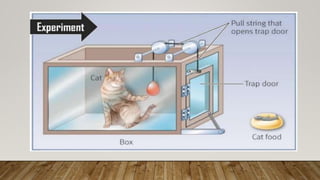
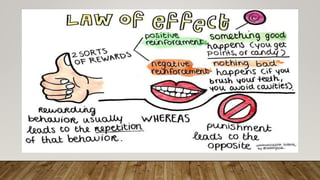
Edward Thorndike conducted experiments with cats in puzzle boxes to understand the laws of learning. He found that cats would initially respond randomly but eventually learn to press the lever to escape the box and receive a food reward. Through successive trials, the cats learned the association between lever pressing and escape more quickly due to reinforcement. Thorndike proposed three primary laws of learning: the law of readiness, the law of effect stating that behaviors followed by rewards will be repeated, and the law of exercise whereby connections are strengthened with practice and weakened without it. His work formed the basis for behaviorism and operant conditioning theories of learning.