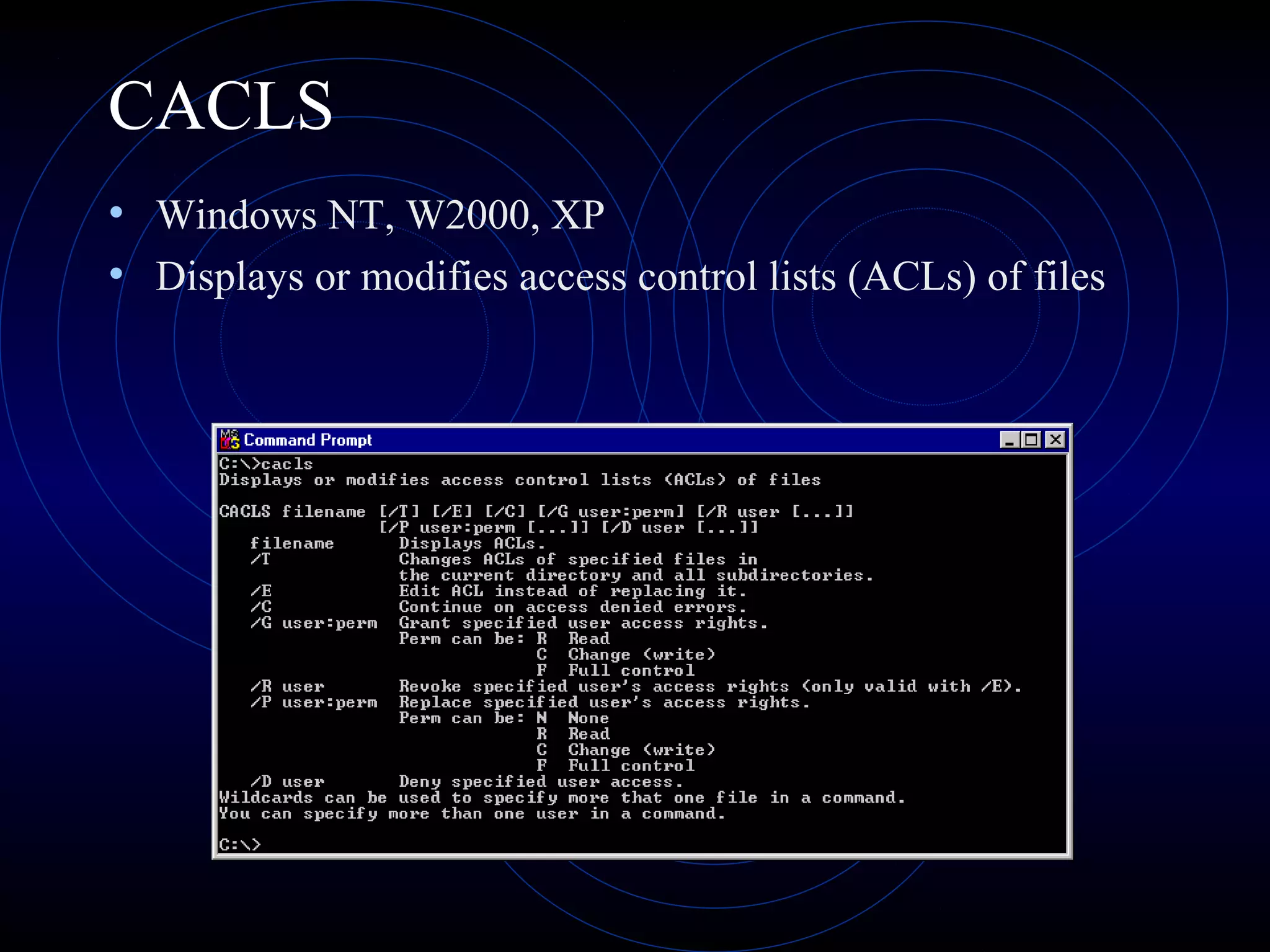
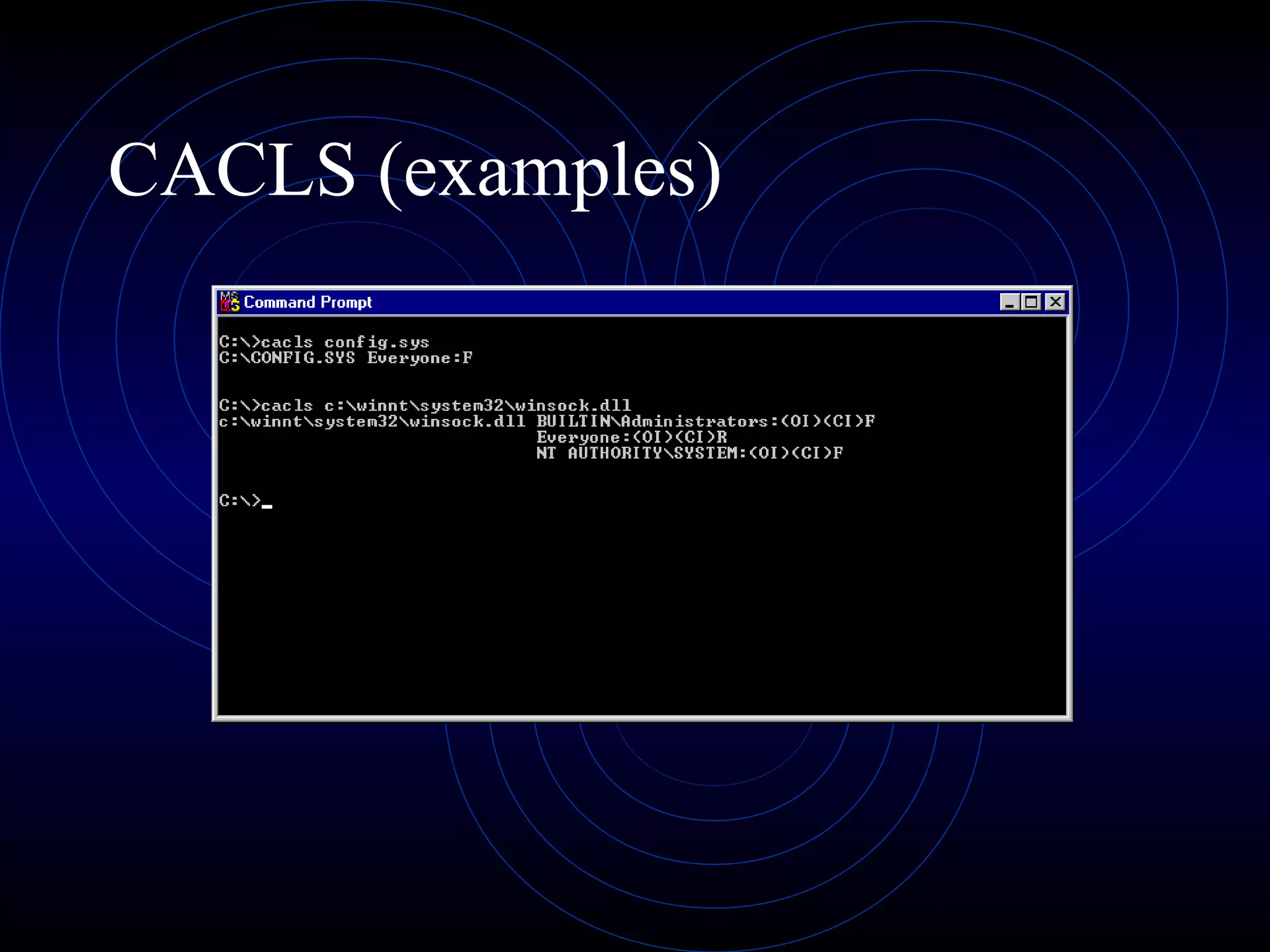
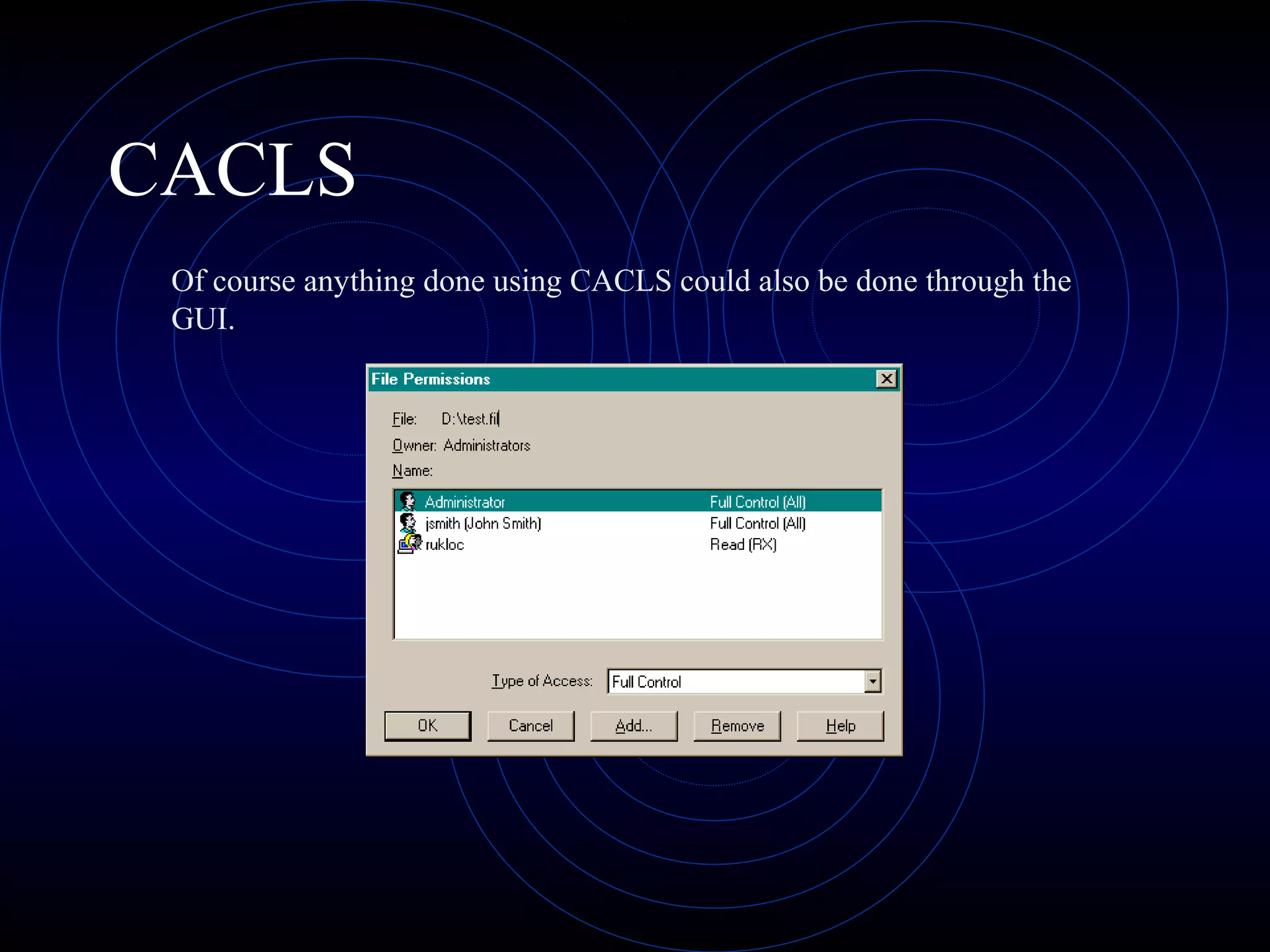
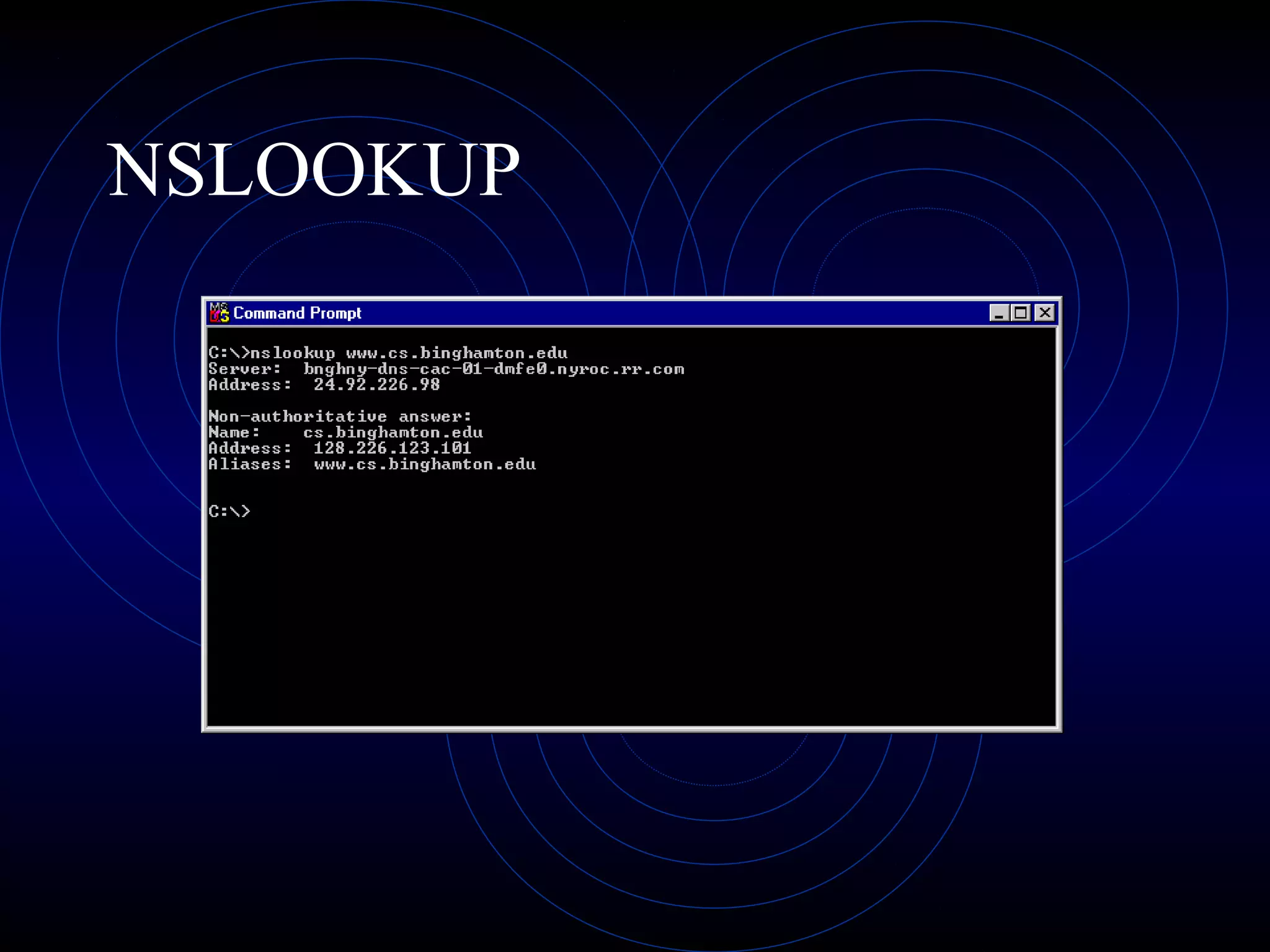
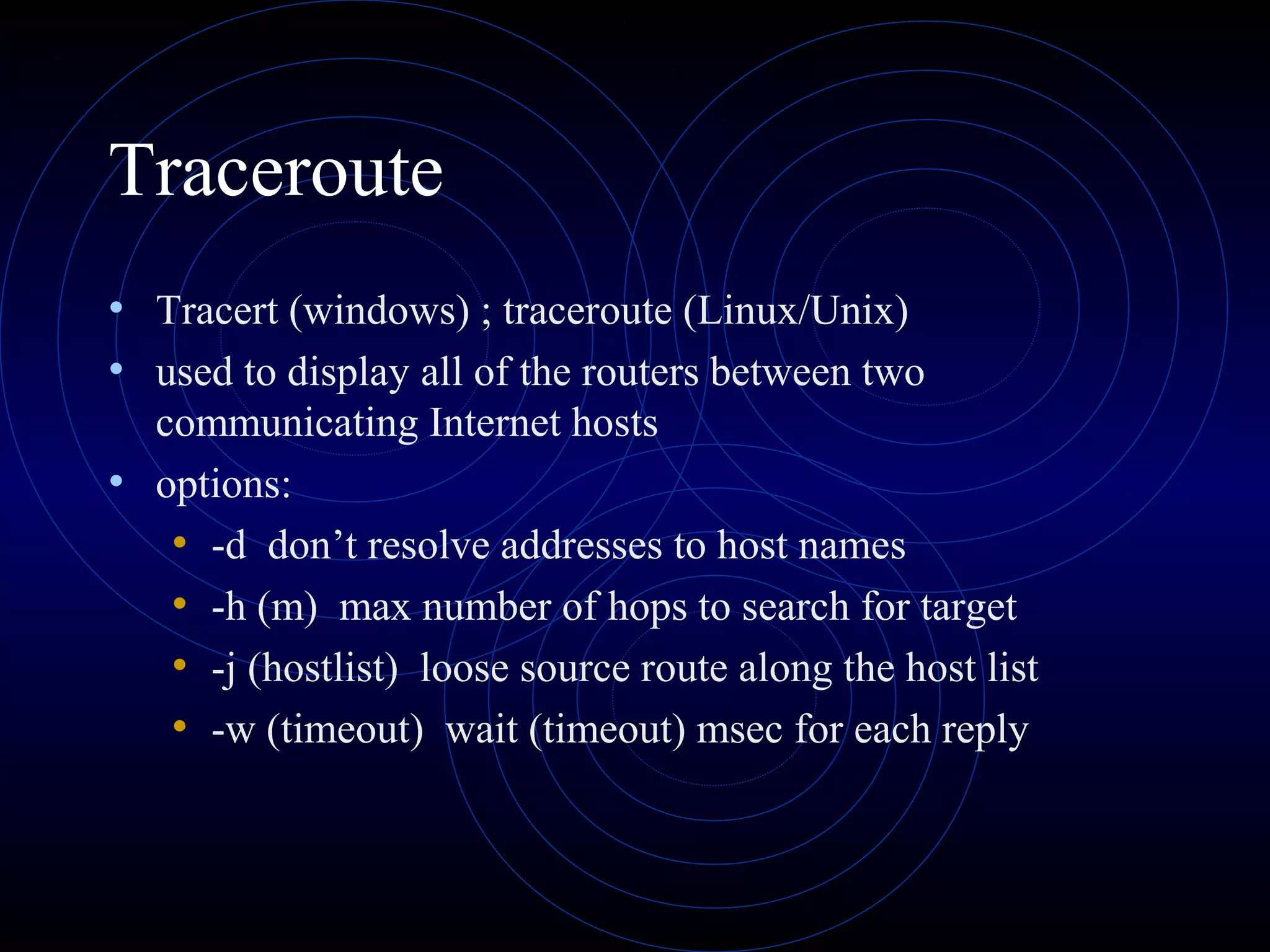
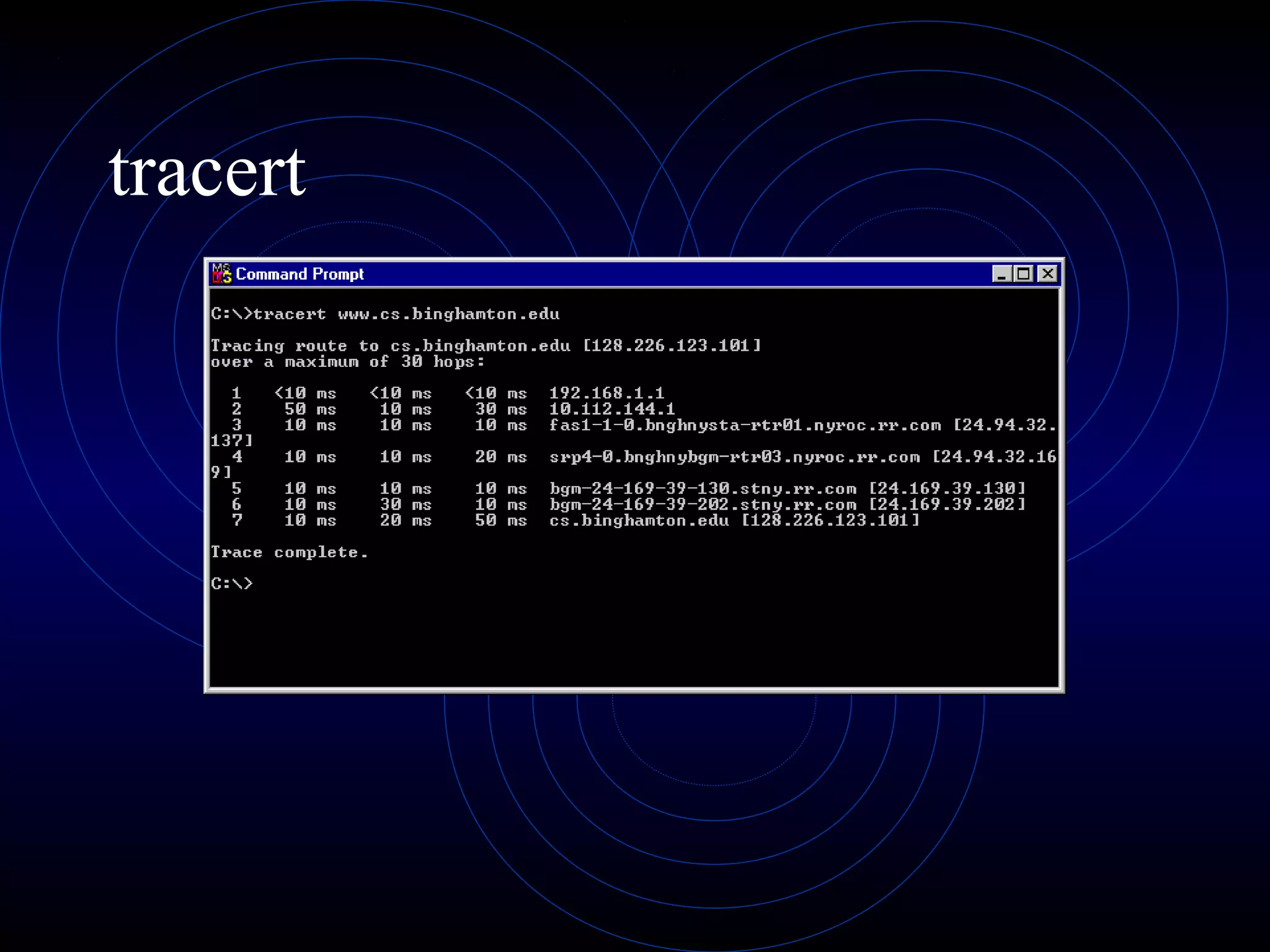
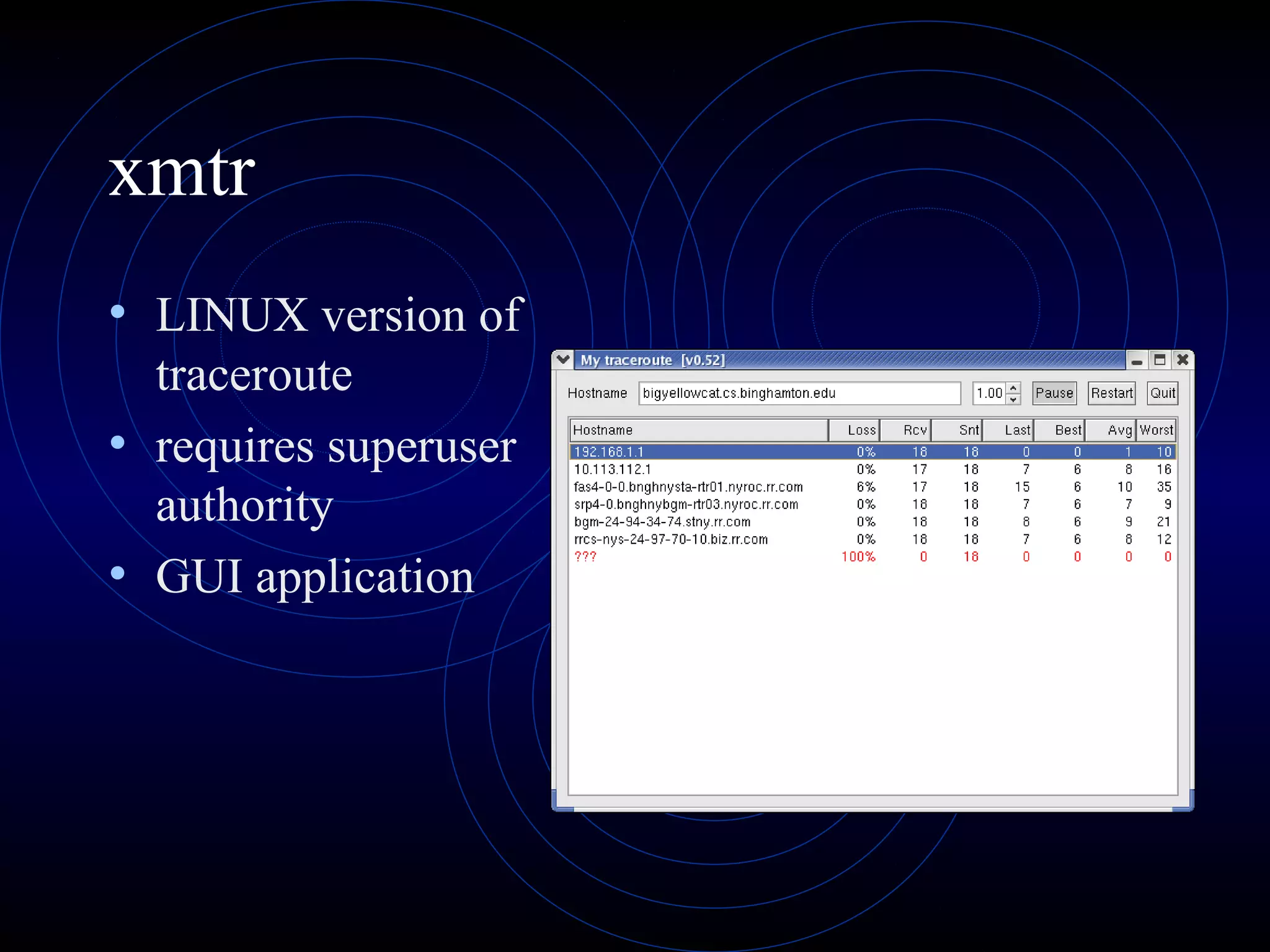
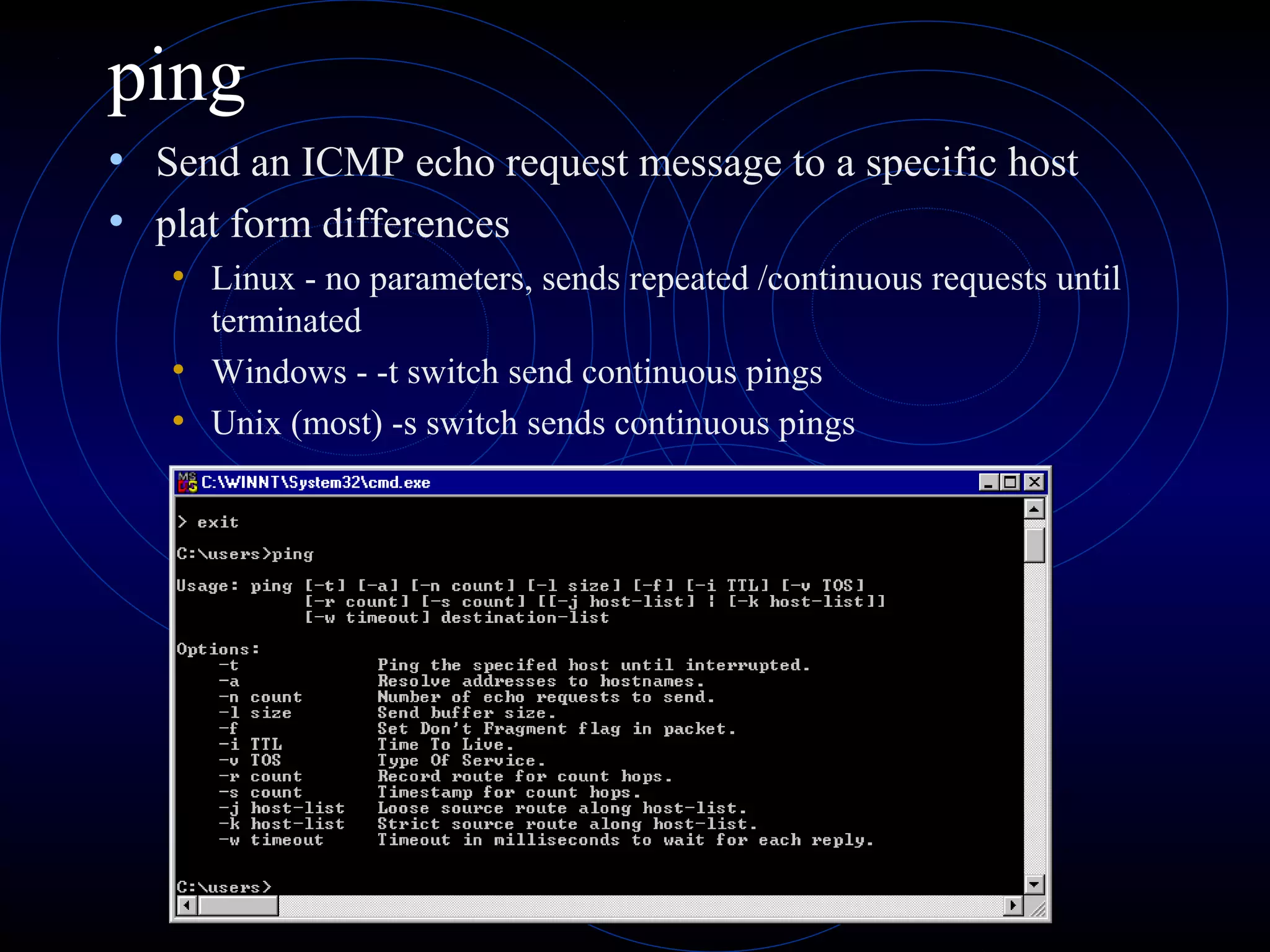
This document summarizes several security analysis tools, including CACLS for modifying access control lists in Windows, NSLOOKUP for resolving domain names to IP addresses, Traceroute/tracert for tracing the network path between hosts, Ping for checking network connectivity, and WS-Ping which combines tools like Ping, Traceroute, network scanning, and information gathering. It also discusses SATAN and Nessus, which are vulnerability scanners that detect potential security issues by analyzing network configurations and services without exploiting any vulnerabilities.