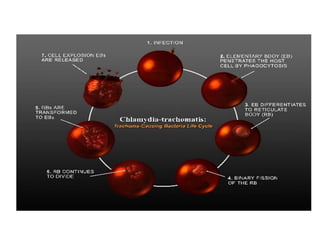
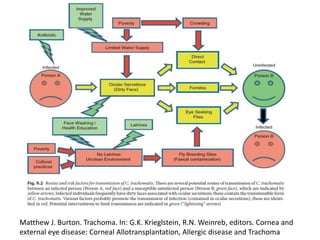
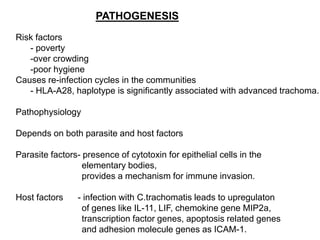
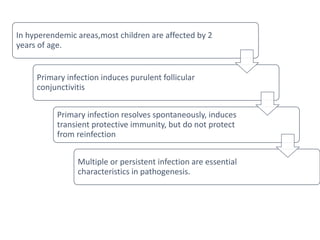
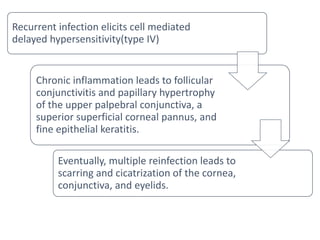
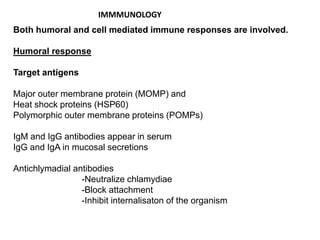
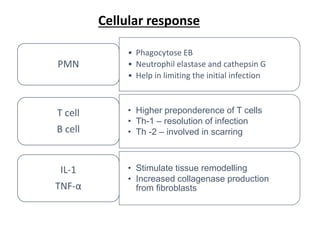
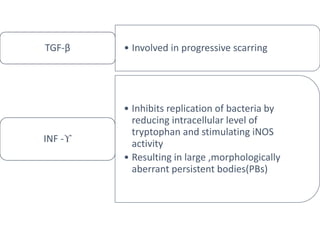
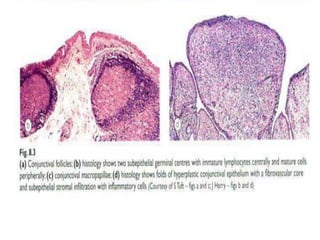
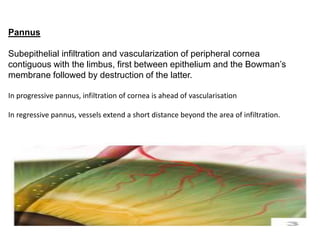
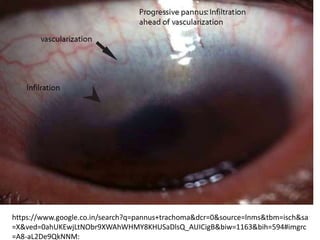
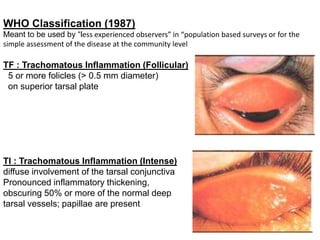
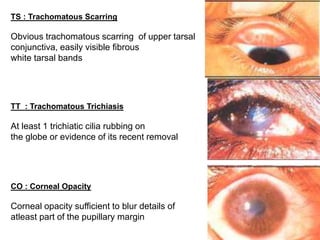
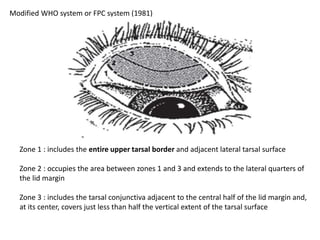
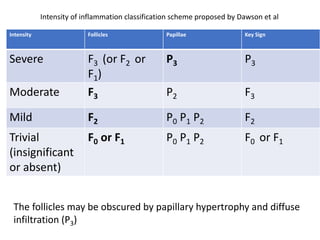
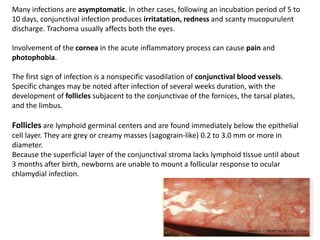
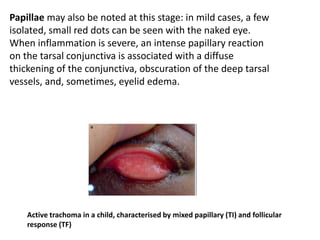
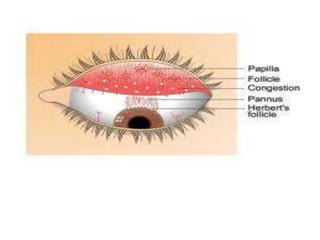
The document discusses trachoma, a preventable cause of blindness primarily affecting children, which has seen a significant reduction in prevalence since WHO's 1996 elimination program. It details the pathology, immunology, clinical features, and classification systems of trachoma, emphasizing factors that lead to infection, inflammation, and eventual scarring. India, being one of the countries significantly affected, has various regions with different prevalence rates of active trachoma cases, highlighting the importance of addressing public health measures for prevention and treatment.