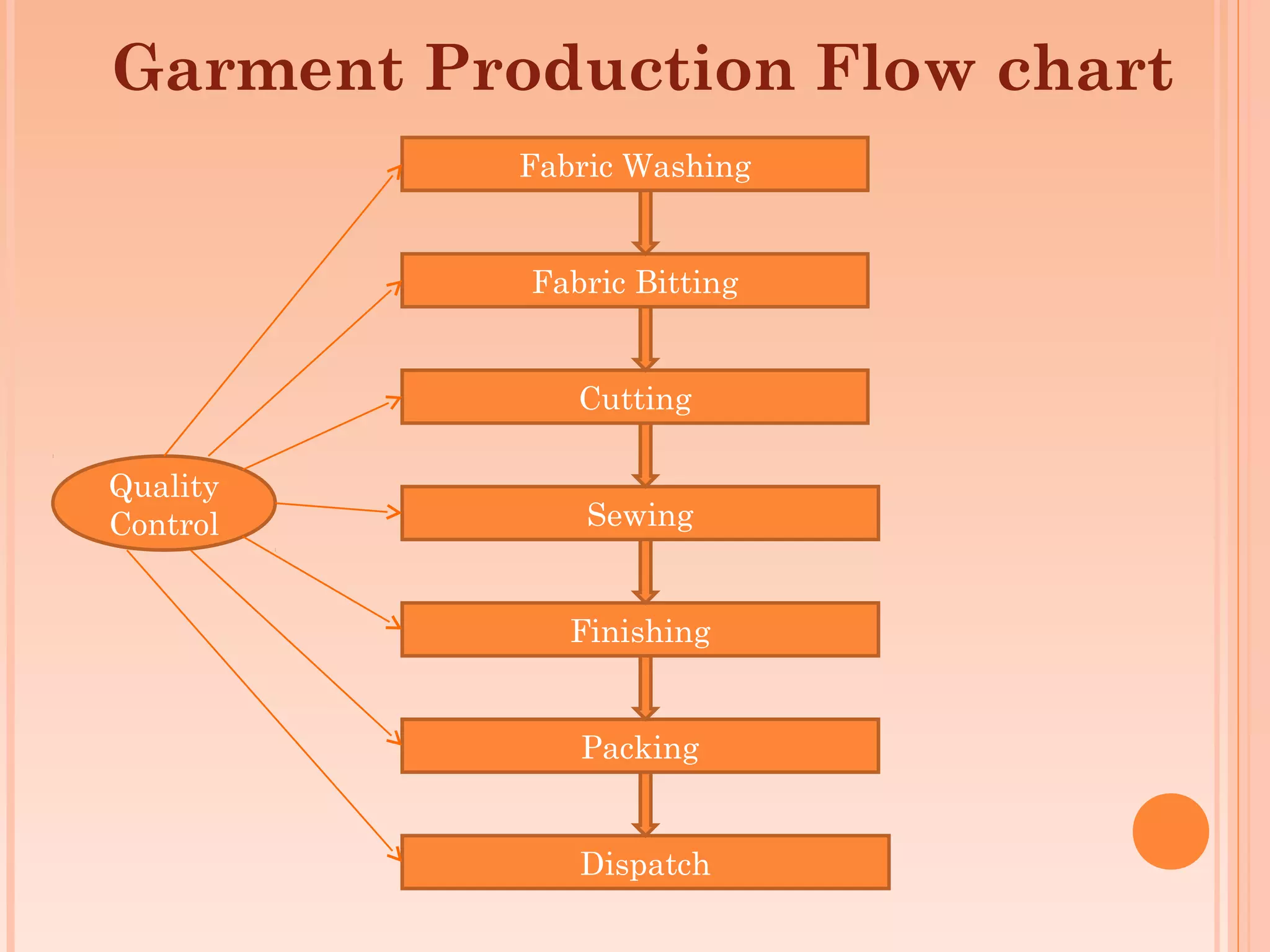
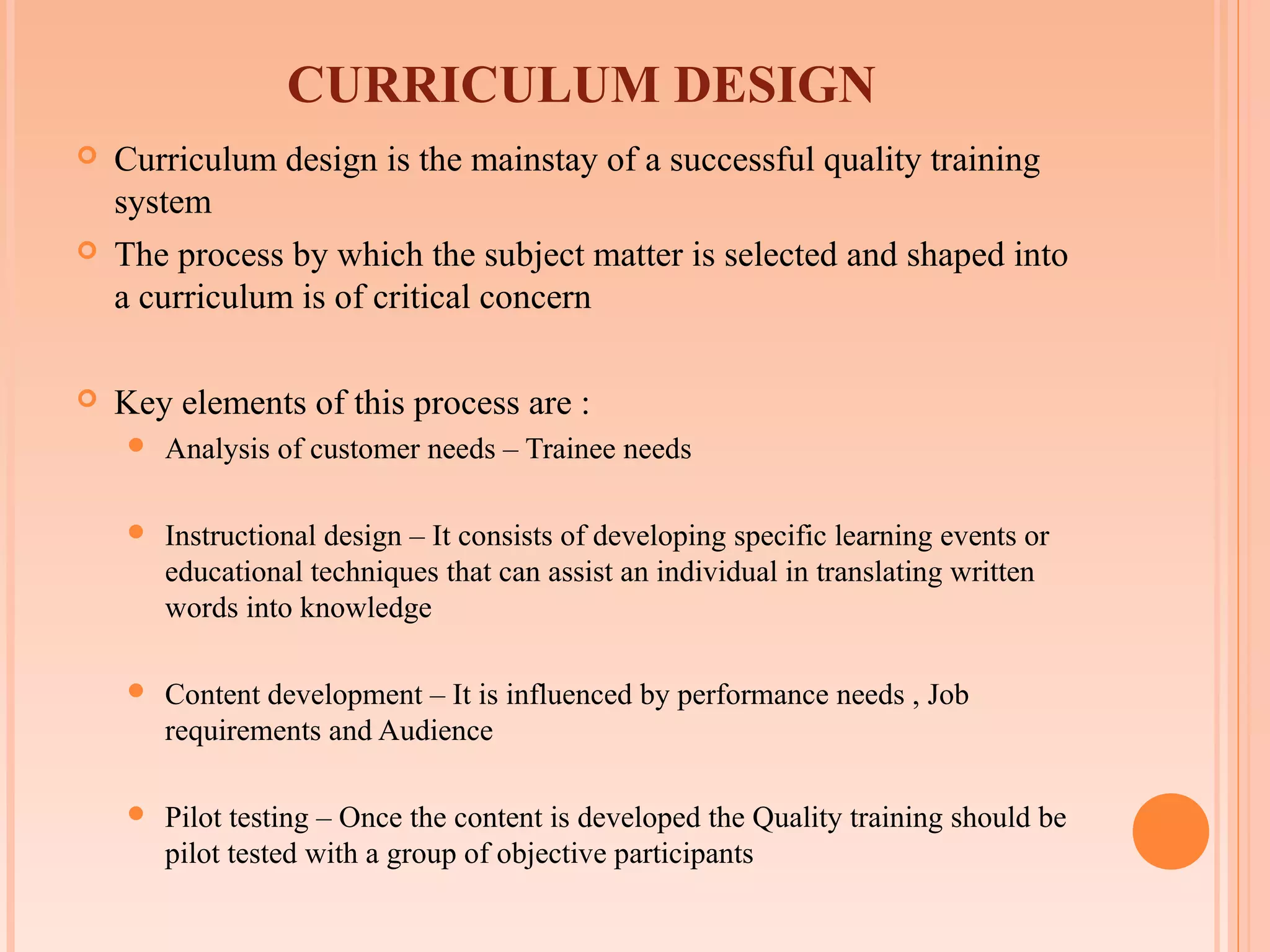
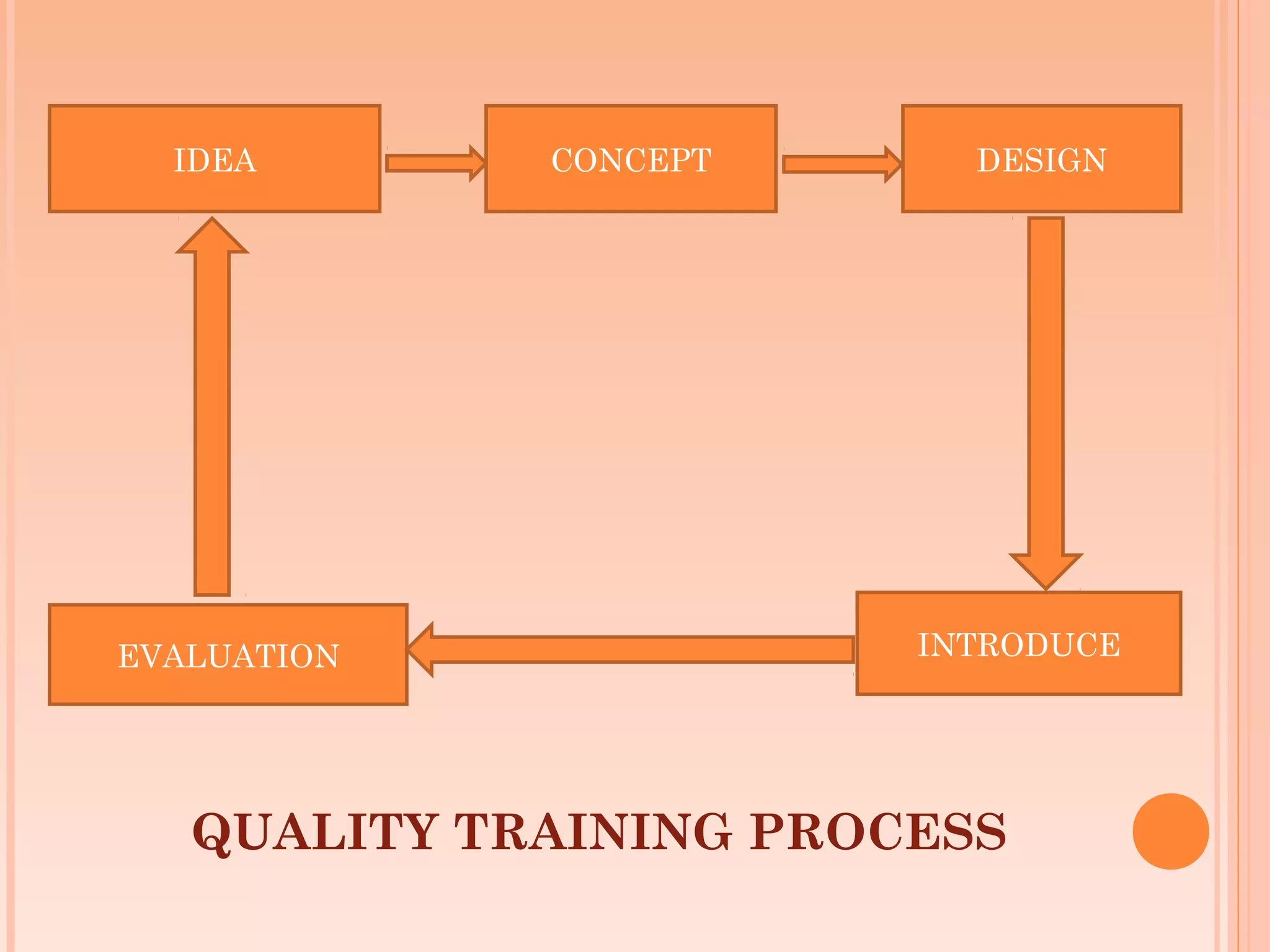
This document discusses training for quality. It begins by introducing quality and different types of training methods. It then outlines the garment production flow chart and discusses managing quality training through delineating responsibilities, focusing on customers, and developing a training plan. It details curriculum design, implementation, delivery methods, measurement, evaluation, and concludes by discussing why training fails and the advantages of quality training. The overall document provides an overview of developing and implementing an effective quality training program.