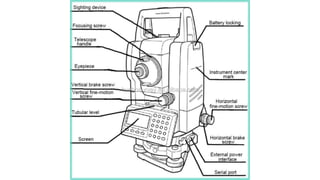
The total station is an electronic surveying instrument that can measure both horizontal and vertical angles as well as distances to targets. It uses a microprocessor to control angle and distance measurements and perform calculations. Measurements are made by sending an electromagnetic beam to a prism reflector and measuring the phase difference between the outgoing and returning signals. The total station is used for topographic surveys, construction layout, and other applications where precise angular and distance measurements are needed.