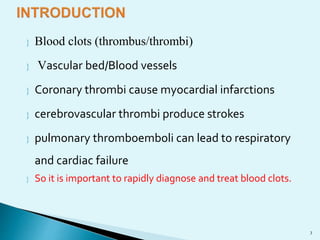
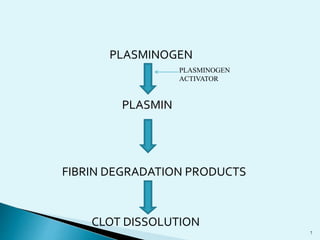
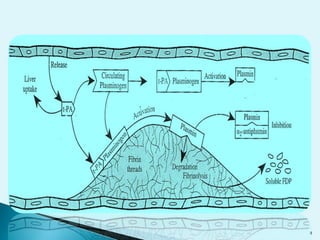
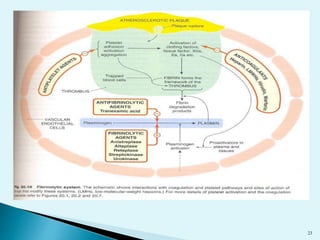
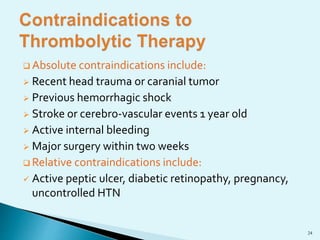
Blood clots can cause serious medical issues if they block arteries or veins. Thrombolytic drugs work by activating plasminogen into plasmin, an enzyme that breaks down fibrin in clots. The three main types of thrombolytic drugs are streptokinase, urokinase, and tissue plasminogen activators (TPA). While all three work to break down clots, TPA is more specific to clots and has fewer side effects than the other drugs. Thrombolytic drugs are used to treat conditions like heart attacks, strokes, and pulmonary embolisms but have risks of bleeding if overused or in the wrong patients.