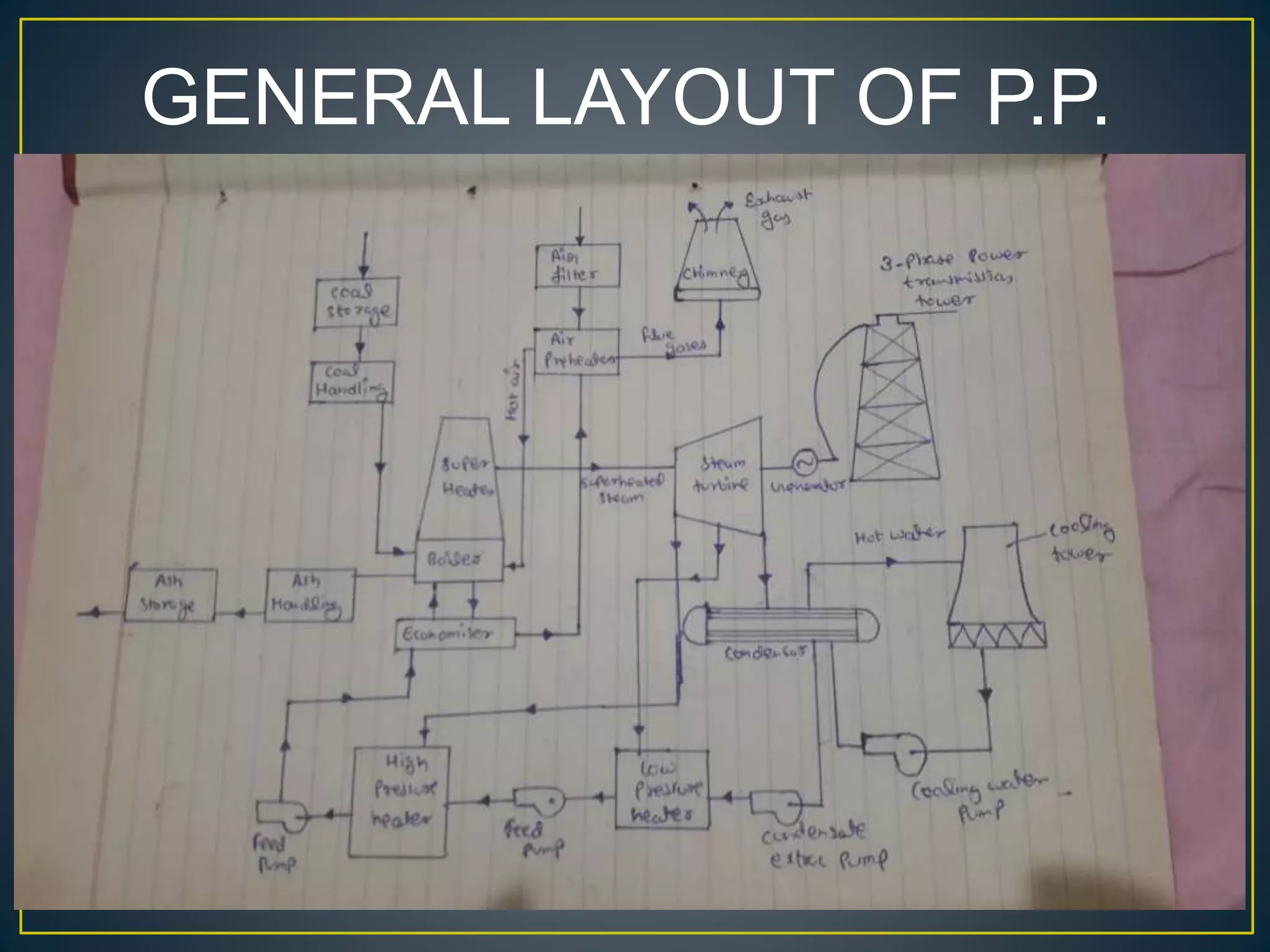
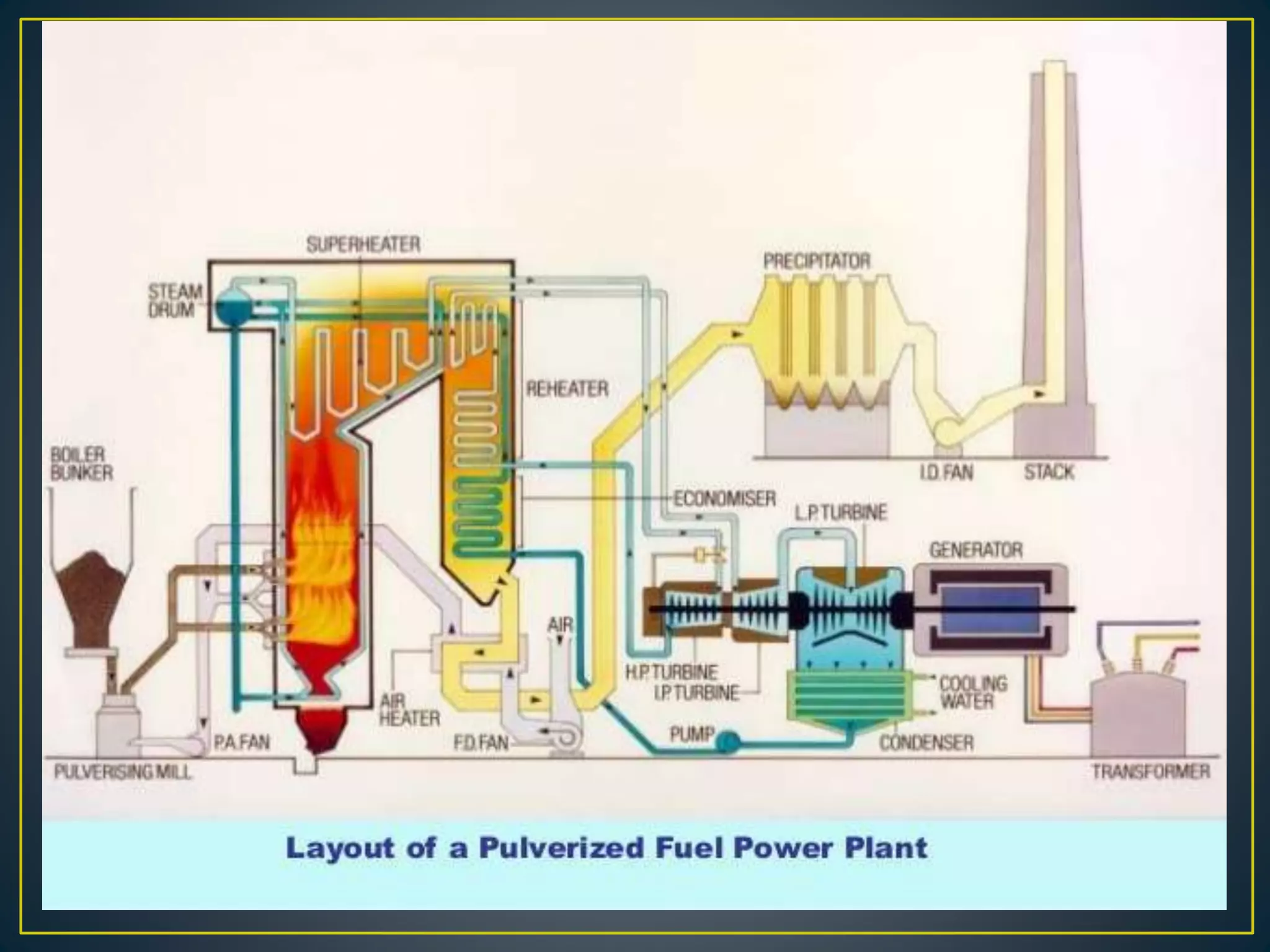
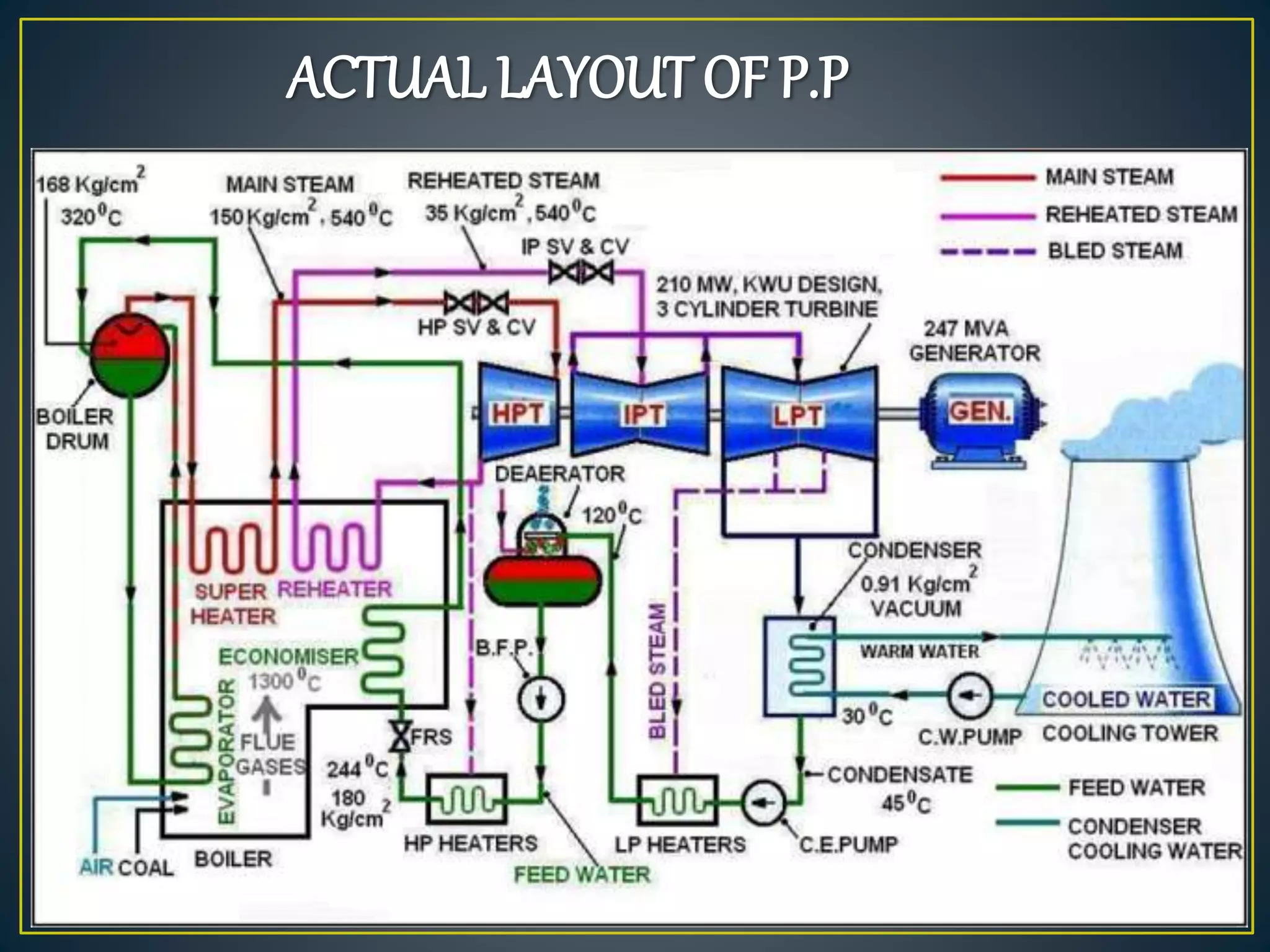
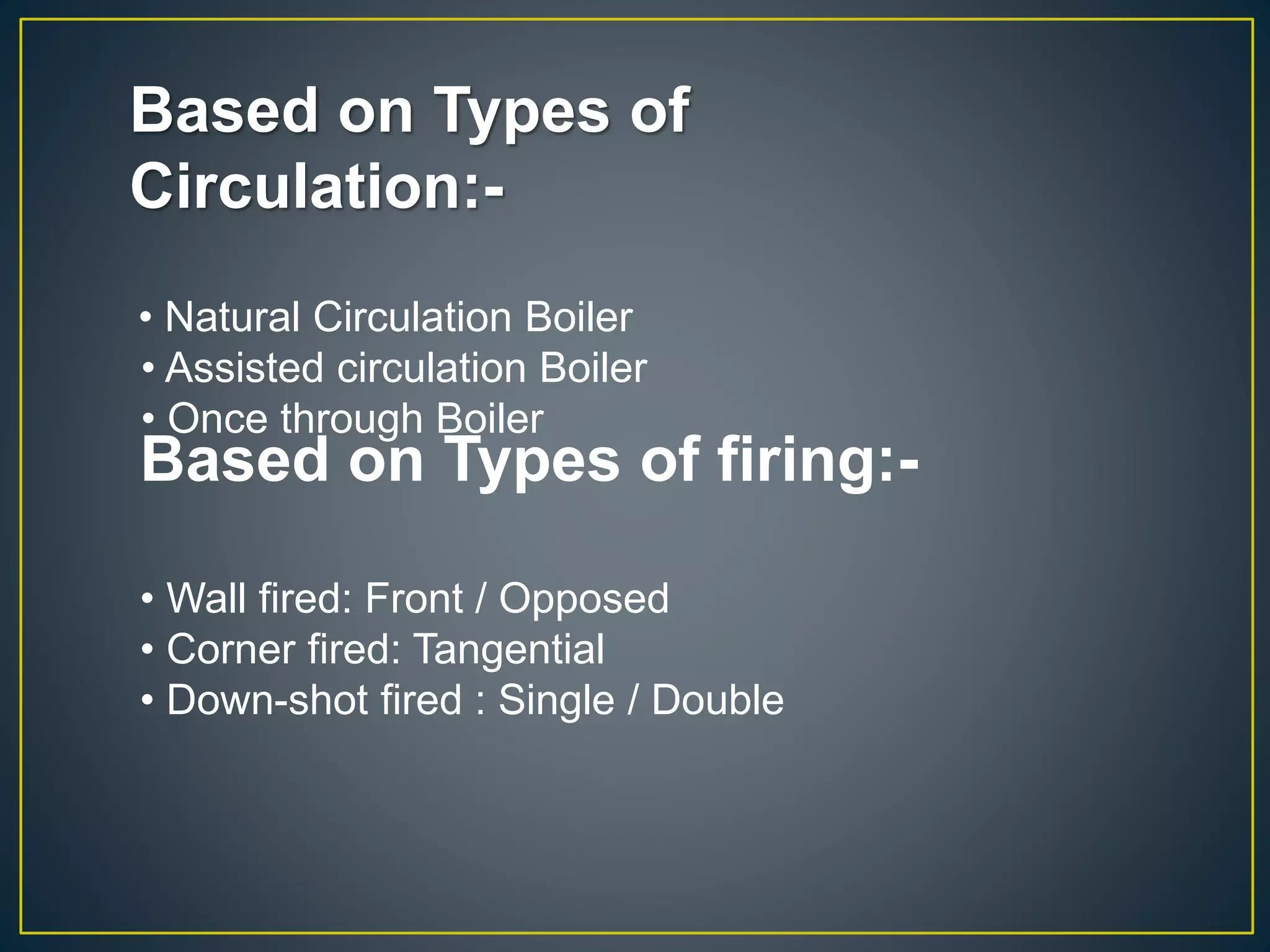
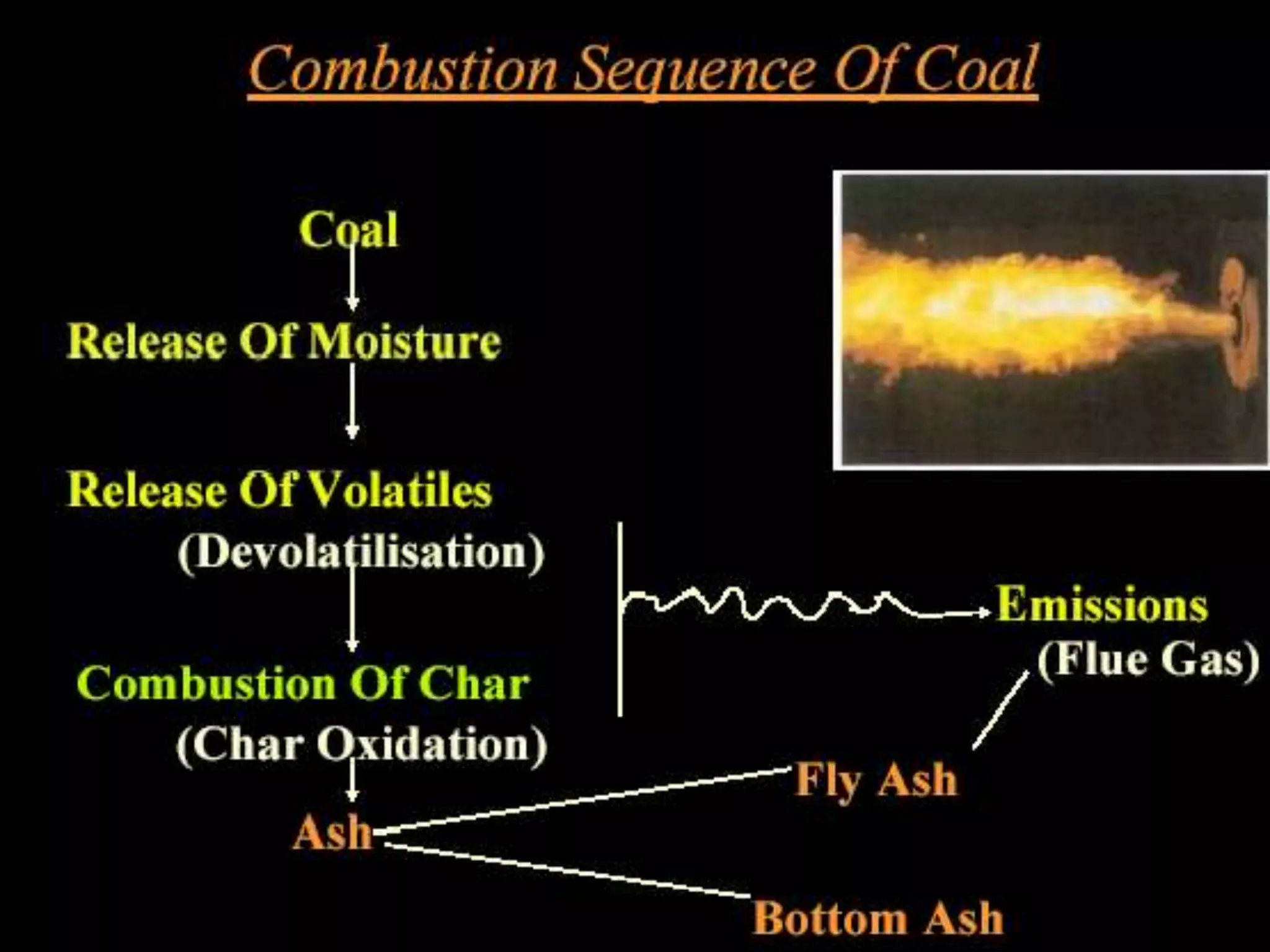
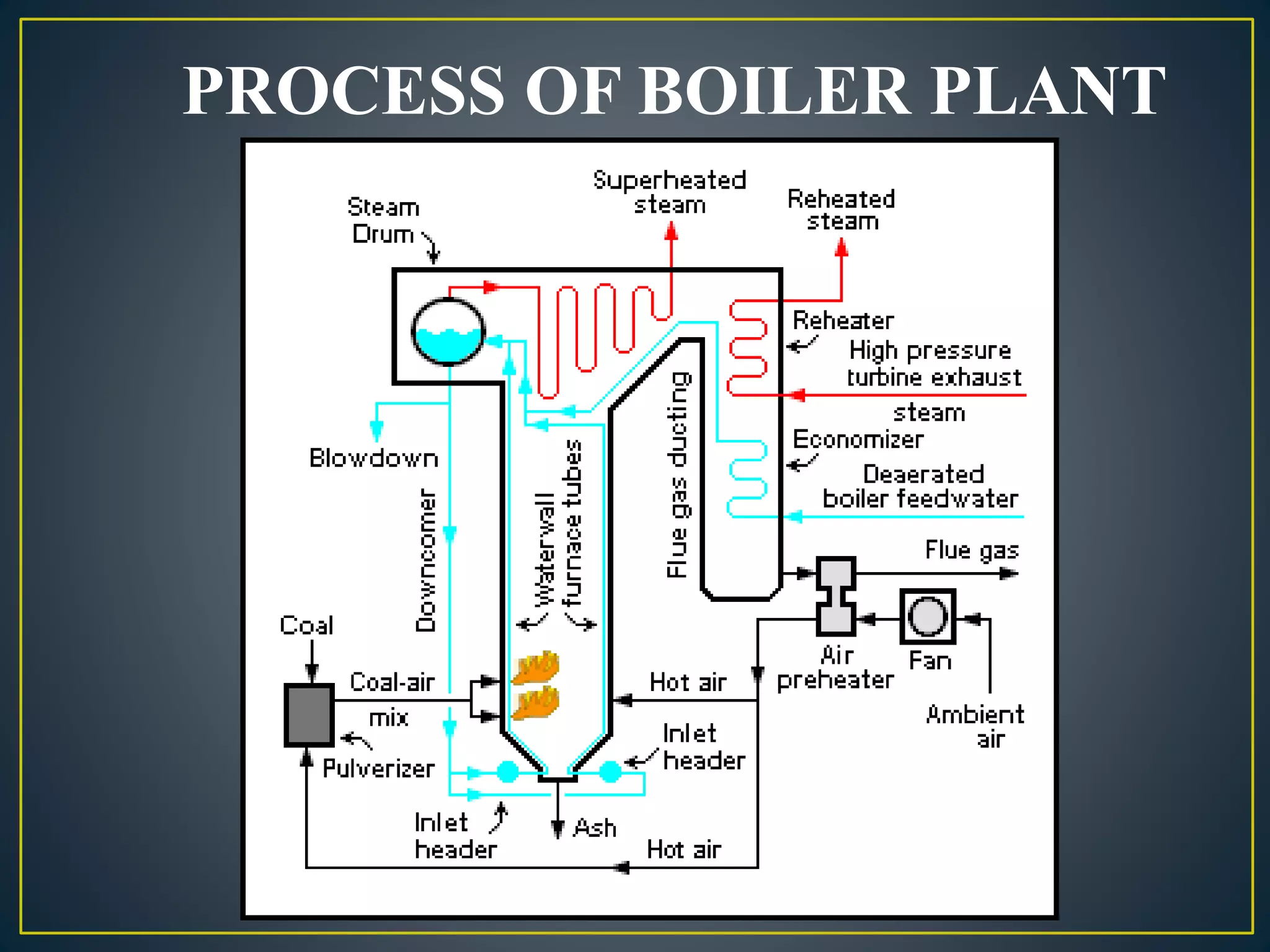
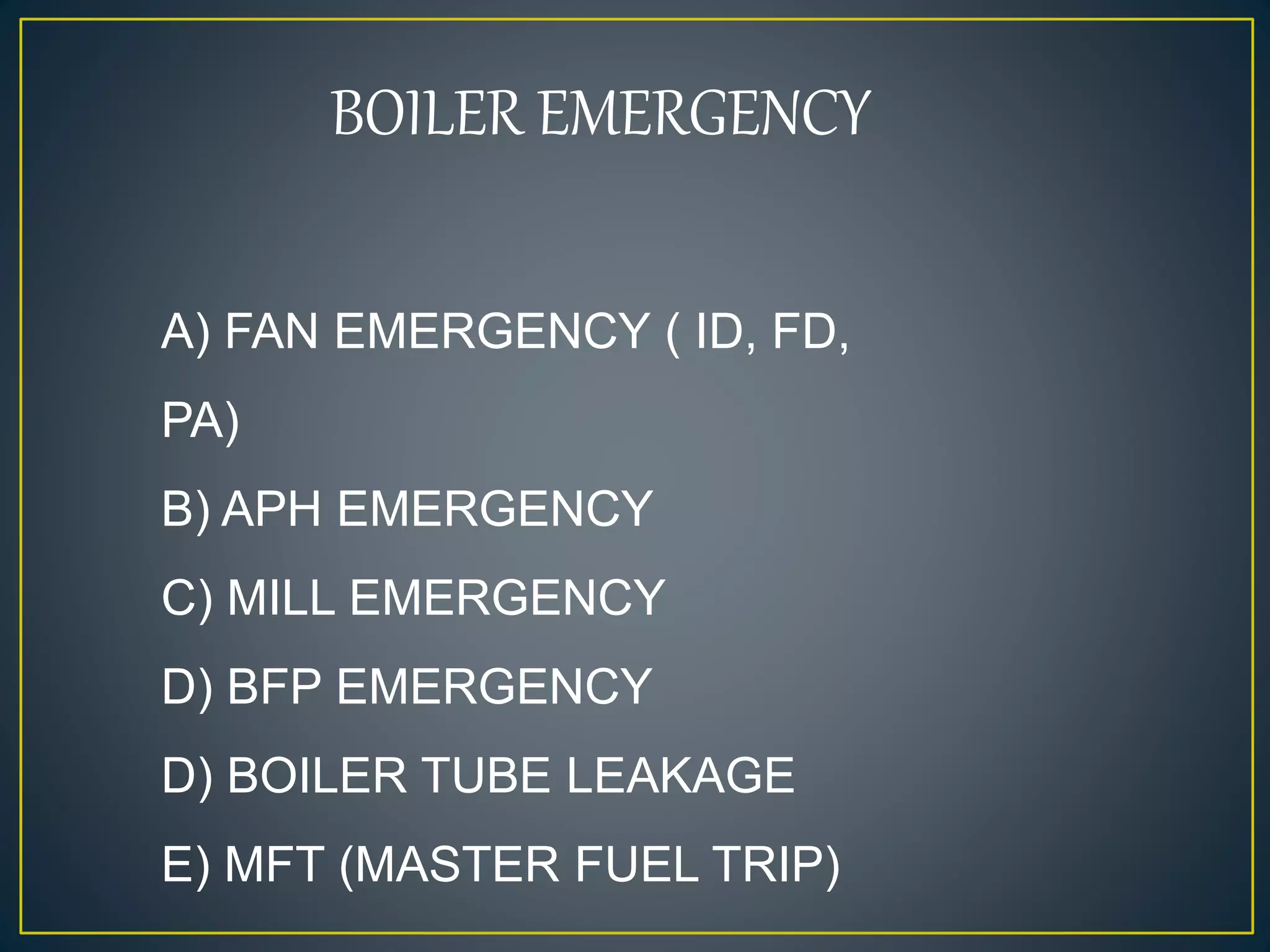
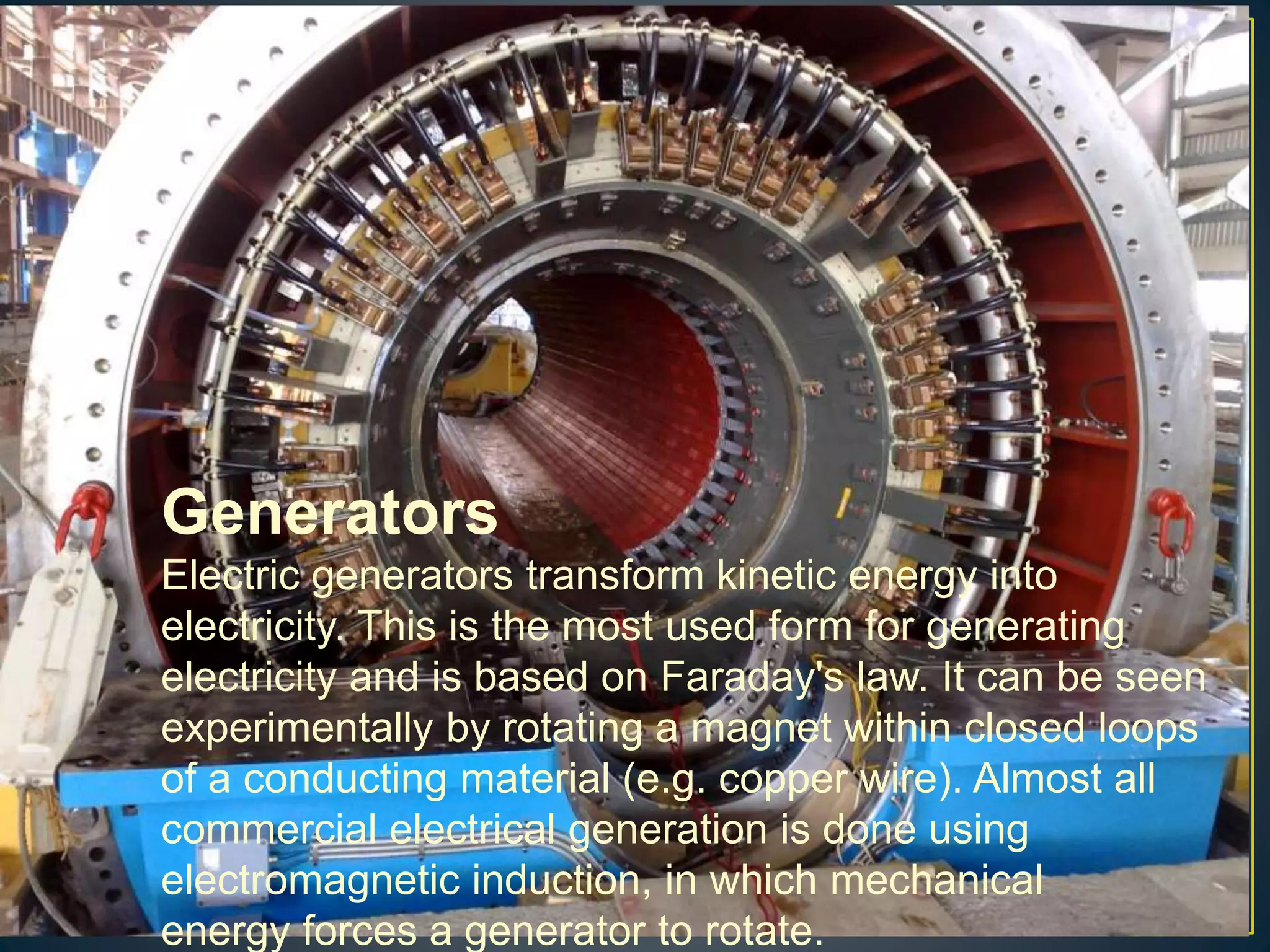
The document provides information about the Sanjay Gandhi Thermal Power Station located in Birsinghpur, India. It has a total installed capacity of 1340 MW distributed across 5 units ranging from 210-500 MW each. The power plant uses coal as its primary fuel sourced from local mines via rail. Water for the plant is sourced from the nearby Johila River and Dam. The plant has conventional systems for coal handling, steam generation in the boiler, power generation in the turbine, and effluent management. It provides key specifications and details of the various units and systems to run the thermal power generation process.