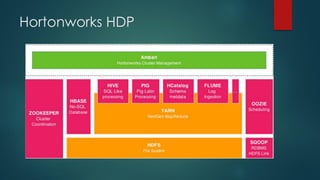
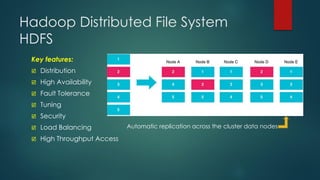
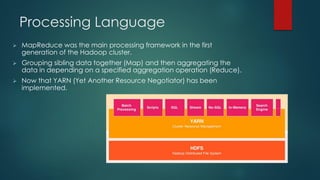
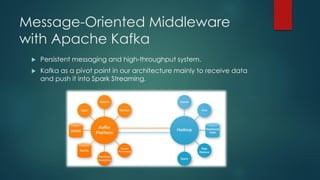
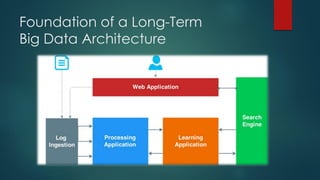
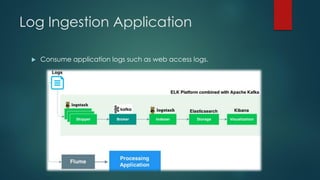
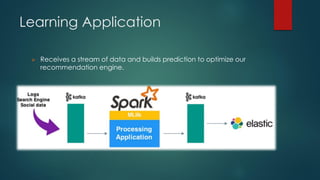
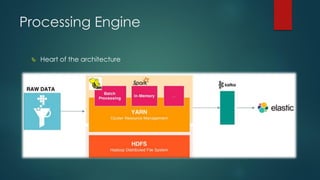
The presentation outlines a scalable big data architecture, focusing on identifying symptoms of big data and the complexities of data management. It covers components like Hadoop distribution, data acquisition, processing languages, machine learning, and NoSQL stores, highlighting their roles in long-term data architecture. Typical business use cases include customer behavior analytics, sentiment analysis, and predictive modeling, emphasizing the need for real-time processing and effective data management strategies.