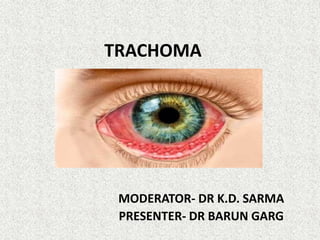
Trachoma is a chronic eye disease caused by Chlamydia trachomatis infection. It is a major cause of preventable blindness worldwide. The infection is transmitted through contact with infected eye or nasal secretions or flies. Recurrent infections during childhood can lead to scarring of the conjunctiva and inwards turning of the eyelashes (trichiasis) in adulthood, causing corneal opacification and blindness. The WHO-led SAFE strategy (surgery, antibiotics, facial cleanliness, and environmental improvement) aims to eliminate trachoma as a public health problem by 2020.