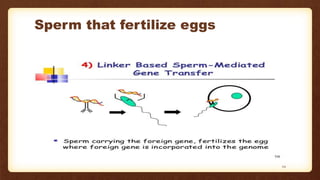
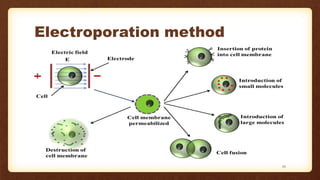
Transgenic animals are organisms whose genome has been altered by the addition of foreign DNA from other species. This document discusses the history of transgenic animals, including the first transgenic mice created in the 1970s. It describes various methods used to create transgenic animals, such as microinjection and viral vectors. The benefits and risks of transgenic animals are outlined. Applications include producing human proteins and studying human diseases. While transgenic animals show promise for agriculture, medicine, and industry, issues around safety, ethics, and environmental impacts require further consideration.