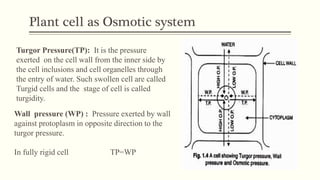
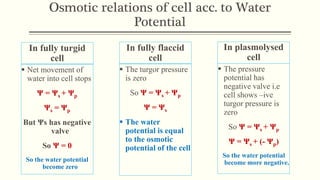
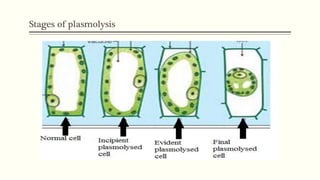
This document discusses diffusion pressure deficit (DPD), water potential, and related concepts in plant cells. It defines DPD as the difference between the diffusion pressure of a pure solvent and a solution. Water moves from areas of low DPD to high DPD. Water potential is the difference in free energy of water between pure water and other systems like plant cells. It depends on matric, solute, and pressure potentials. Plasmolysis occurs when cells are placed in hypertonic solutions, causing water to move out by exosmosis. Deplasmolysis is the reverse process when cells return to hypotonic solutions.