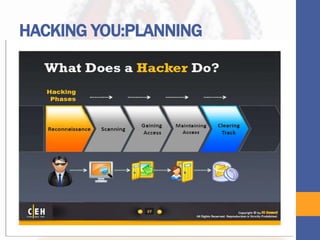
This document provides information about an upcoming cyber security workshop in Lesotho. The workshop will be presented by Mr. Theko Moima, a certified ethical hacker. It will be aimed at government officials from the ministries of education, defense, police, and justice. The objectives are to equip government with cyber skills, enable protection against threats, and demonstrate cyber attacks and vulnerabilities. The workshop will use both Sesotho and English and include both technical and everyday language explanations. It will involve demonstrations of attacks and defenses using attendees' own devices. The document outlines topics that will be covered including cyber crime, security, hackers, the CIA triad model, hacking methods, and examples of common attacks.