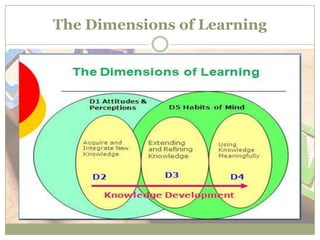
The Dimensions of Learning (Dol) is a framework for educators to plan student learning experiences based on research about effective learning methodologies. It encompasses five essential dimensions: attitudes and perceptions, knowledge acquisition and integration, knowledge extension and refinement, meaningful knowledge application, and productive habits of mind. By utilizing this model, educators aim to enhance overall learning outcomes and adapt teaching strategies to meet diverse student needs.