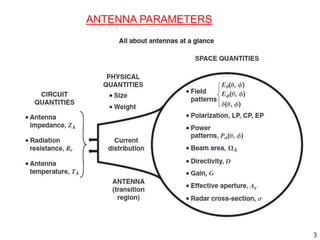
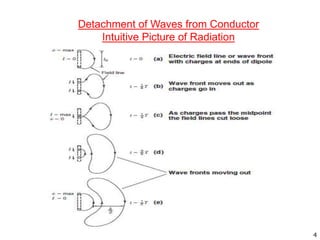
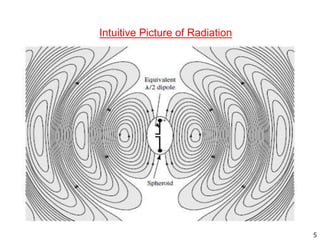
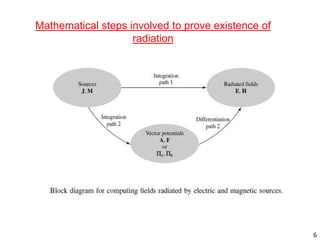
The document discusses different types of antennas including aperture antennas. It defines an aperture antenna as an opening or closed surface that is considered an antenna opening. Aperture antennas are surface mountable antennas suitable for fast moving vehicles, aircrafts, and missiles. The different types of aperture antennas discussed are horn and open waveguide antennas, reflector antennas, slot antennas, and microstrip antennas. The document also mentions several analysis methods and principles for aperture antennas including current distribution, aperture analysis, Fourier transform, field equivalence, Hygens, and Babinets principles. It notes that aperture antennas have geometries and designs that can be analyzed.