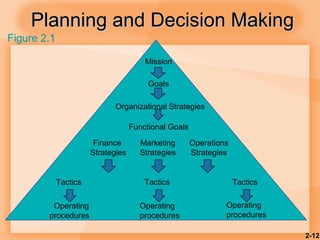
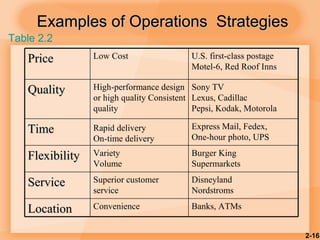
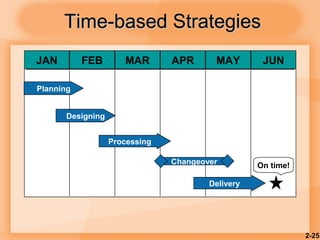
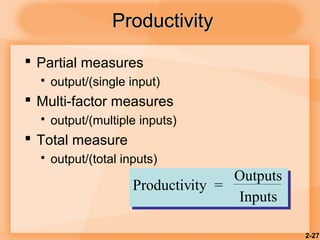
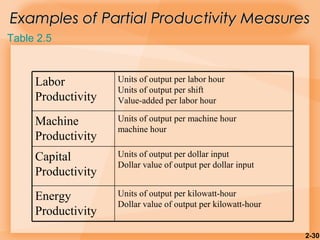
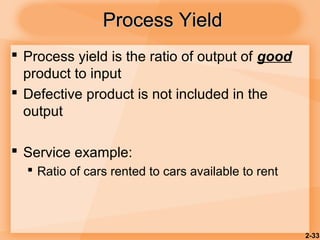
This document discusses competitiveness, strategy, and productivity. It defines key terms like strategy, tactics, and productivity. Strategy is important for competitiveness and involves setting goals and plans to achieve an organization's mission. Operations strategy must be linked to overall organizational strategy. Time-based and quality strategies are discussed. Productivity is defined as a ratio of outputs to inputs and can be improved through methods like developing measures, determining bottlenecks, and setting reasonable goals.