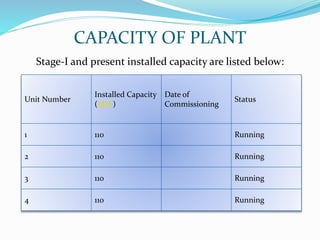
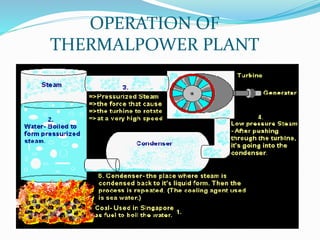
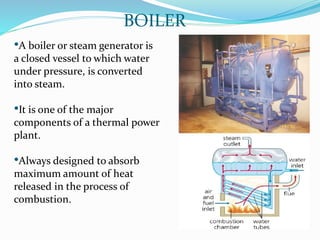
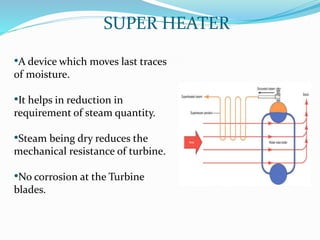
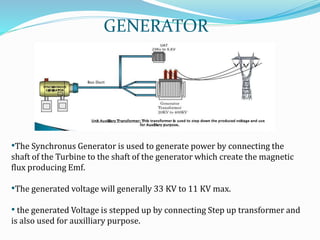
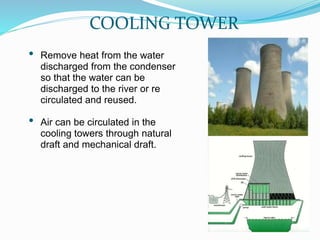
The document provides details about a presentation on summer training at NTPC Tanda power plant. It discusses that NTPC is the largest power company in India. It then summarizes information about NTPC Tanda power plant including its capacity, sources, main departments like coal handling plant, boiler, turbine, and generator. It also mentions advantages like low cost of fuel and disadvantages like atmospheric pollution of thermal power plants.