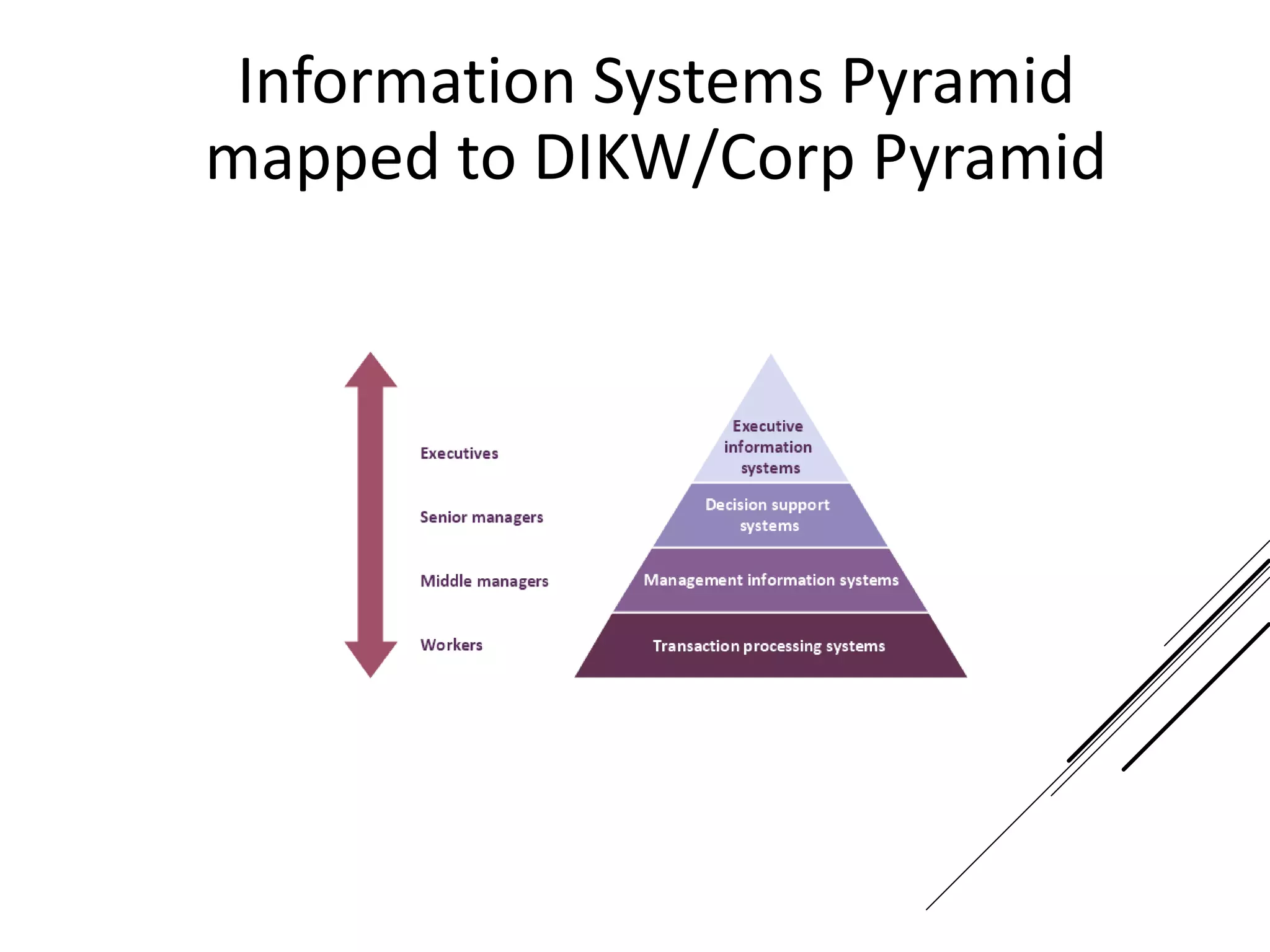
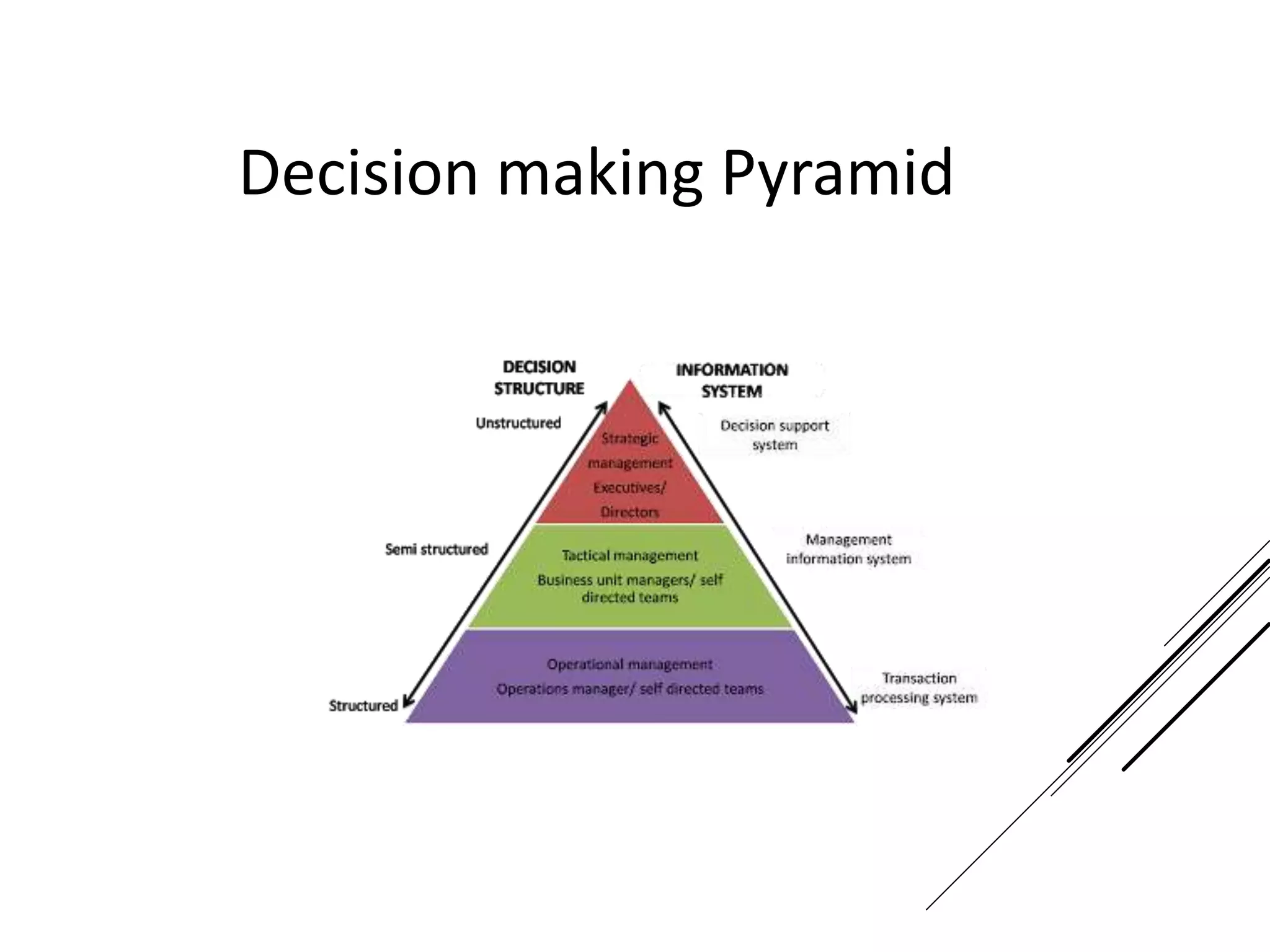
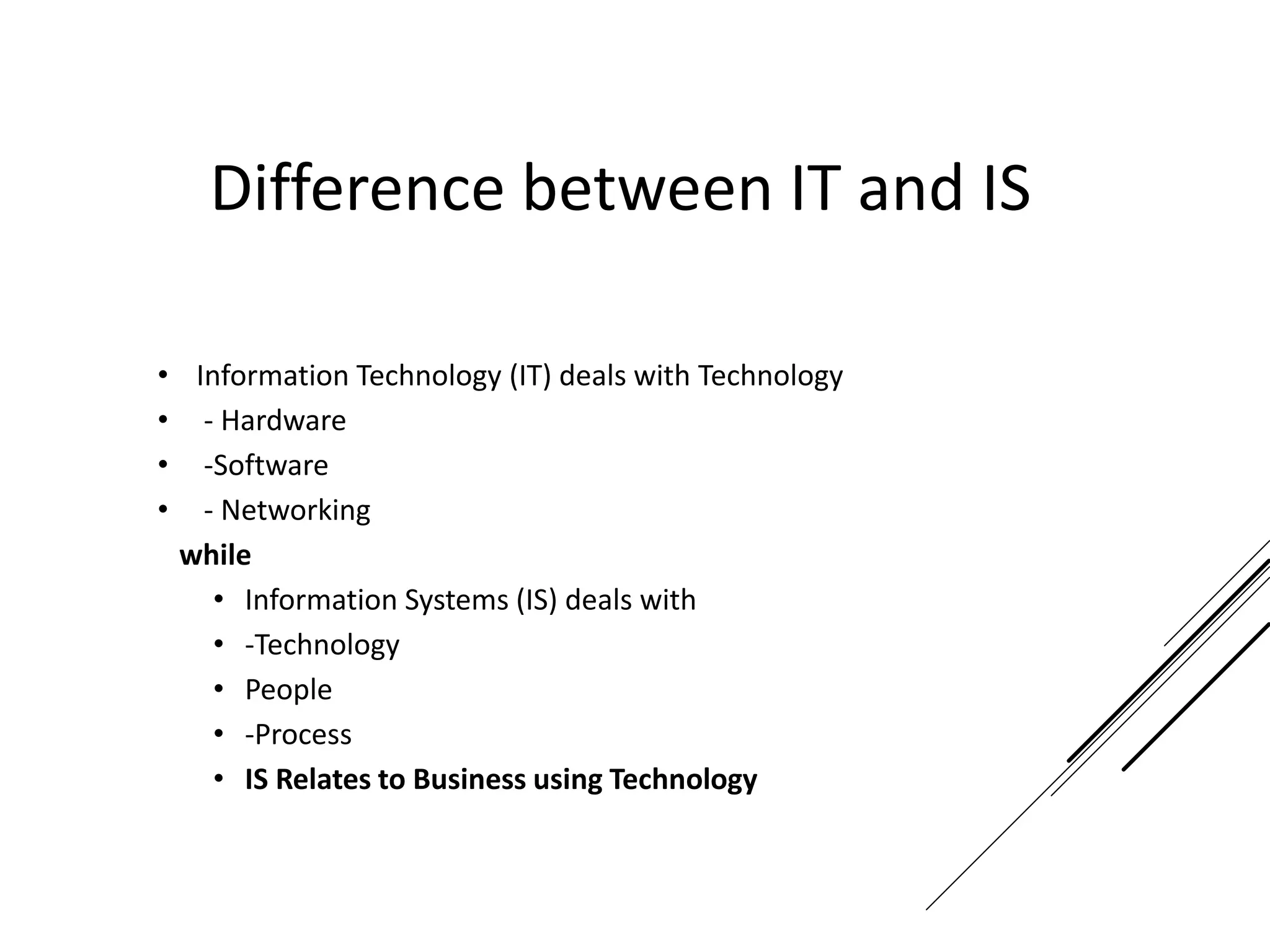
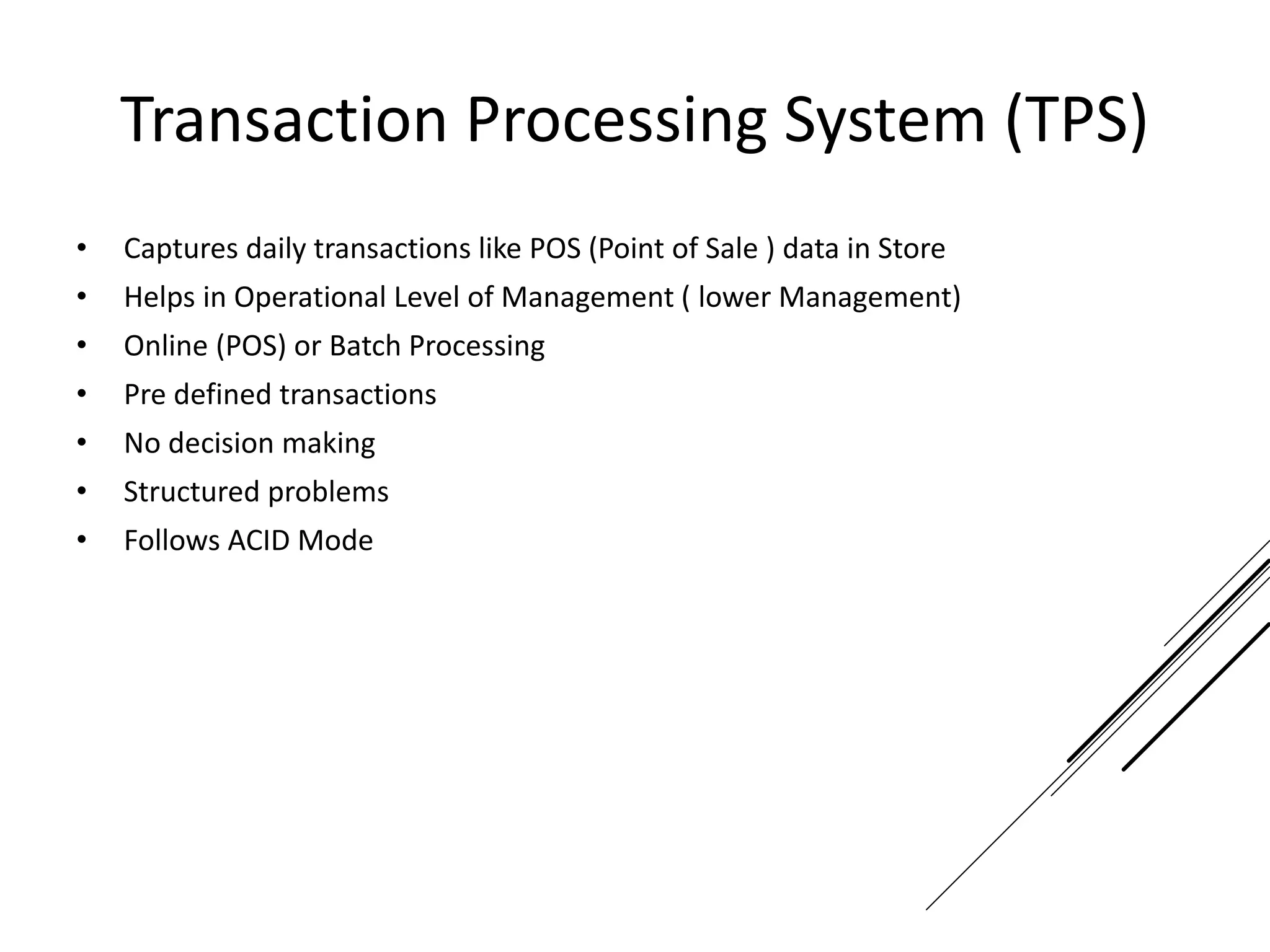
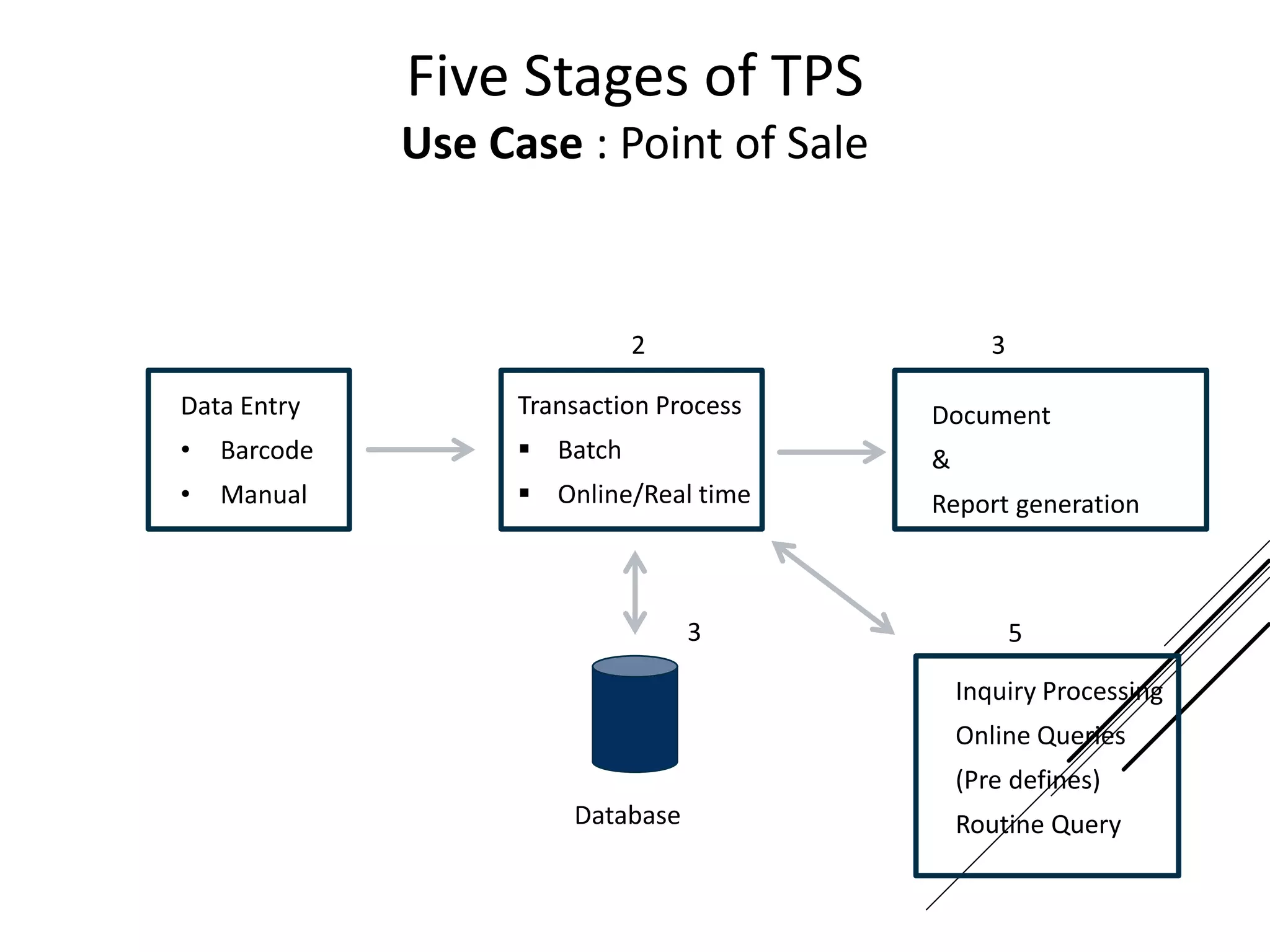
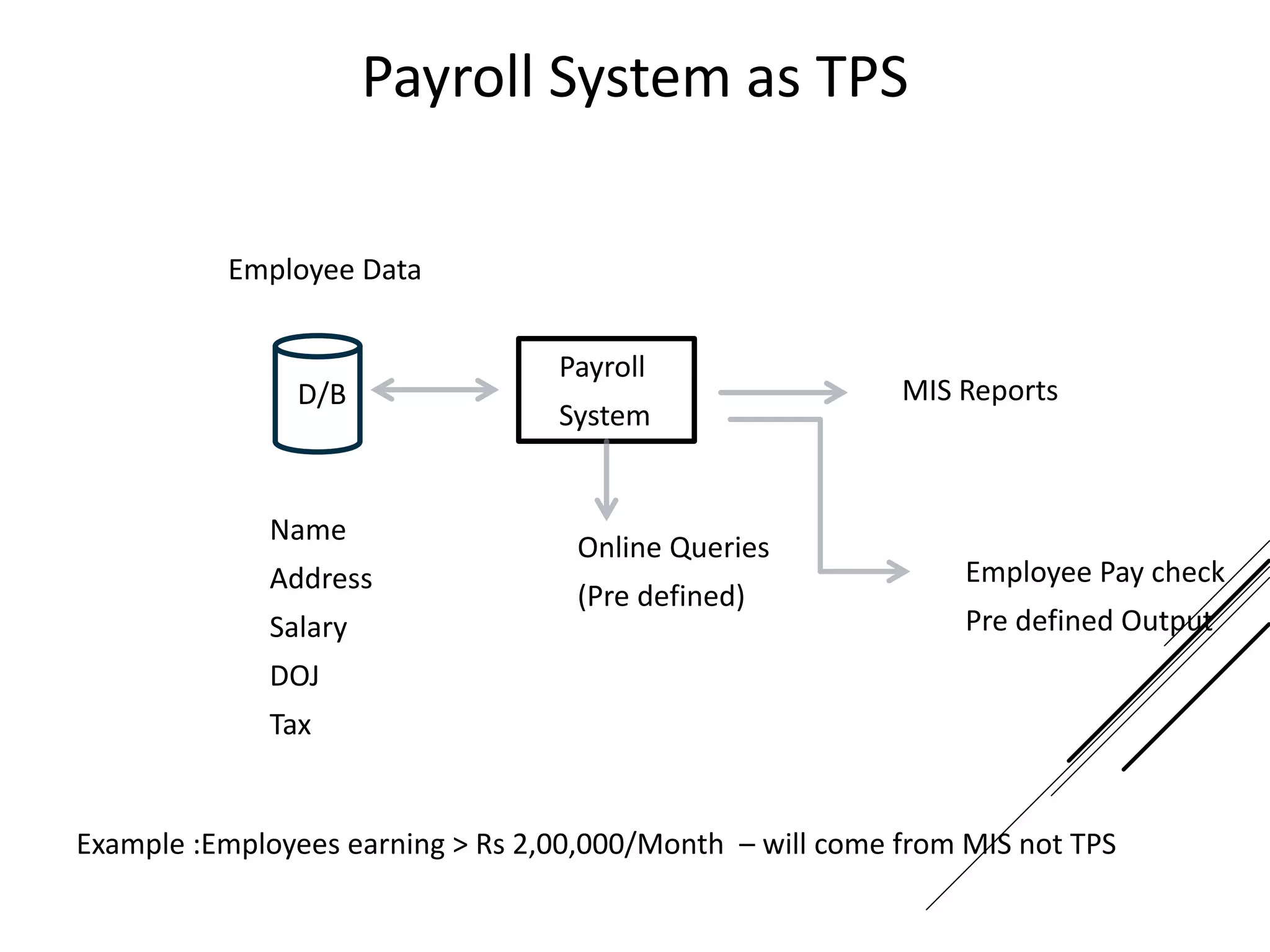
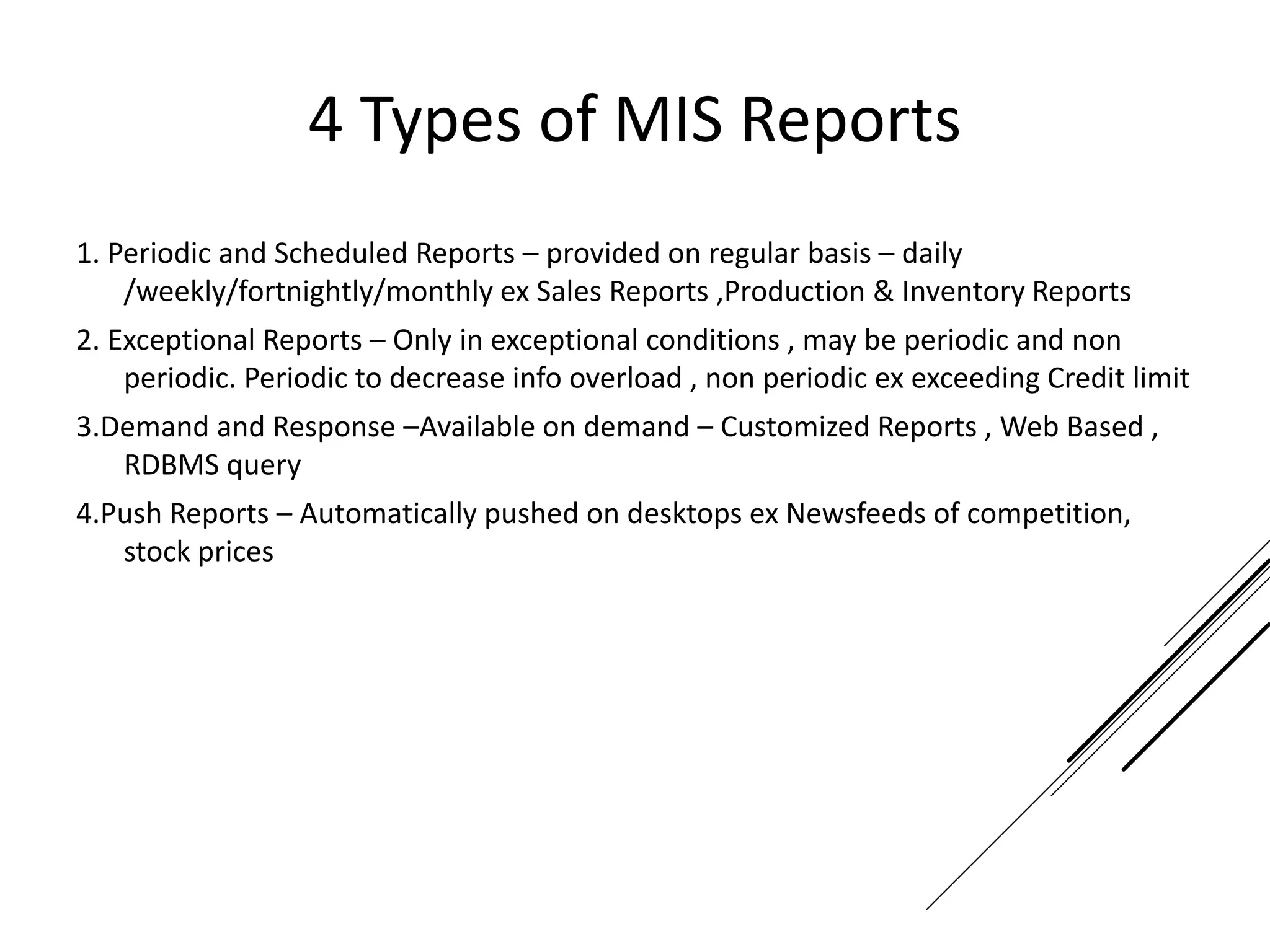
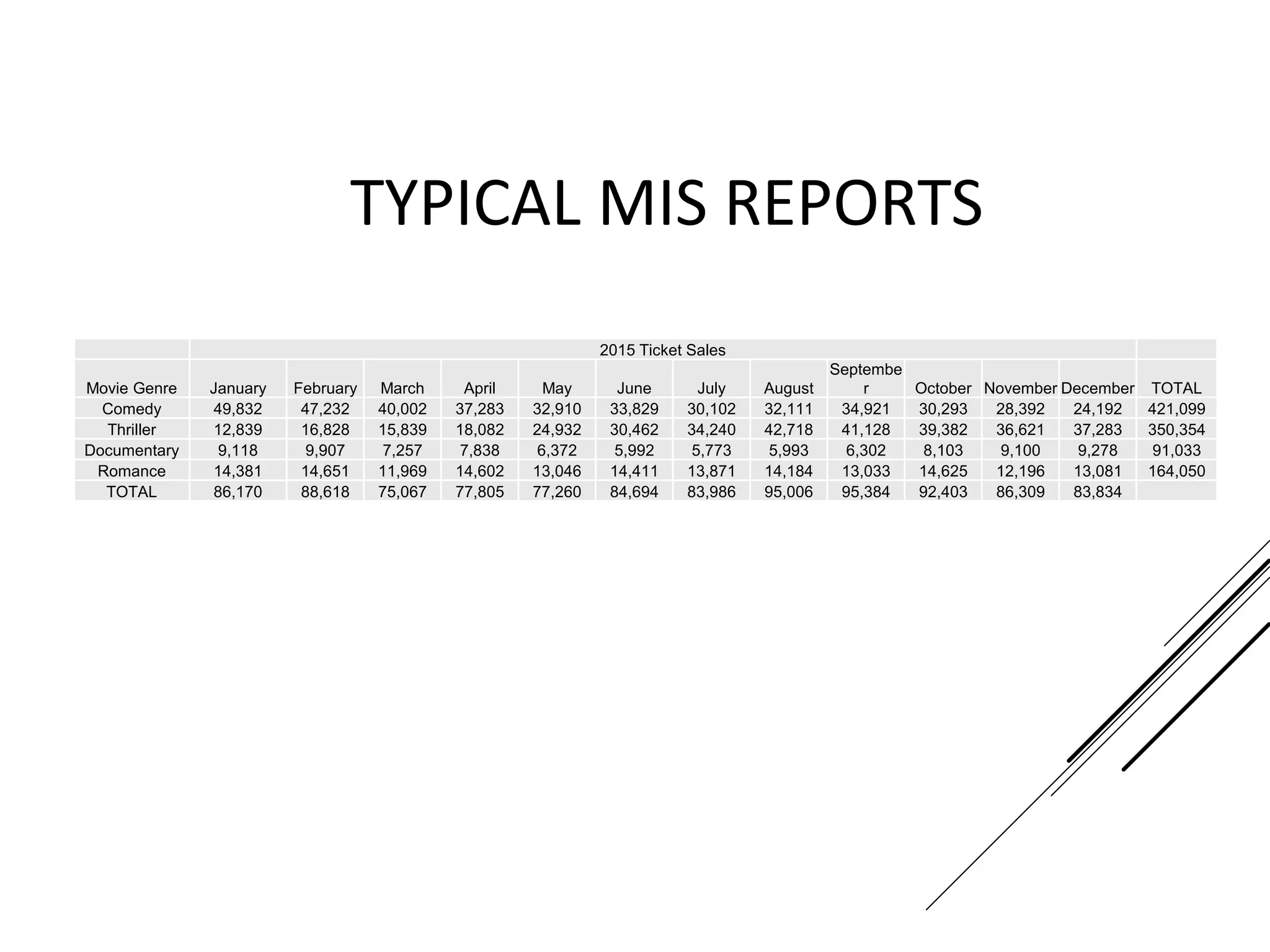
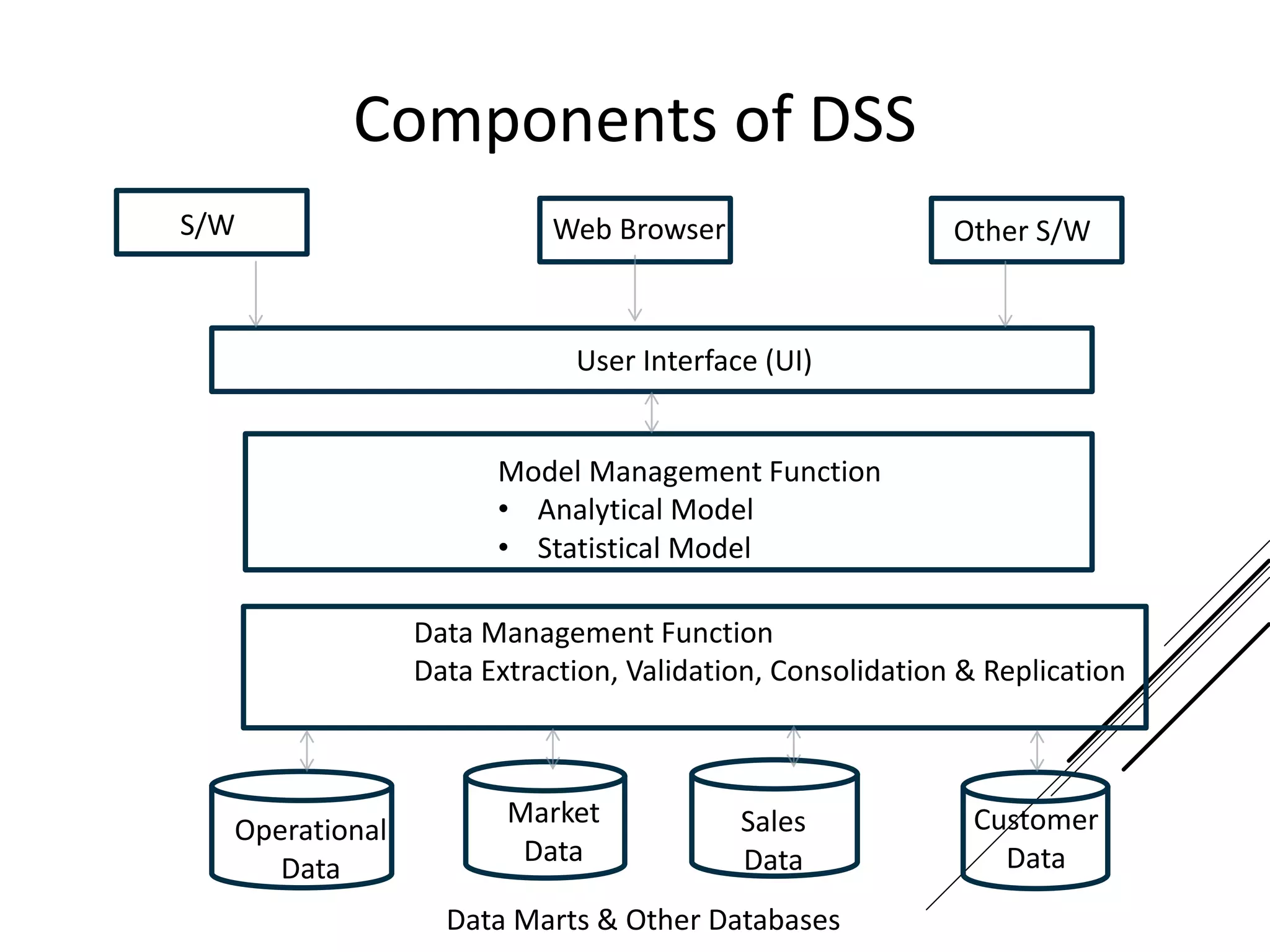
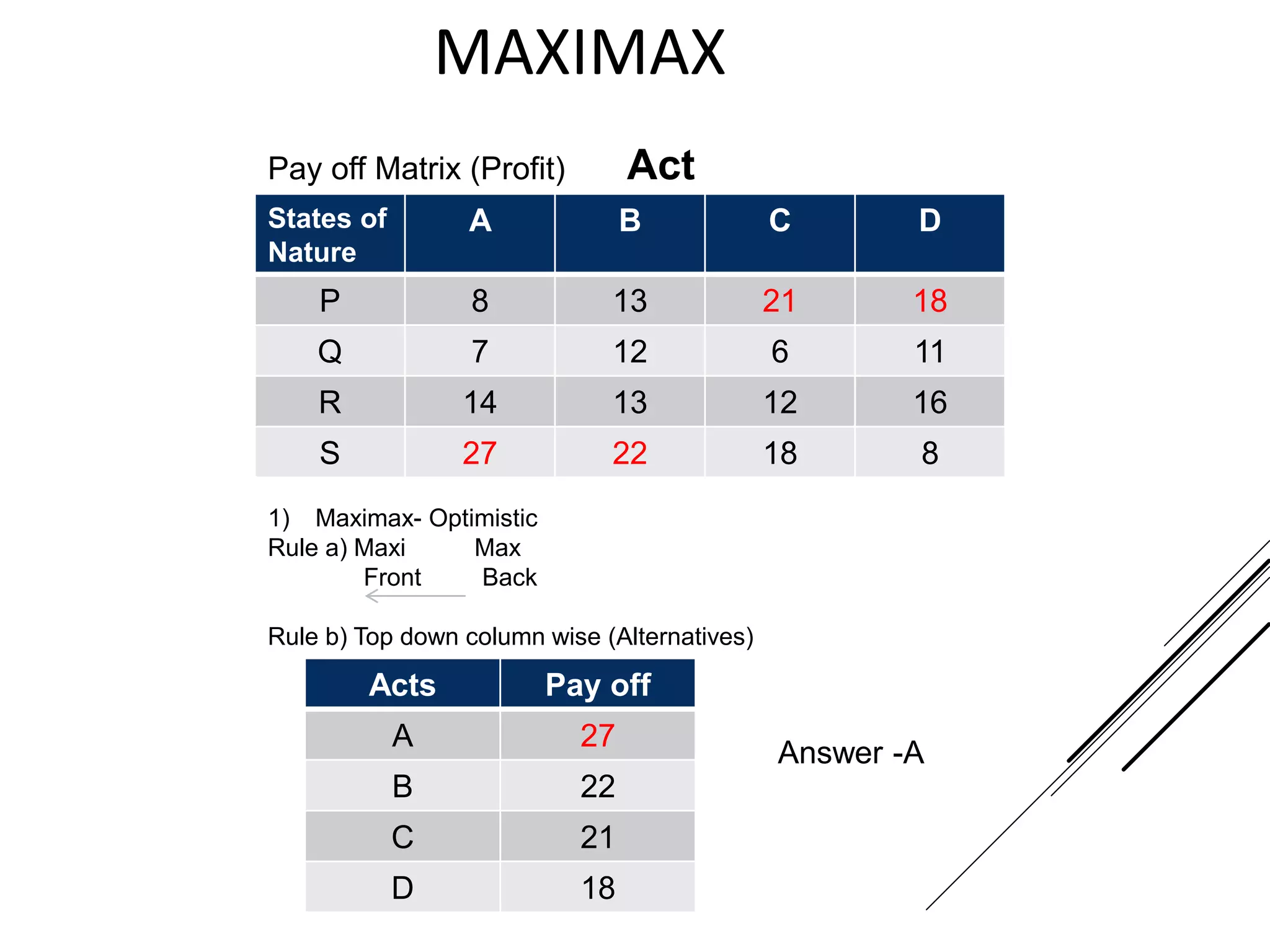
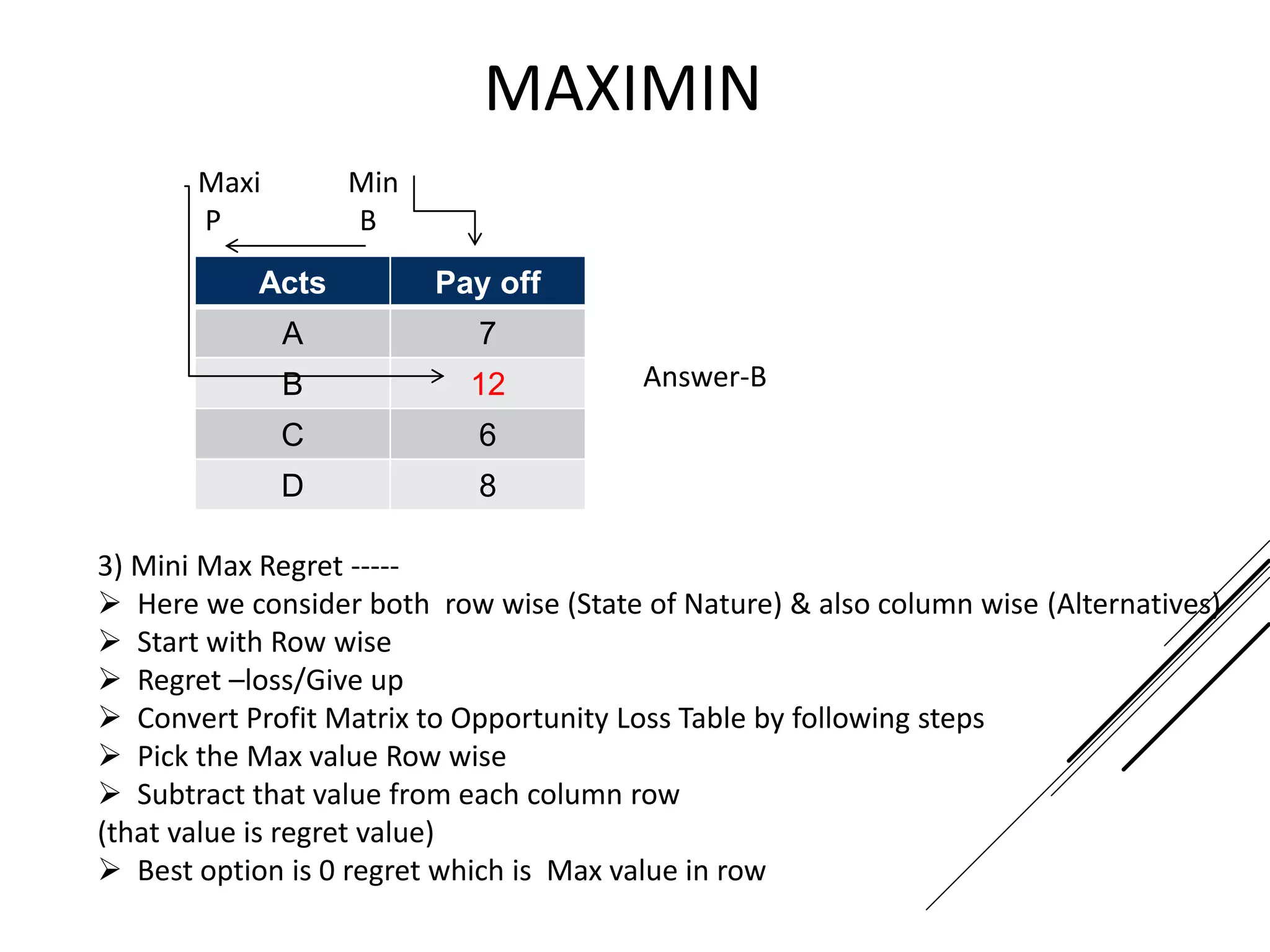
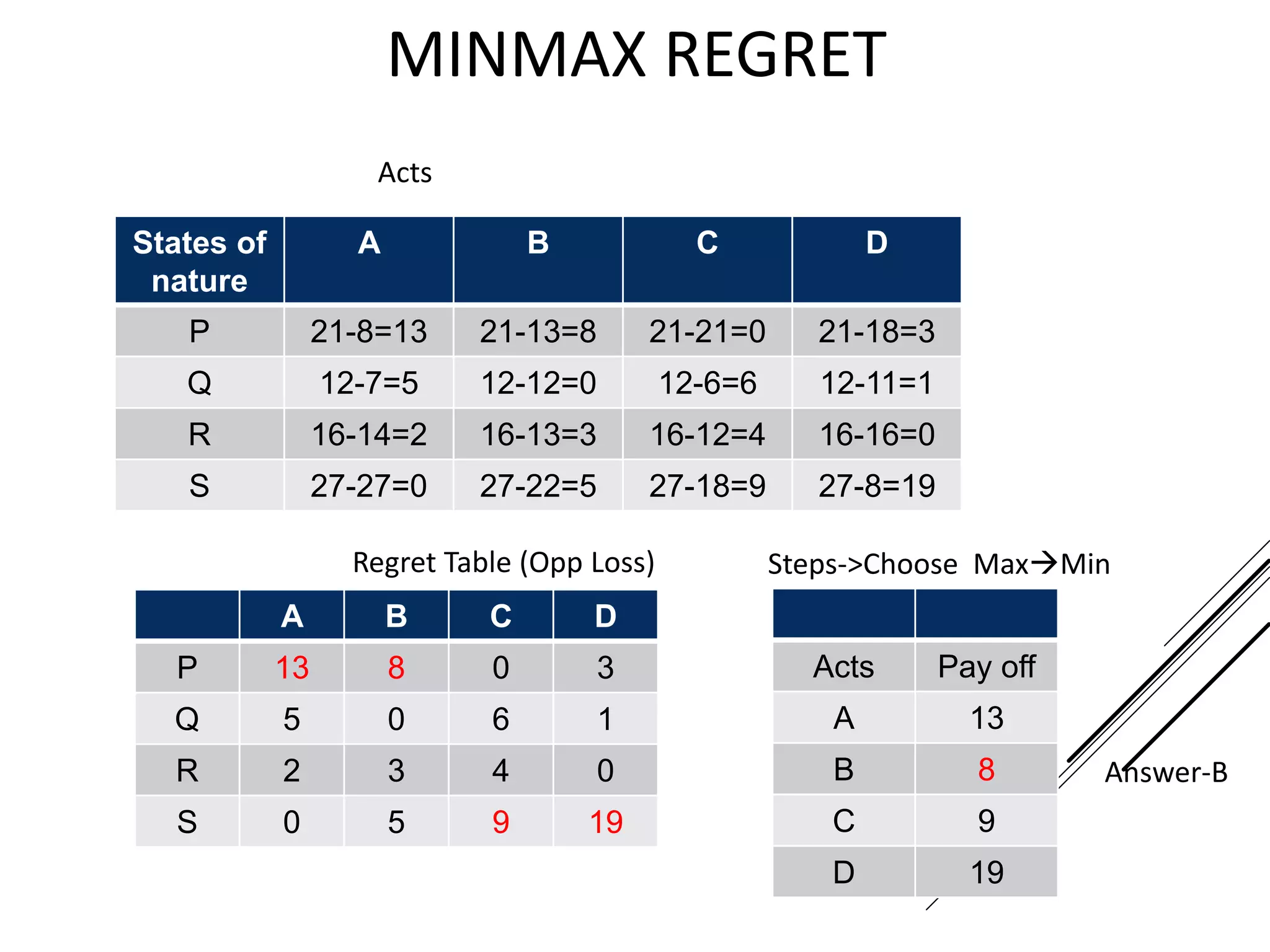
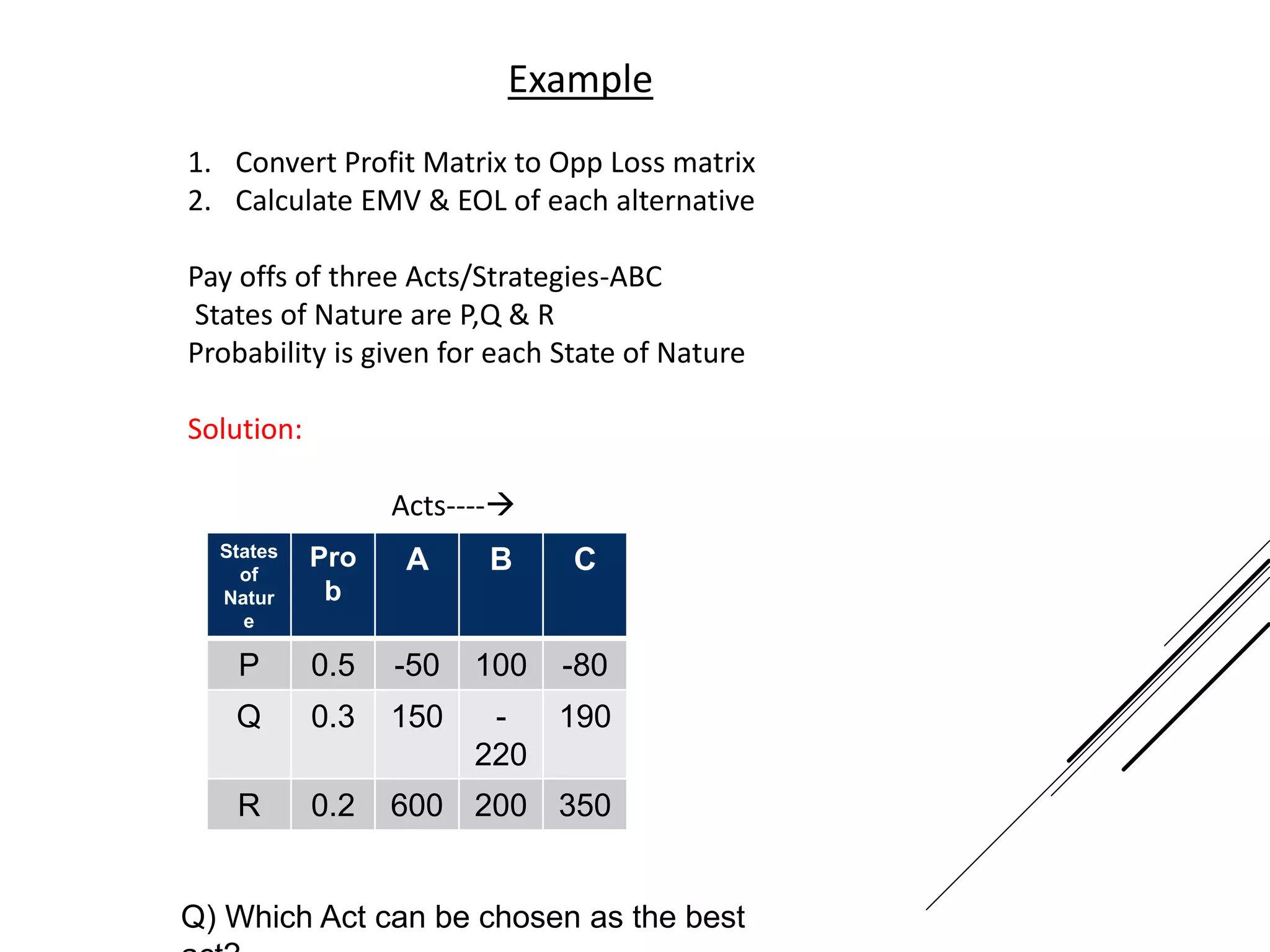
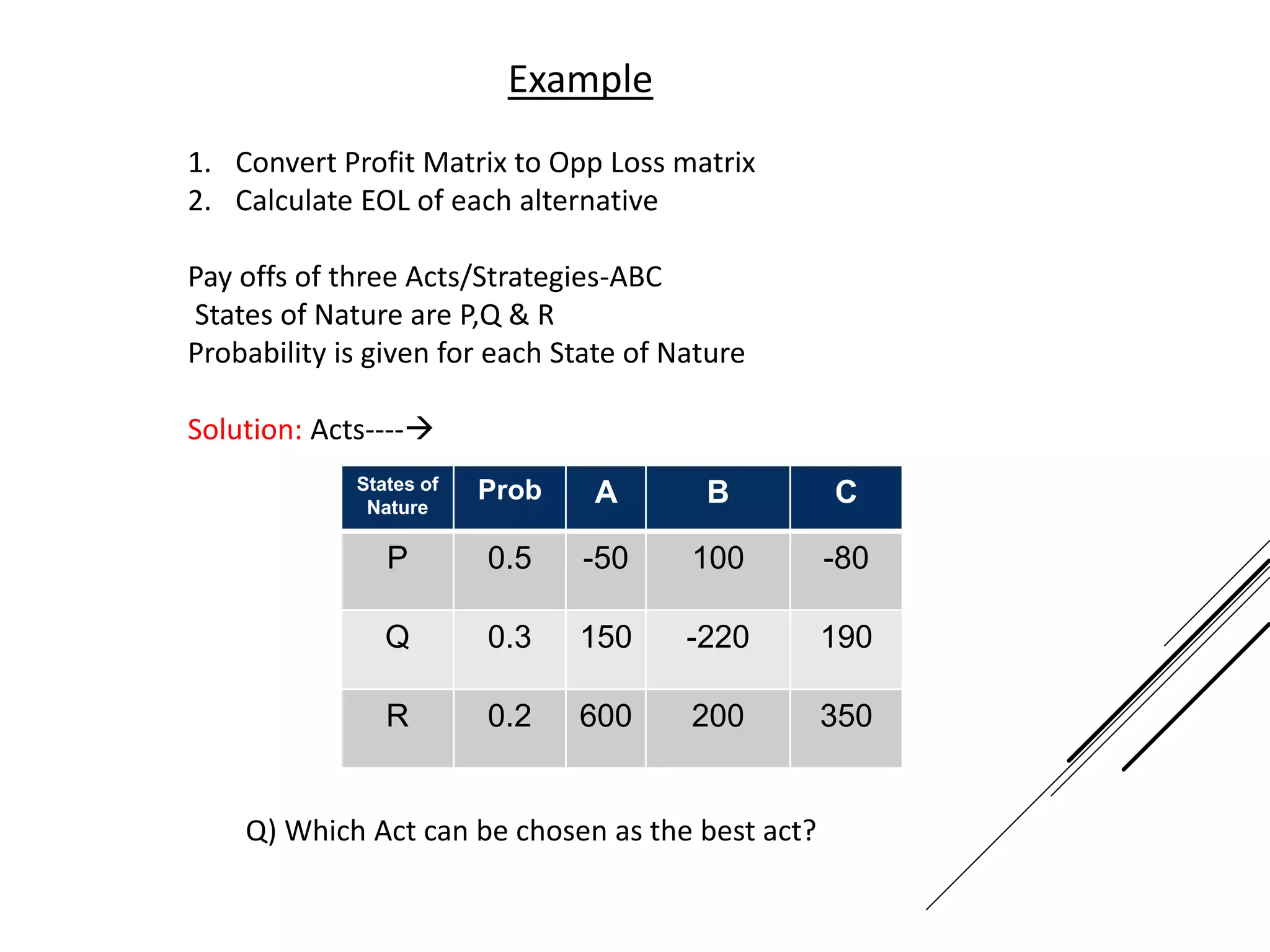
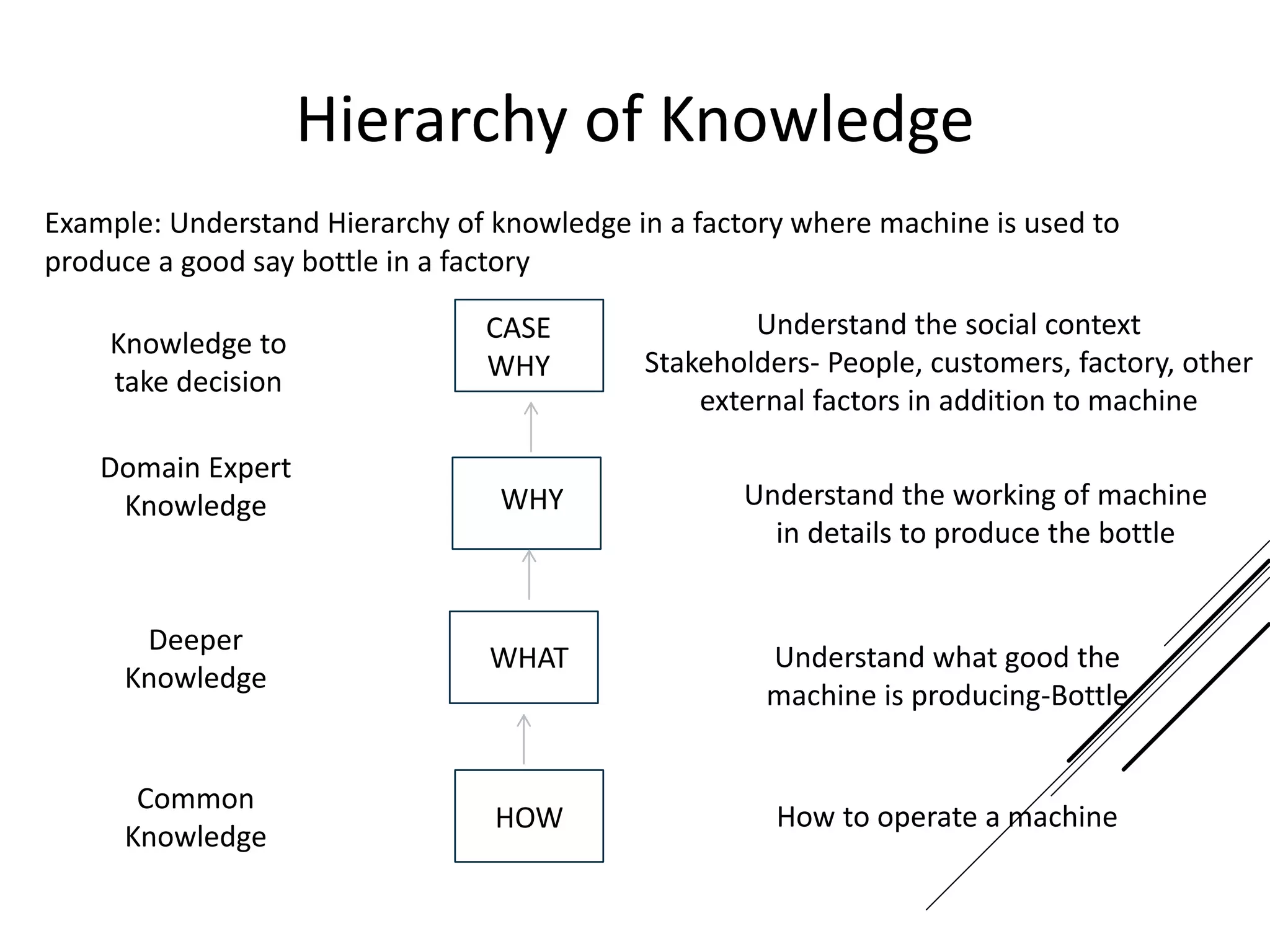
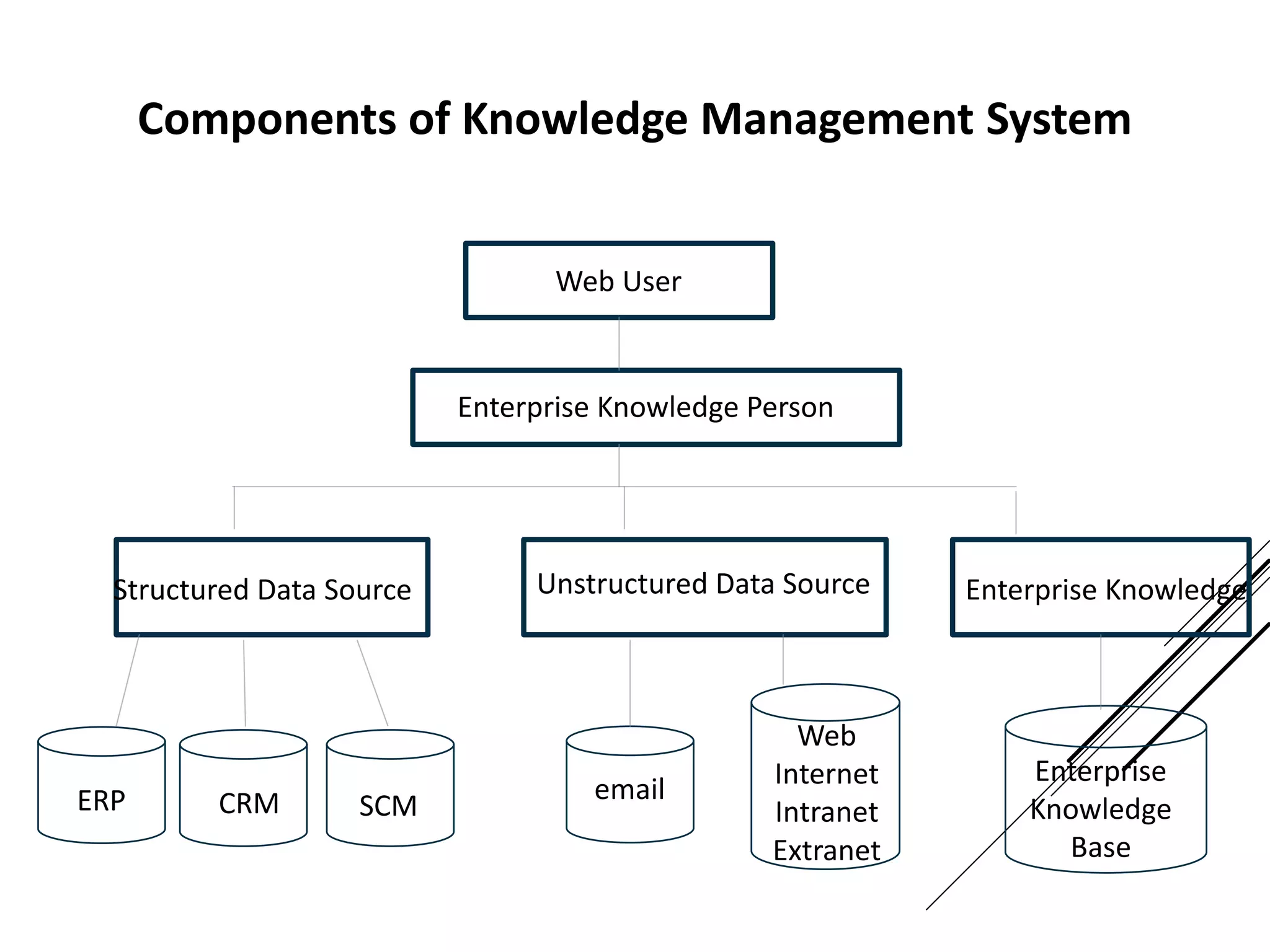
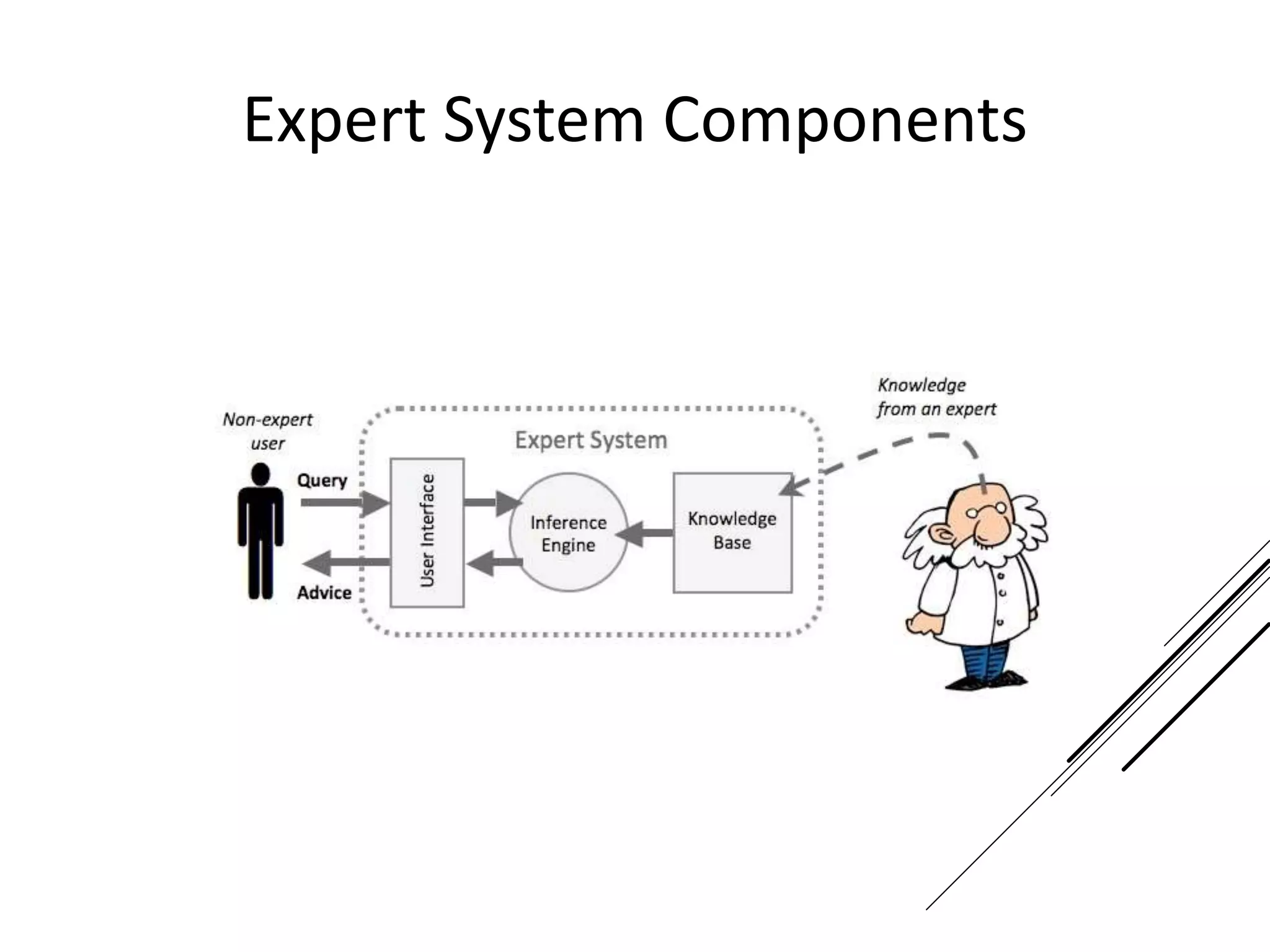
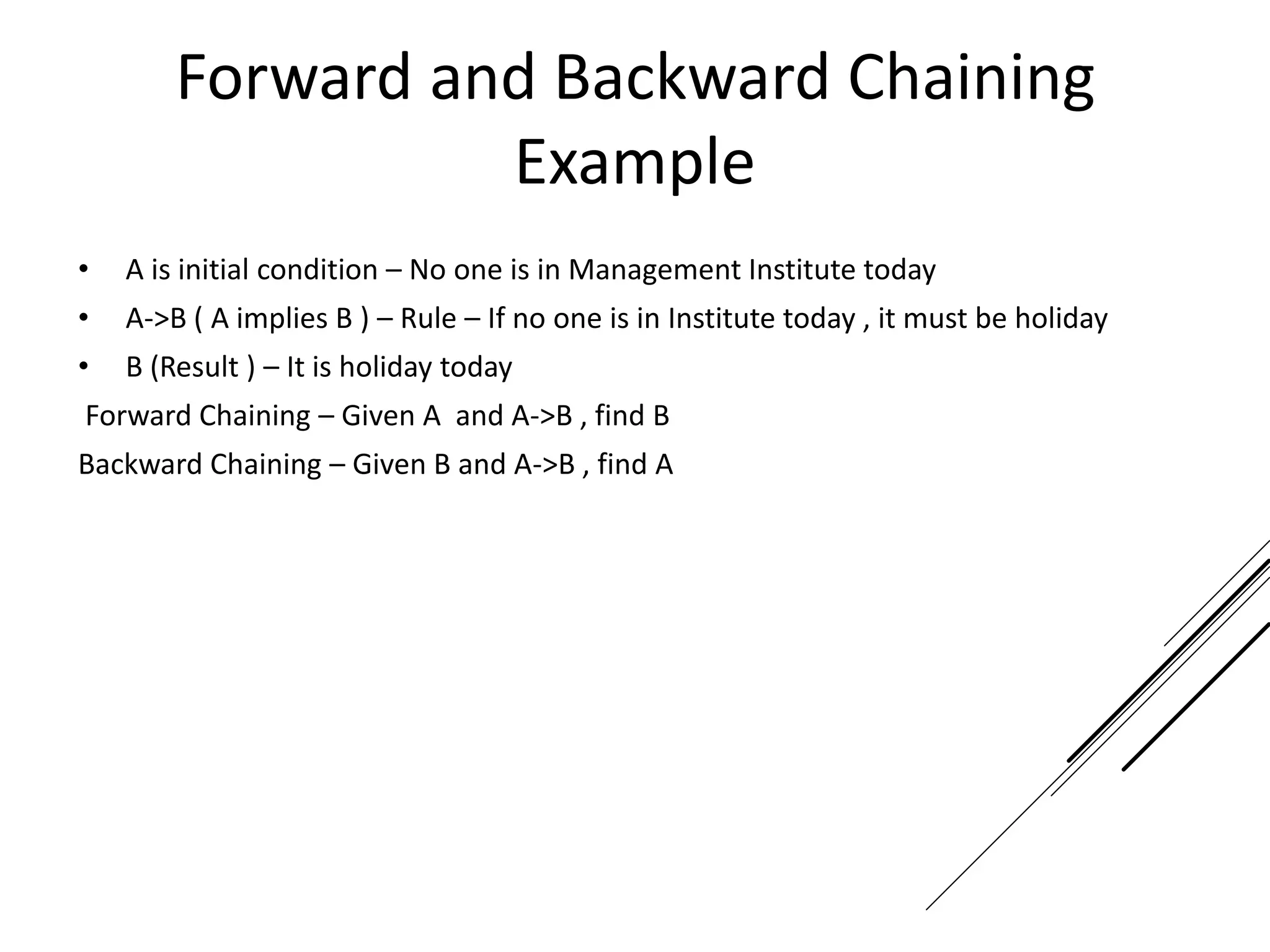
This document provides an introduction to decision theory and different methods for decision making under uncertainty and risk. It defines the key elements of decision theory as actions/alternatives, states of nature, outcomes, and objective variables. For decision making under uncertainty when probabilities are not known, it describes non-probability methods like maximax, maximin, and minimax regret. Maximax seeks to maximize the maximum possible outcome, maximin seeks to maximize the minimum outcome, while minimax regret takes a more balanced approach weighing both profits and losses.