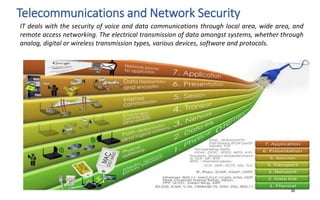
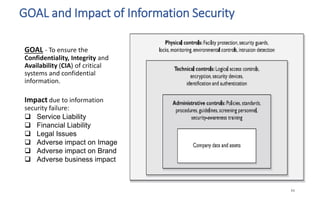
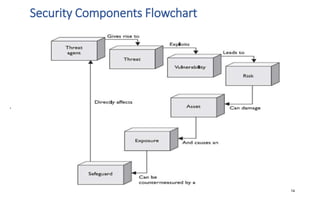
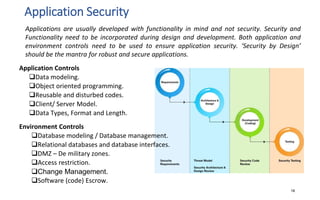
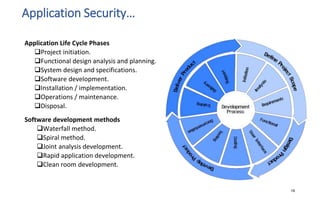
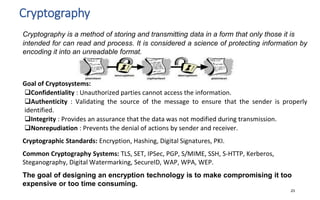
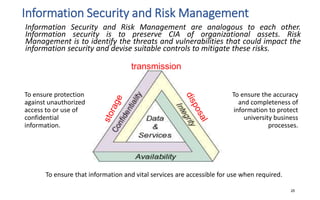
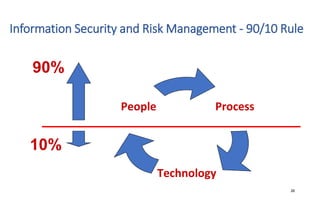
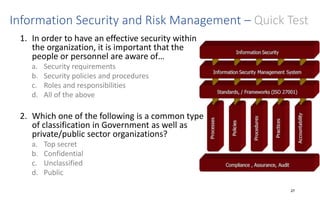
The document discusses various topics related to IT security basics. It begins by providing two examples of security breaches to illustrate why security is important. It then discusses the four virtues of security and the nine rules of security. The document also defines information security, its goal of ensuring confidentiality, integrity and availability of systems, and the potential impacts of security failures. Additionally, it outlines common security definitions, 10 security domains, and provides an overview of access control and application security.






















![Security Architecture and Design
37
Two fundamental concepts in computers and information security are Policy and Security Model.
While the Policy outlines how data is accessed, the level of security required and the actions that
need to be taken when the requirements are not met, the Security Model is a statement that
outlines the requirements necessary to properly support and implement the policy. Architecture
defines how they are implemented.
Some basic security models:
Bell-LaPadula: [Protects Confidentiality] A subject cannot read data at a higher security level, a
subject cannot write data to a lower security level, a subject that has read & write capability can
perform these functions at the same security level.
Biba: [Protects Integrity] A subject cannot read data at a lower security level, a subject
cannot modify data to a higher security level, a subject cannot modify an object in a higher
integrity level.
Clark Wilson: Subjects can only access objects through authorized programs ,
separation of duties is enforced and auditing is required.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/informationtechnologysecuritybasics-linkedin-191208135628/85/Information-Technology-Security-Basics-37-320.jpg)