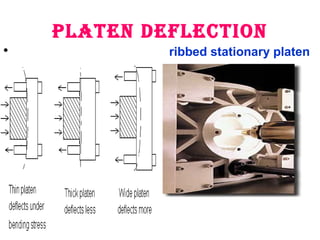
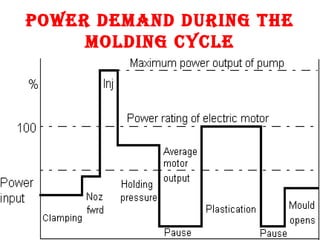
The document outlines essential considerations for selecting a Plastic Injection Molding Machine (PIMM), emphasizing the importance of matching the machine's attributes with job requirements, such as shot weight, clamping force, and injection speed. Key parameters such as screw diameter, plasticizing capacity, and cycle time are discussed to ensure efficiency and suitability for molding specific articles. Ultimately, the selection criteria hinge on the desired product characteristics and the machine's operational specifications.