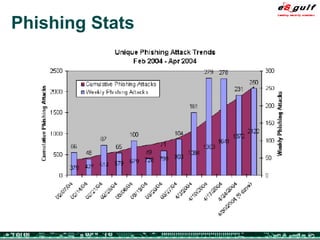
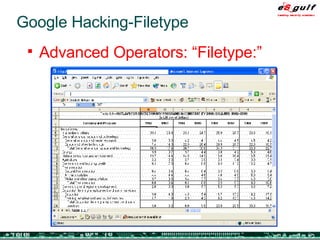
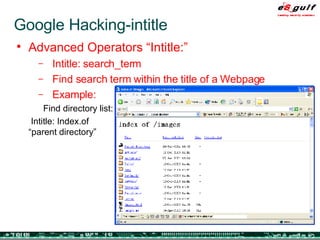
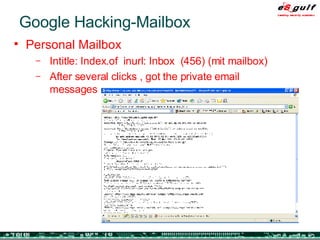
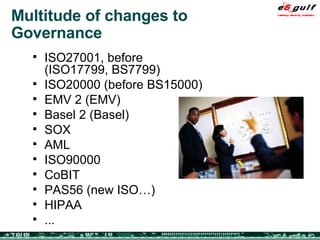
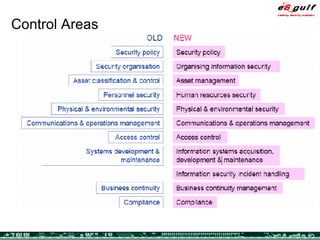
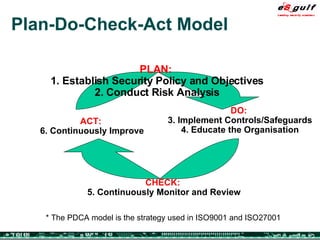
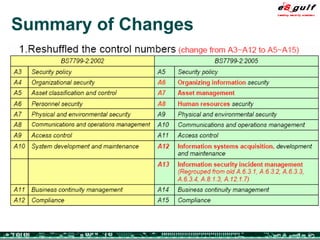
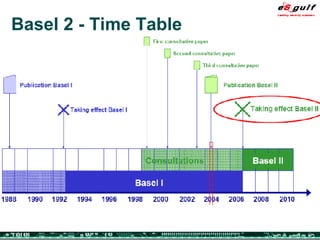
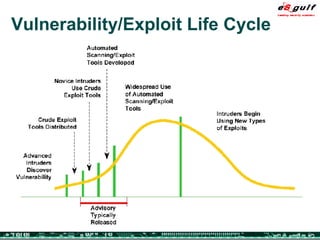
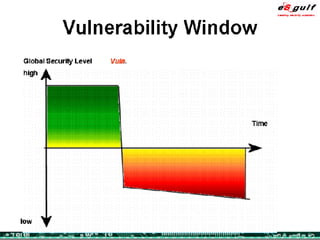
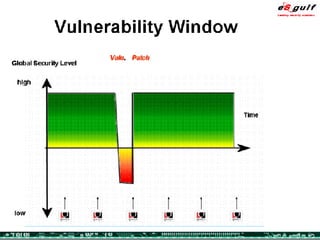
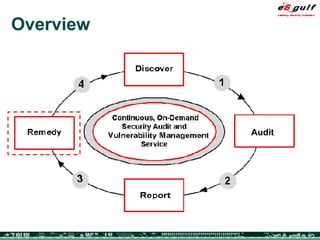
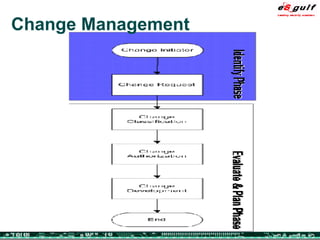
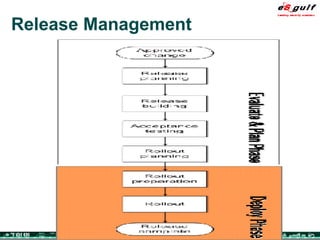
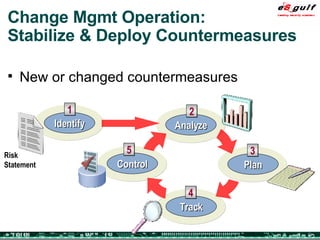
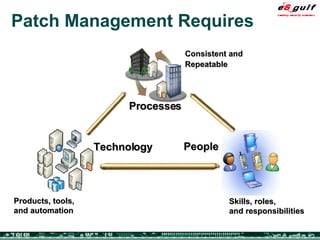
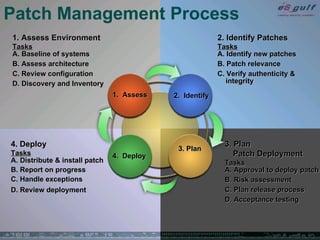
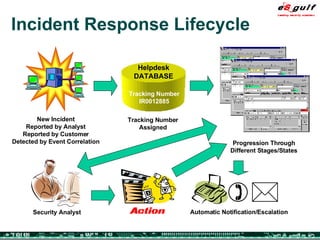
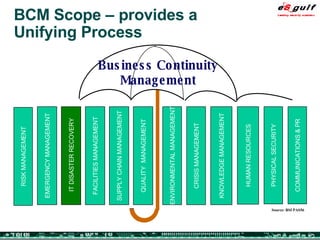
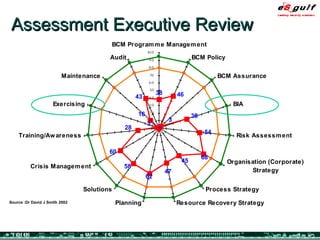
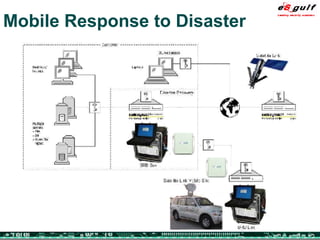
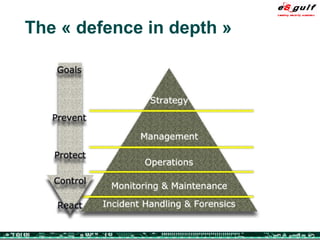
The document outlines the top 10 security challenges of 2006, highlighting the major issues such as security awareness among end users, vulnerability management, compliance with standards, and effective incident response. It emphasizes the risks associated with social engineering, data exposure through platforms like Google, and the importance of formal procedures for change management and patch management. Additionally, it addresses the dangers of outsourcing and the need for comprehensive disaster recovery and business continuity plans.
![Top 10 Security Challenges/Issues 2006 Jorge Sebastião Founder and CEO [email_address] www.esgulf.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/top-10-security-challenges-1200591198915603-5/75/Top-10-Security-Challenges-1-2048.jpg)