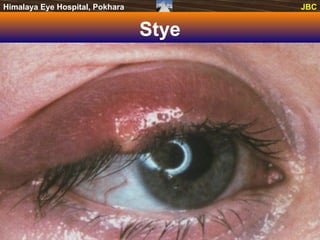
This document discusses various disorders of the eyelids and conditions that cause red eye. It describes several conditions including blepharitis, styes, chalazions, entropion, trichiasis, lagophthalmos, ptosis, dacryocystitis, orbital cellulitis, conjunctivitis, hemorrhagic conjunctivitis, allergic conjunctivitis, phlyctenular conjunctivitis, vernal conjunctivitis, pterygium, and corneal ulcers. Treatment options focus on antibiotic ointments, compress, referral for surgical correction if needed, and systemic antibiotics in more severe cases.