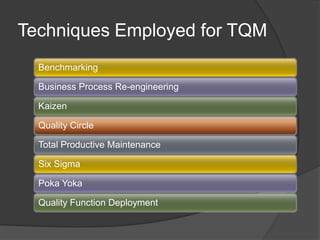
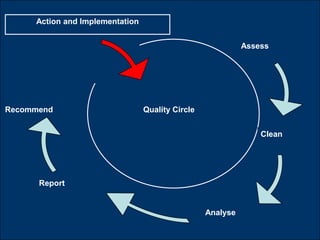
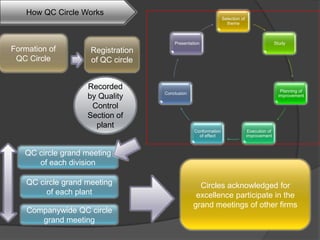
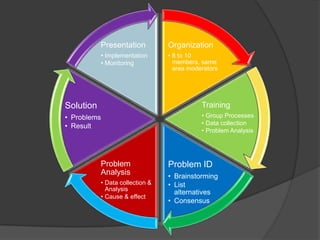
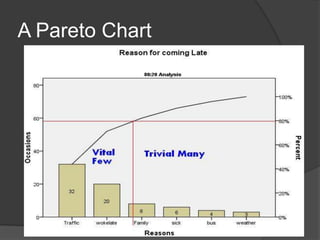
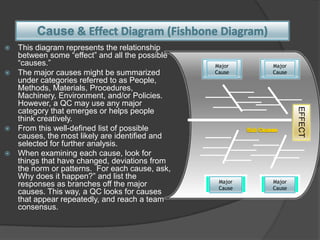
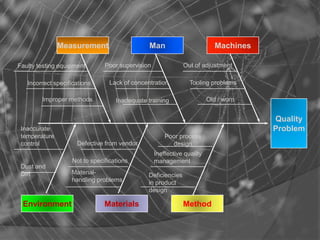
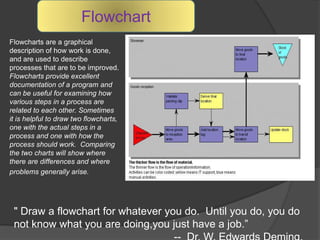
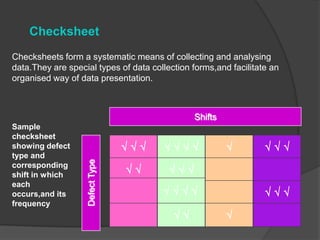
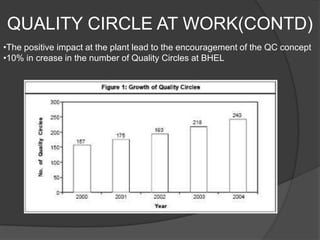
Quality Circles are small groups of employees who voluntarily meet regularly to identify, analyze, and provide solutions to work-related problems. The goals of Quality Circles include improving quality, productivity, and morale. They utilize techniques like brainstorming, control charts, flowcharts and checksheets to solve problems. Quality Circles require management support, appropriate training, and well-defined roles for leaders, facilitators, coordinators and members. Organizations that have implemented Quality Circles successfully include Xerox, United Airlines, and BHEL in India. Quality Circles provide both tangible benefits like cost savings and quality improvements as well as intangible benefits such as increased motivation, skills development and better communication.