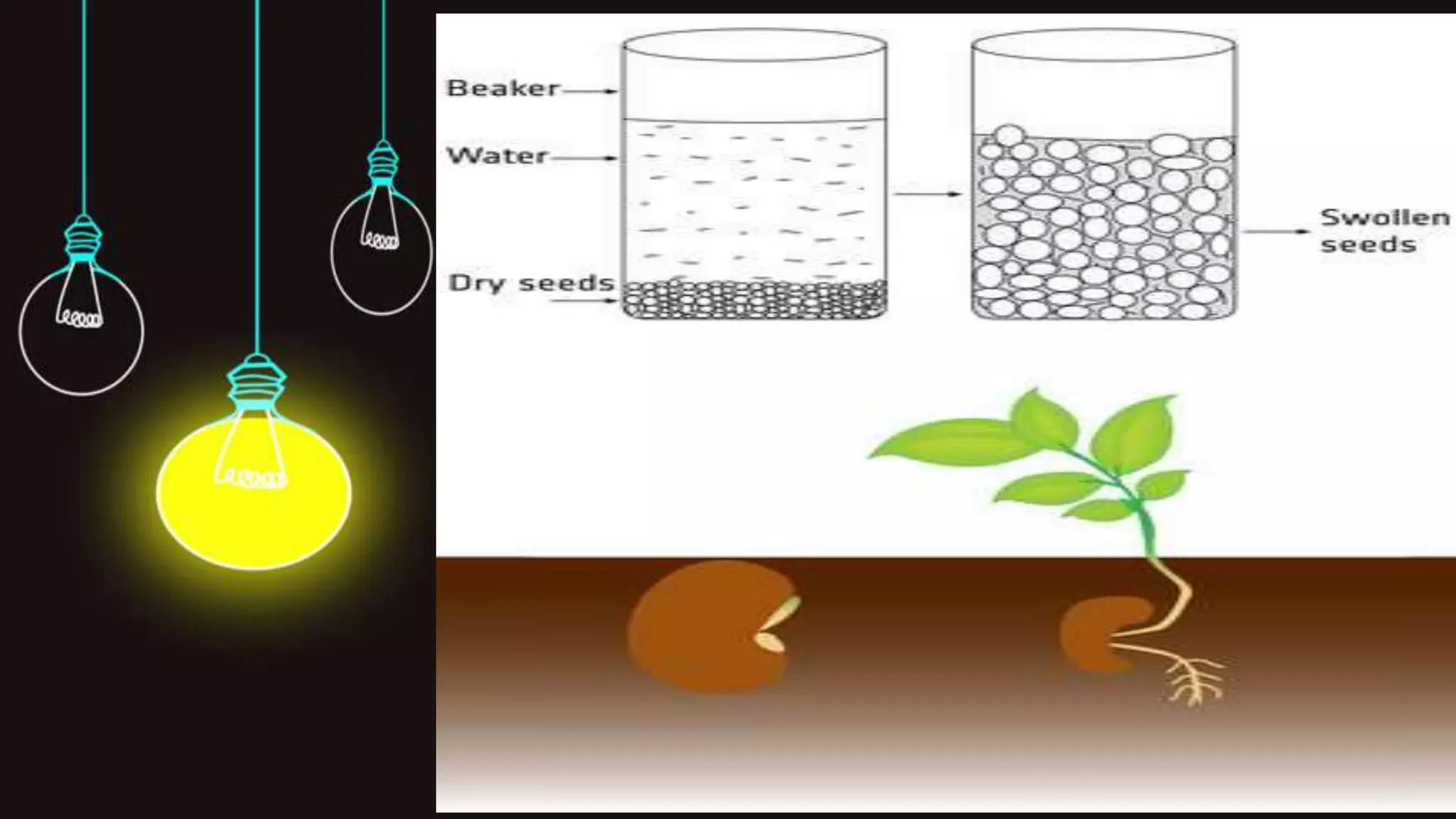
The presentation discusses key concepts in plant biology, including imbibition, water potential, turgor pressure, osmotic pressure, and diffusion pressure deficit. Imbibition is a process in which water is absorbed by solids, leading to significant volume increase, and is essential for seed germination and root water absorption. Water potential is defined as the energy of water, influencing its movement through various factors, while turgor pressure is crucial for plant rigidity and osmotic pressure and diffusion pressure deficit describe the relationship between solute concentration and water movement.