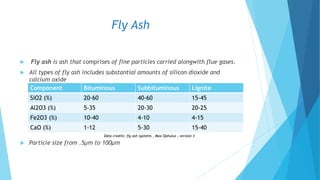
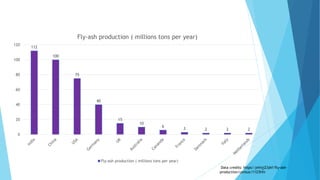
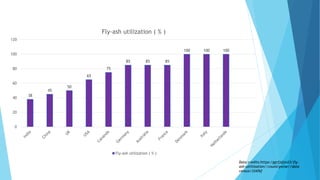
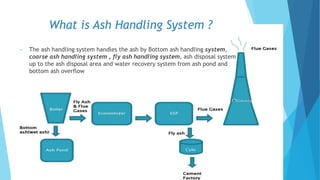
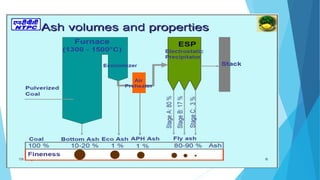
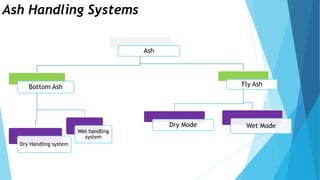
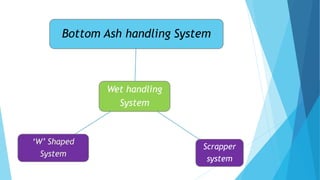
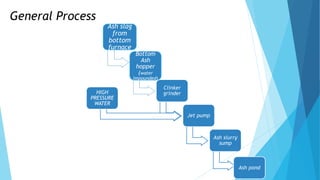
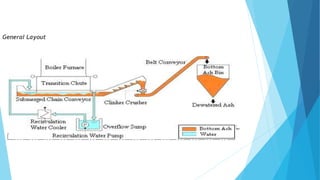
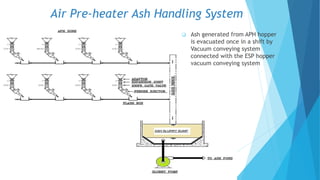
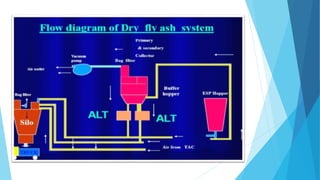
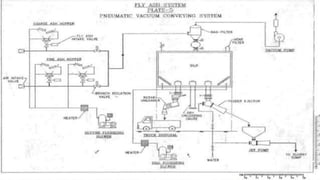
The document summarizes ash handling systems used in thermal power plants. It describes the two main types of ash - bottom ash and fly ash. Bottom ash is heavier and collected at the bottom of furnaces while fly ash is lighter and carried by flue gases. Wet and dry handling systems are used to transport and store bottom ash and fly ash. Ash is an important byproduct that can be utilized in cement, bricks and construction if handled properly through integrated ash handling systems.