Congress, and Central Road Research Institute.
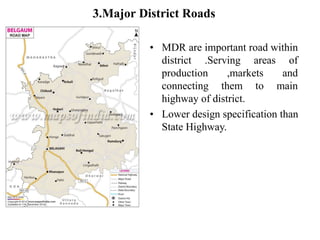
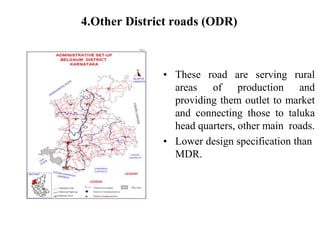
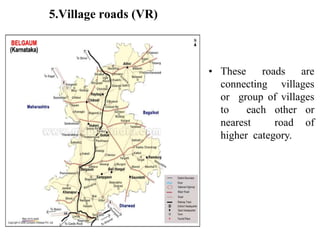
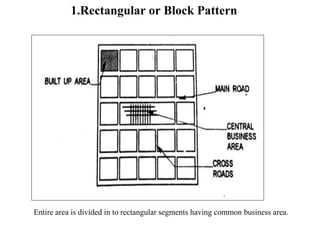
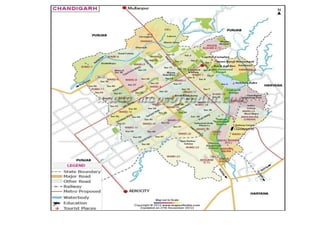
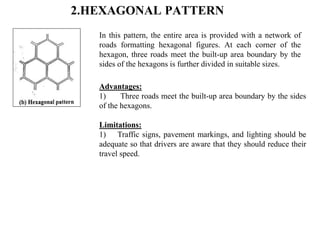
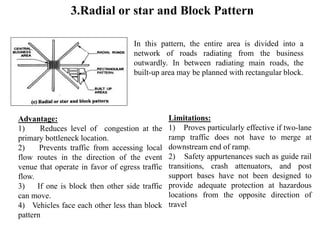
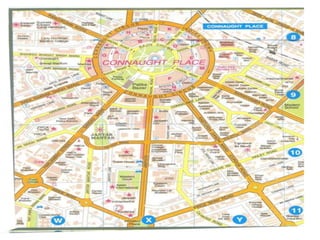
3) Roads are classified based on factors like traffic volume, transportation tonnage, importance, location, and materials used. Urban roads are classified as arterial, sub-arterial, collector, and local streets.