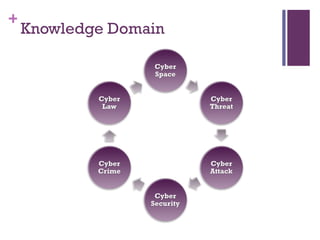
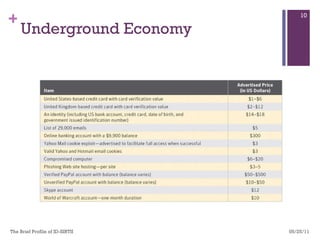
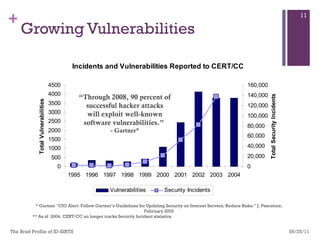
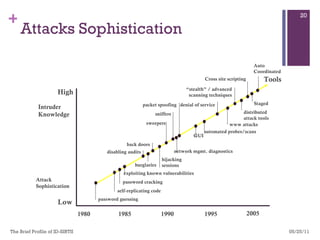
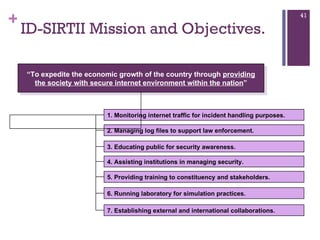
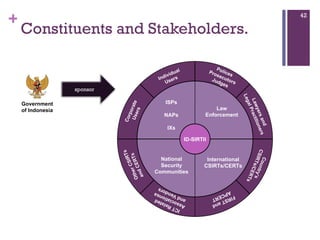
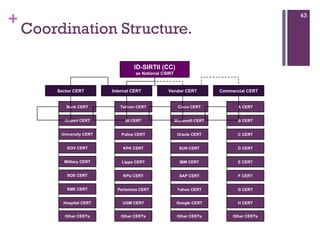
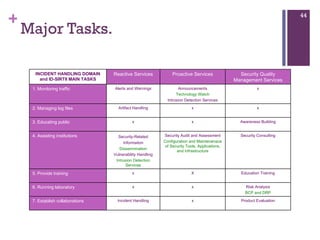
The document discusses various aspects of cyberspace, including cybersecurity, cybercrime, and the role of cyberlaw in mitigating threats. It highlights the increasing prevalence and sophistication of cyberattacks, the importance of information security, and the need for international collaboration to protect critical infrastructures. Moreover, it outlines the mission and responsibilities of the Indonesian Security Incident Response Team (ID-SIRTII) in monitoring and managing internet security incidents.
![Cyber-6 Cyberspace. Cyberthreat.Cyberattack. Cybersecurity. Cybercrime. Cyberlaw. Prof. Dr. Ir. Richardus Eko Indrajit MSc, MBA, MA/Msi, MPhil, ACPM, CWM, ICWM, CEH Website: http://eko-indrajit.info Email: [email_address] Chairman of ID-SIRTII and APTIKOM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pr7-cybersix-esdm-110524214847-phpapp02/75/Cyber-Six-Managing-Security-in-Internet-1-2048.jpg)