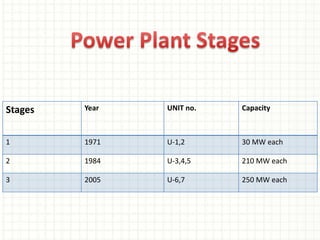
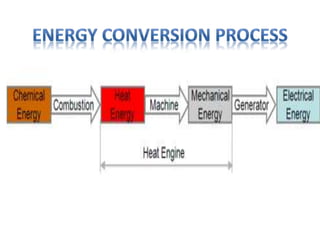
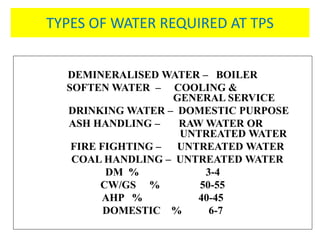
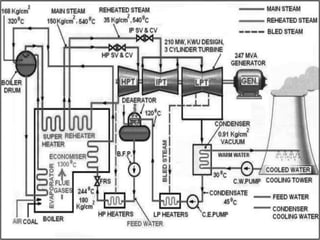
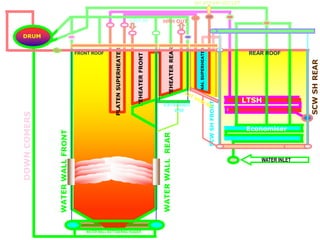
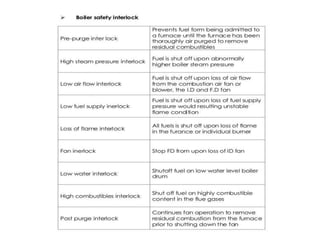
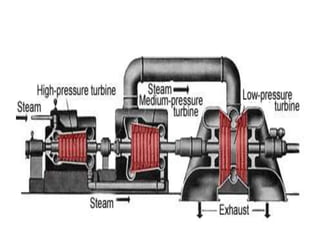
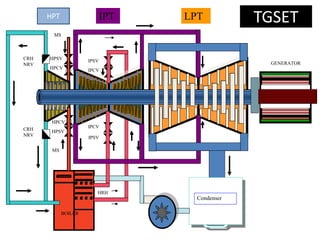
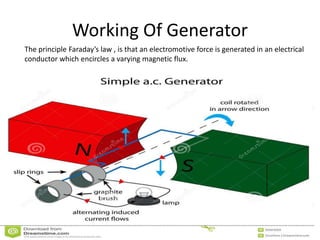
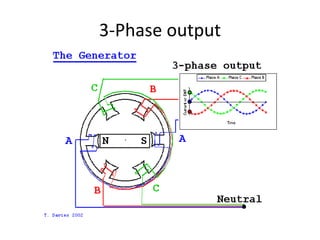
This document provides information about the Parali Thermal Power Station located in Beed district, Maharashtra, India. It has a total installed capacity of 1130 MW across 6 units built between 1971-2005. Key components of the power plant include the coal handling plant, water handling plant, boiler system, turbine, generator, and transformer. Coal is used as the primary fuel source due to its relatively low cost compared to other fuels. The document describes the basic processes of energy conversion from coal to electricity at the thermal power station.