This document discusses consumer behavior in services. It covers several key topics:
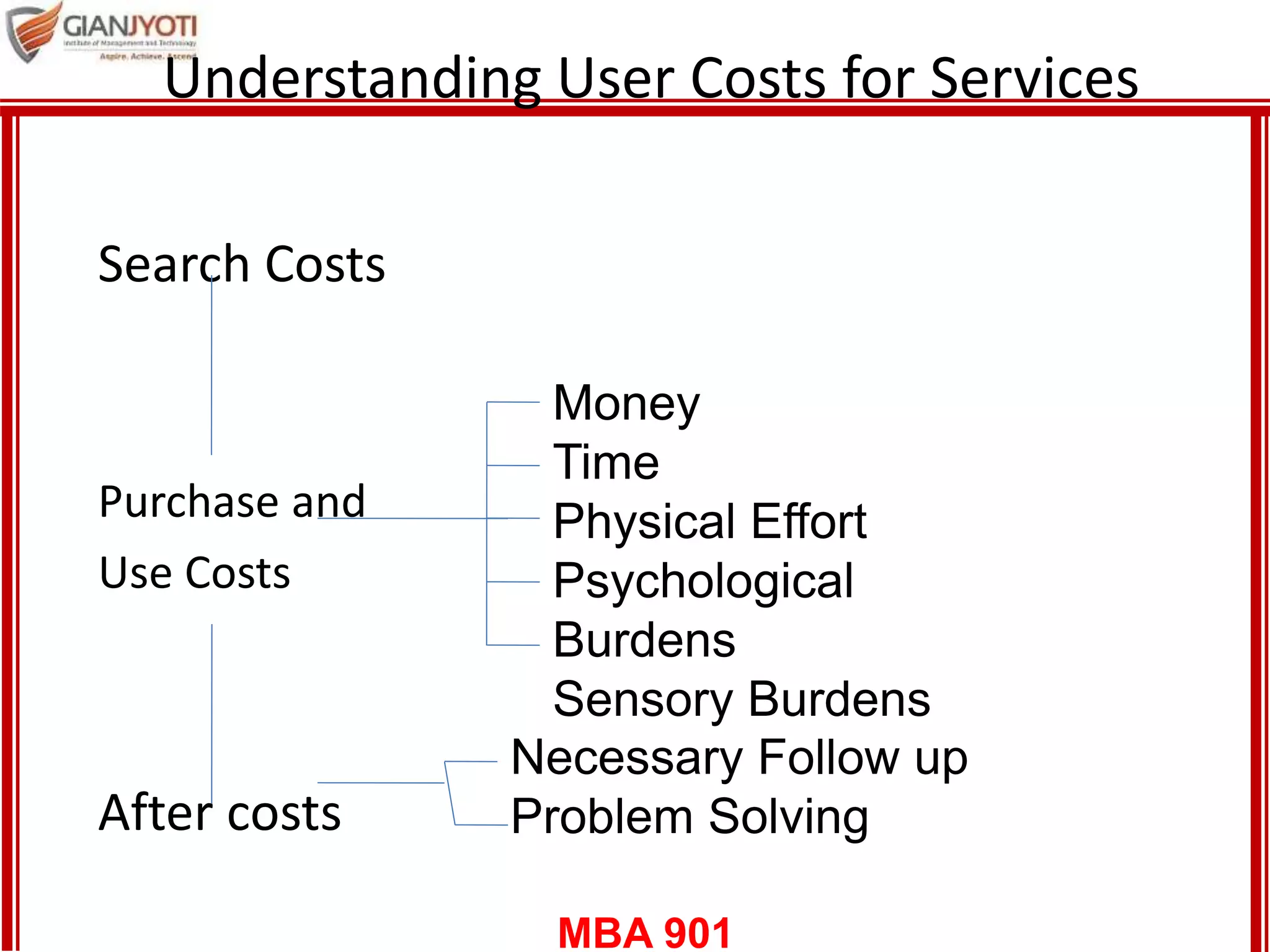
1) The behavior consumers display when searching for, purchasing, using, evaluating and disposing of services. This includes understanding triggers of need, user costs of services, and information search.
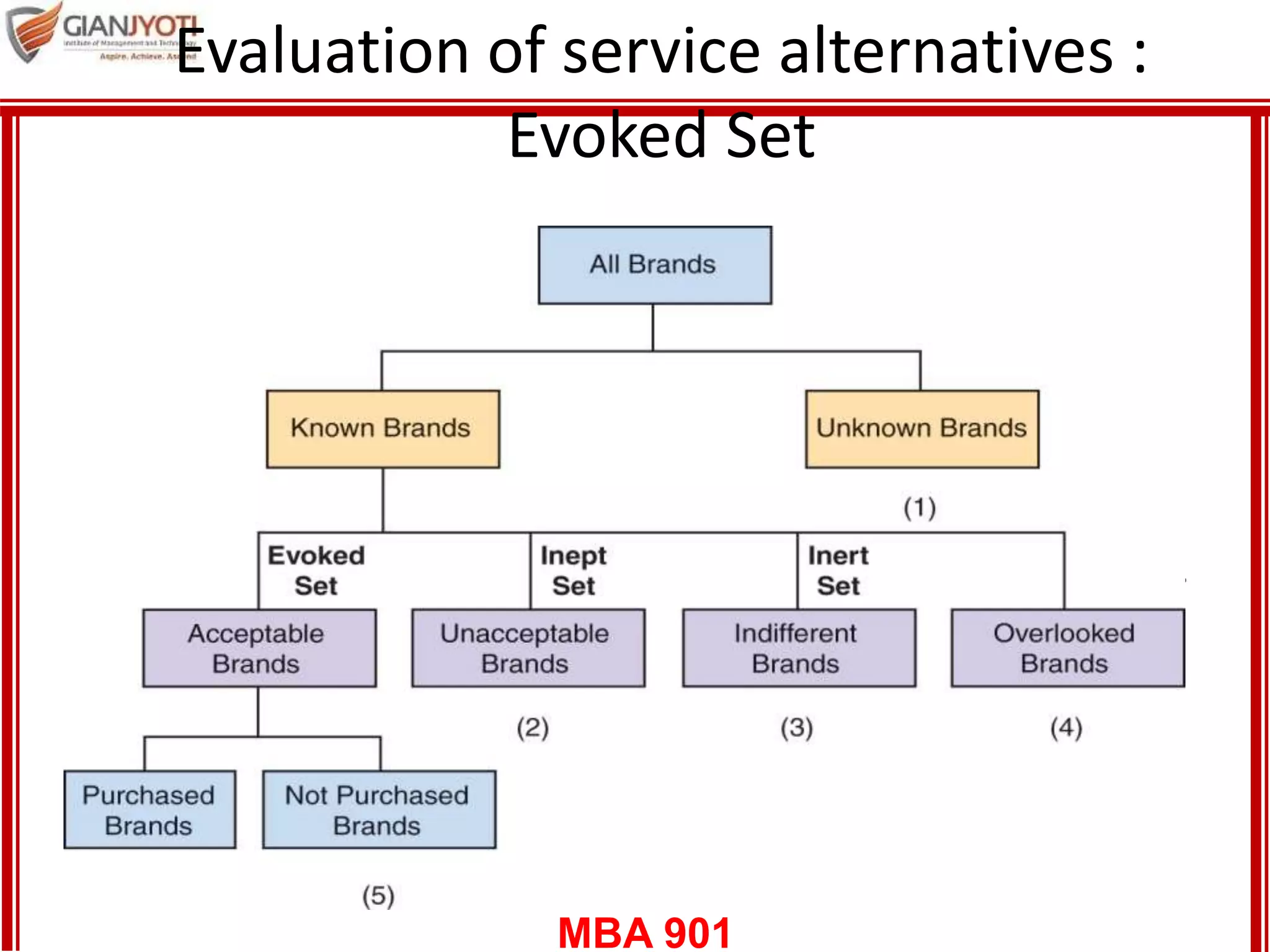
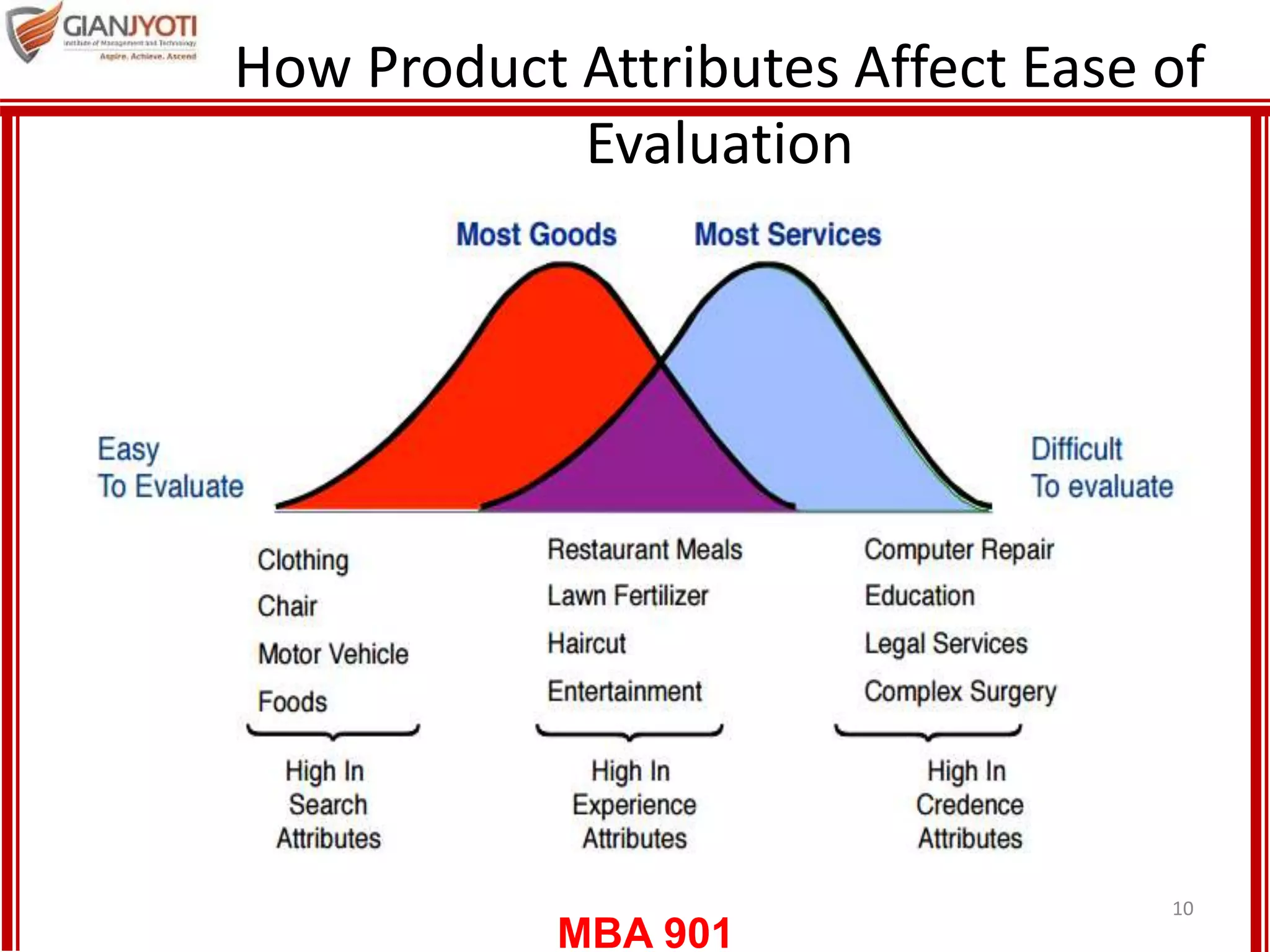
2) Evaluating service alternatives including attributes that can be evaluated before or after purchase. It also discusses perceived risks of services.
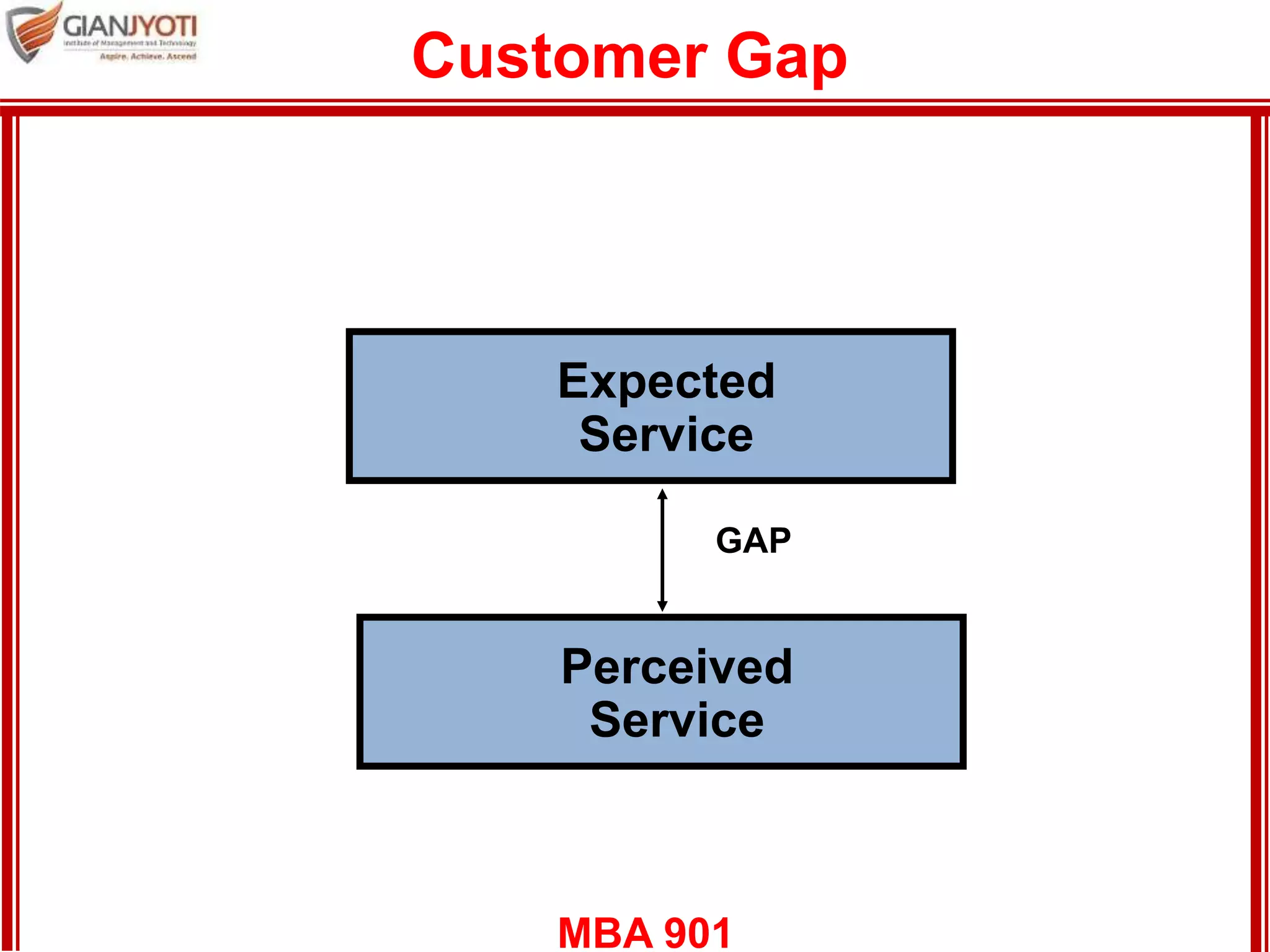
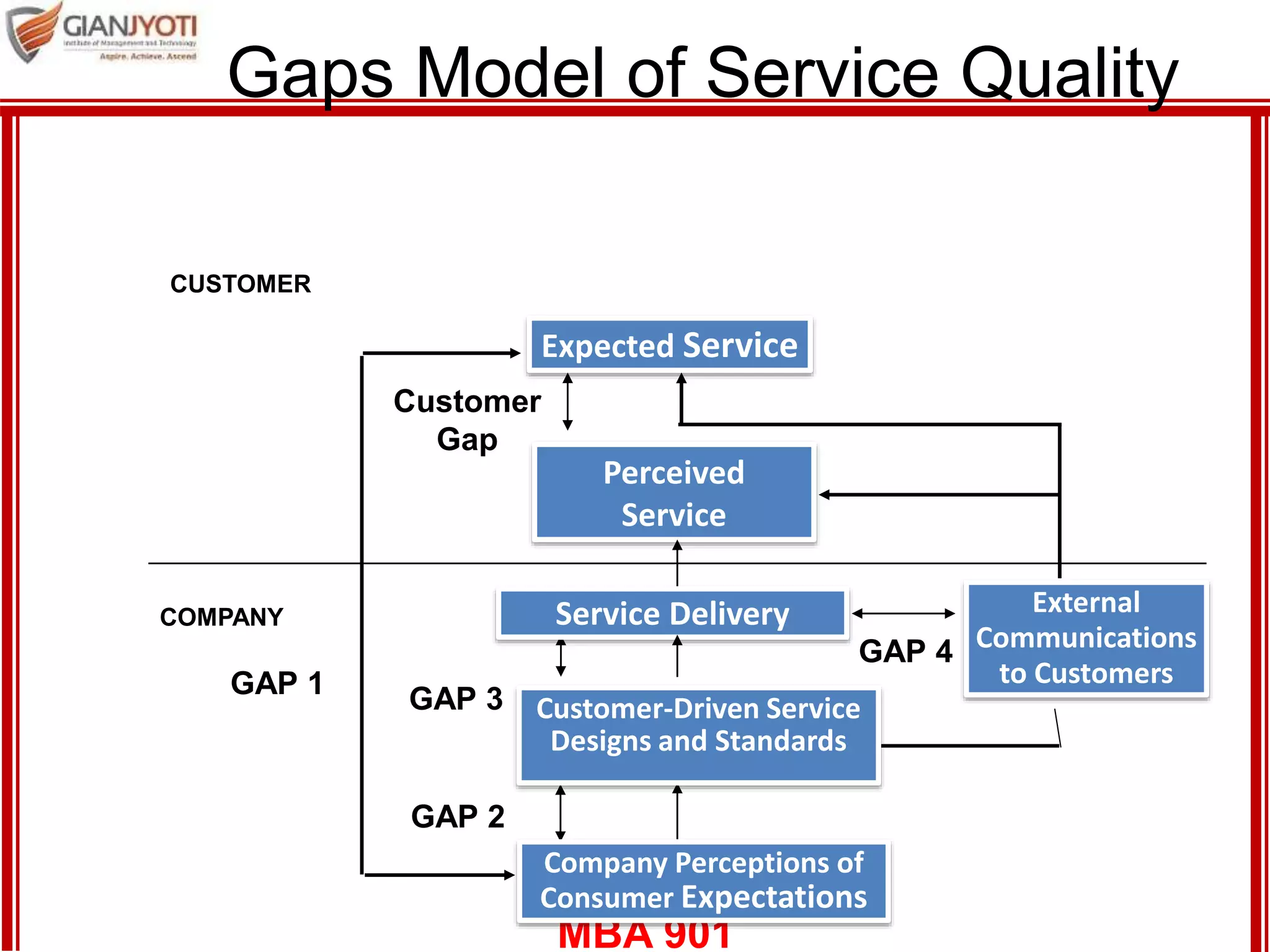
3) Customer expectations of services which are formed by situational and personal factors. Expectations can change over time.
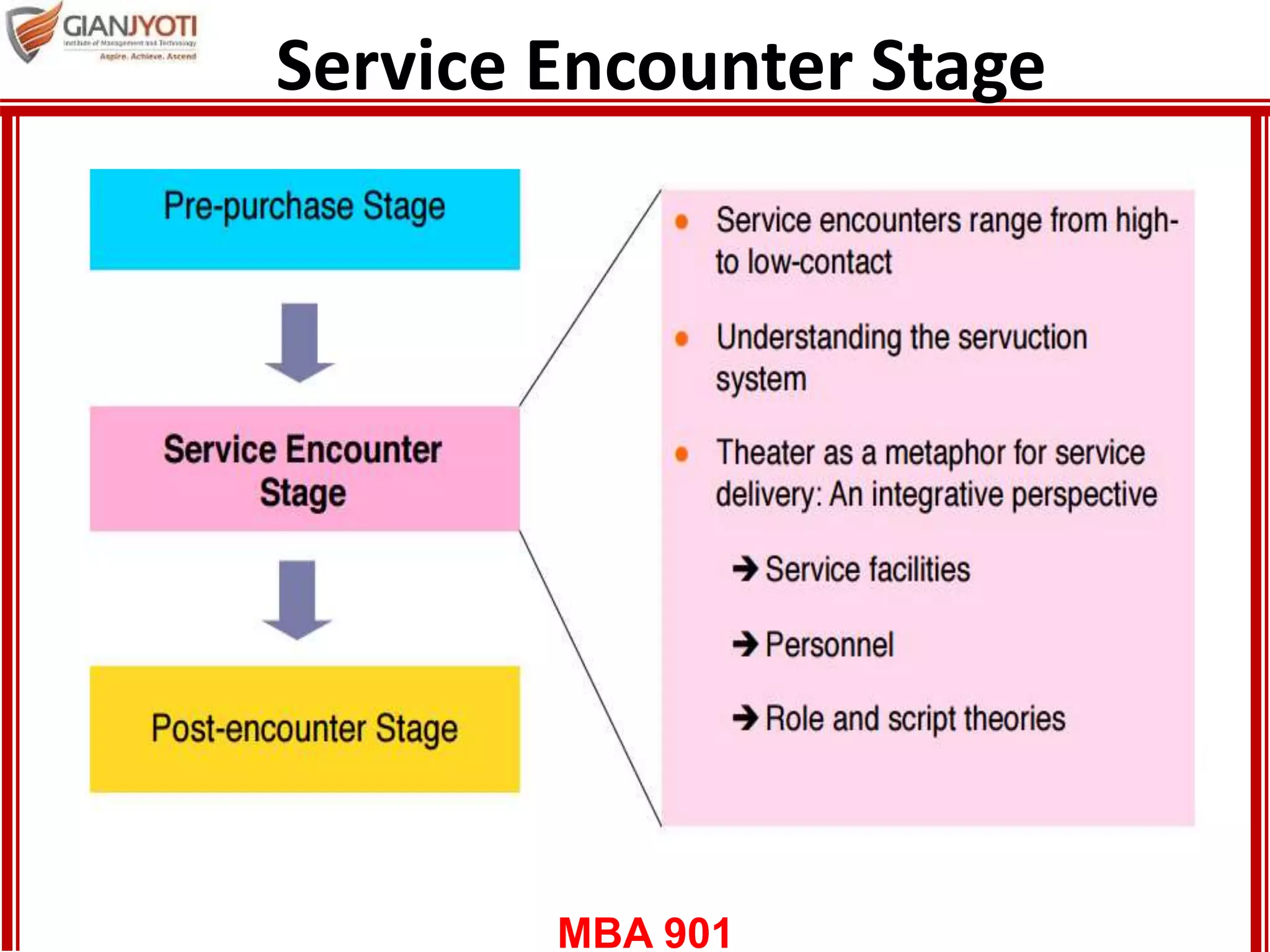
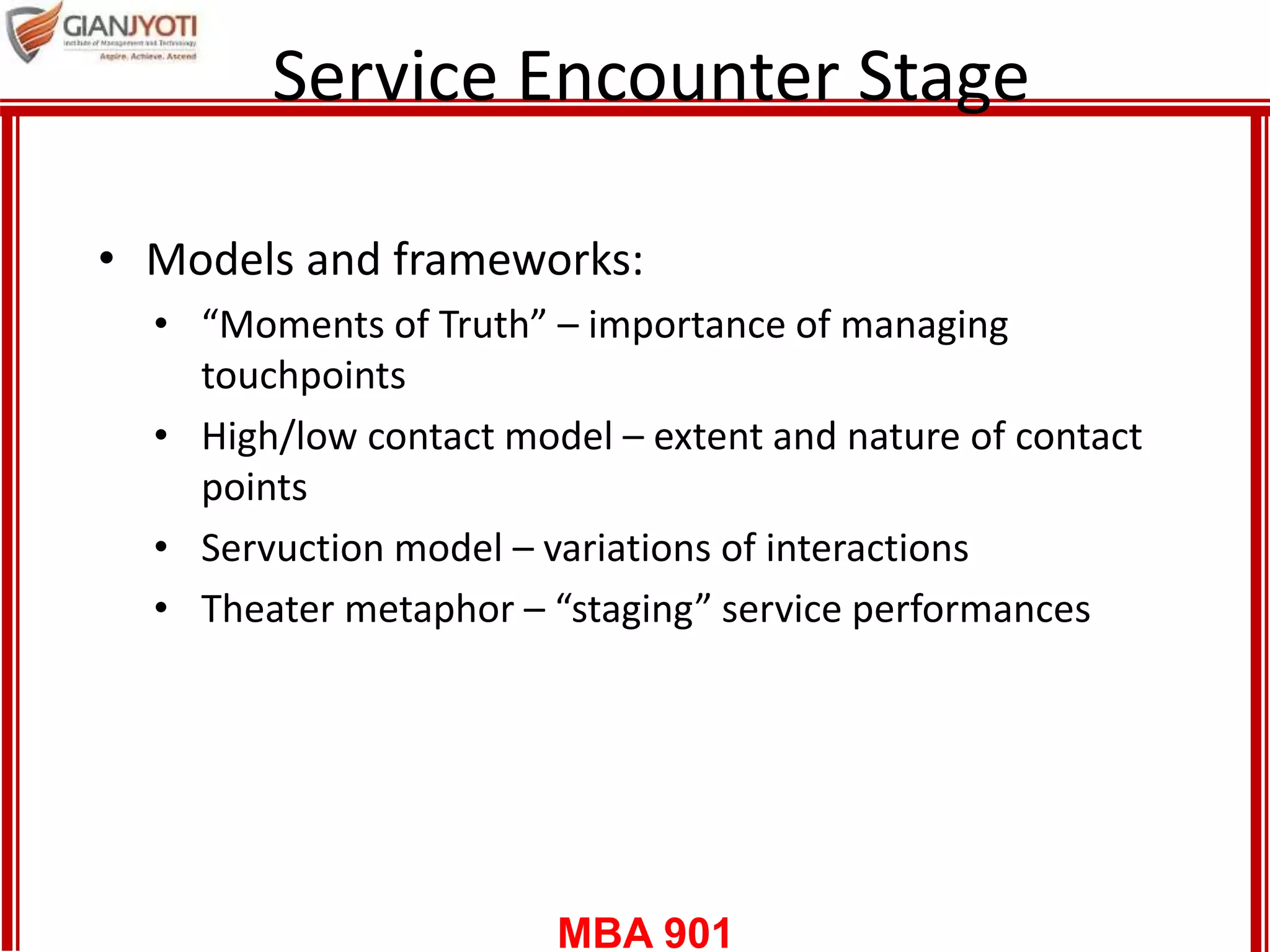
4) The service encounter stage where customers interact with service providers. Models for conceptualizing this include "moments of truth", high/low contact services, and viewing service as drama with roles and scripts