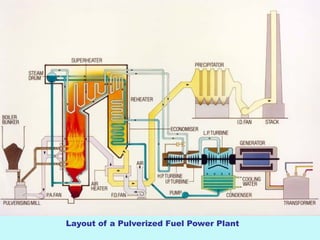
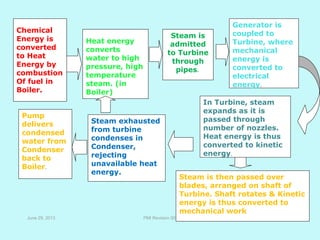
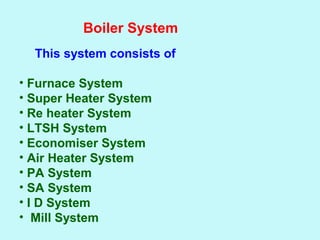
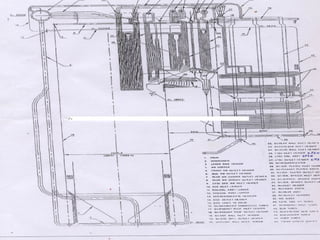
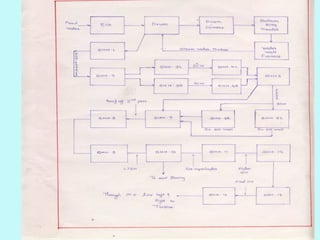
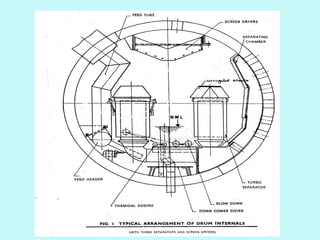
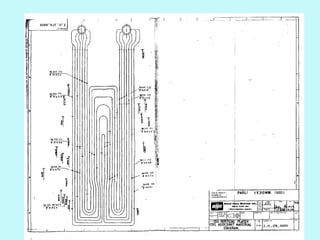
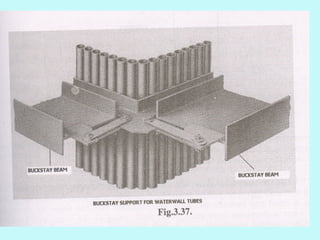
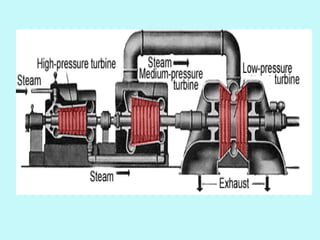
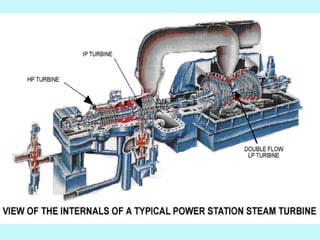
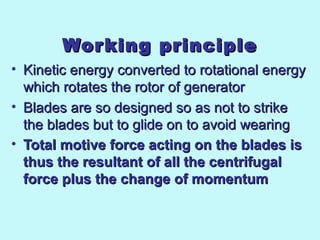
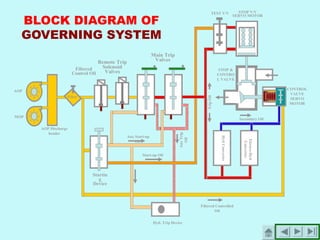
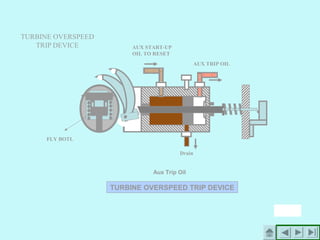
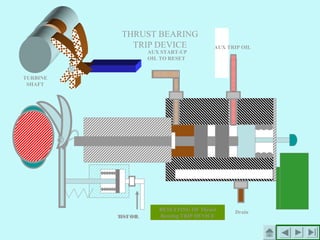
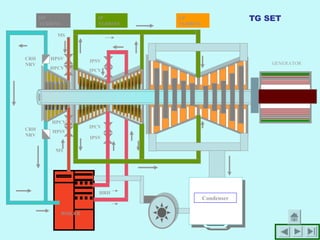
The document provides an overview of thermal power generation and the key components involved. It discusses how chemical energy from fuel is converted through various processes into electrical energy. The main components that enable this conversion are the boiler, turbine, and generator. Steam generated in the boiler powers the turbine, which spins the generator's rotor to produce electricity via electromagnetic induction. The turbine has high, intermediate, and low pressure sections to efficiently extract energy from the steam.