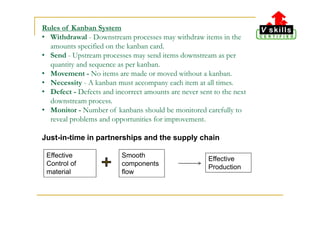
Module 5 discusses the importance of partnerships and resources, emphasizing that effective partnerships enhance business goals through resource maximization, leading to improved quality, efficiency, and innovation. It also explains supplier partnerships and Just-In-Time (JIT) management, which reduces inventory costs while meeting customer demands efficiently. Additionally, the kanban system is introduced as a method to streamline production processes by controlling material flow based on demand.