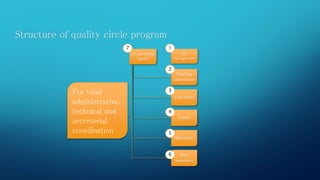
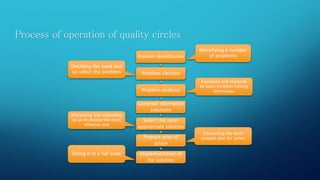
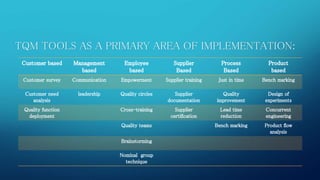
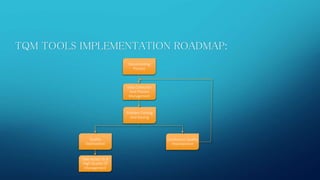
This document provides information on Total Quality Management (TQM) and Quality Circles. It defines TQM as a process focused on customer expectations, preventing problems, building workforce commitment to quality, and promoting open decision making. Quality Circles are defined as small groups of employees who meet regularly to identify and solve work-related problems. The document outlines the differences between TQM and Quality Circles, objectives of Quality Circles, tools and processes used in each approach, and advantages of implementing TQM.