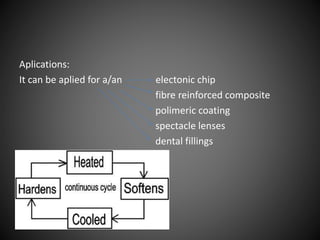
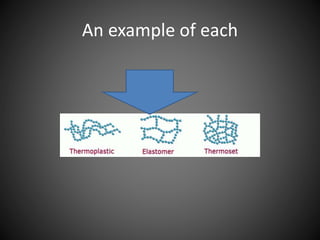
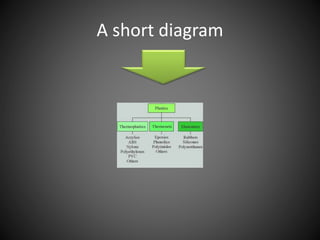
This document summarizes three types of polymers - thermosetting polymers, thermoplastics, and elastomers. Thermosetting polymers retain their shape even when heated and are used to produce permanent components. Thermoplastics can be melted and reshaped but thermosettings cannot. Common applications of thermoplastics include food storage containers and plastic bags. Elastomers are polymers that are flexible and elastic. They are used to make products like shoe heels, wheels, and wetsuits.