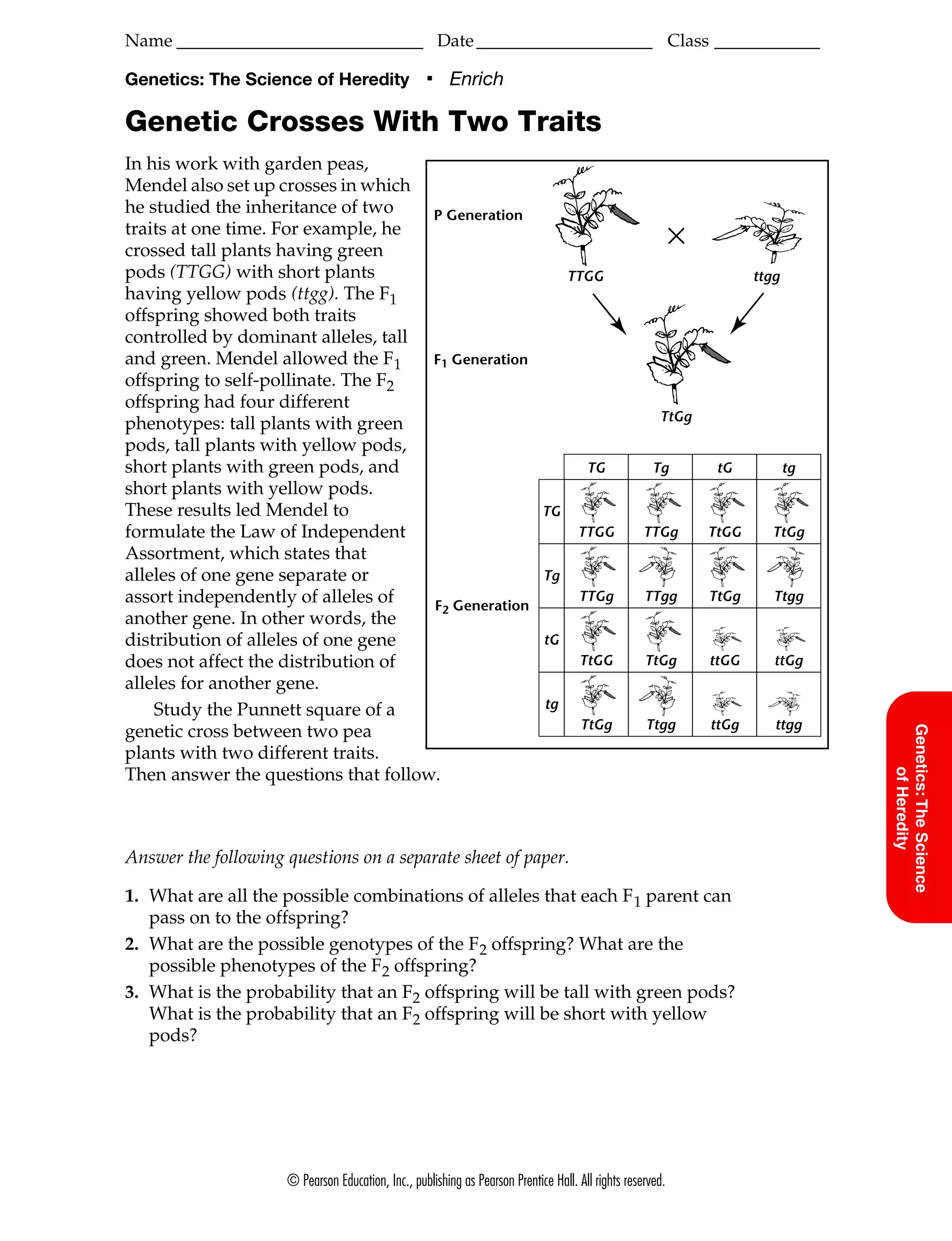
Mendel studied inheritance of two traits by crossing tall pea plants with green pods and short pea plants with yellow pods. The F1 offspring all showed the dominant traits of tall and green. When the F1 offspring self-pollinated, the F2 offspring showed four phenotypes - tall/green, tall/yellow, short/green, short/yellow. This led Mendel to formulate the Law of Independent Assortment, which states that alleles of one gene separate independently of alleles of another gene during gamete formation and fertilization.